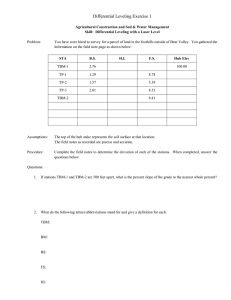
i
I
1?-1. DIFFBREXTIIL LEVELING.
Differential
leveling is the process of determininE
difference in elevation between two or more points
distance apart. It requires a series of set ups of the
trument along a general route and, for each set up,
reading back to the point gf known elevation and for
a point of unknown elevation are taken. The basic egu
used in differential leveling include a graduated Ie'
rod and a leveling instrument such as a dumpy }evel,
matic Ieve1, ox an engineerrs transit. These levelinE
truments are used to estabLish a horizontal llne of
i
lin
and to meaaure the verticaL distance between the
sight and the point on which the rod is held.
L7_2. DEFINITION OF
!il
TERHS.
The different terms conimonly used in differential
work are graphically illustrated in Figure 1?-L.
1e
A
look at the figure may imply that'the points al.ong t he
veling route ai1 1ie in a straight 1ine. It is impor
.understand that it is not always the case in actual
1ng work. The points and the lnstrument stations
fact be positioned in plan along a zigzagging pattern.
llllii
17-1. gillQ^ential levzliag.
Fig.
Lcvellng
cllng
Rod
Rod
L.val
Horlzonlol Ll
of slght
Hor lzontol
inc of Sight
BS
I
BS
xdlrf^ Ll
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
in
I
BMi
TPI
I
BMo
(Known)
lEtov
i
letov
Ground Surfoc.
IH lz
I
tsMo
L2
I
TPt
E
I
I
D
I
I
I
I
I
--t
I
l.t
(Tr
I
-f
!:J:u nca
(M
ron
s.€
Do tum
Lcv.l)
-----{
1. Bench Hark {Bll). A bench mark ls a flxed poi
reference whose elevation is either known or assumed.
may be permanent or tdmporary. Permanent bench marks
are those which are established at .intervals throughout
country by the Philippine Coast and Geodetlc Surveys
or the Buieau of Lands. They serve as points of re
for leve1s ln a glven locallty and thelr elevations arc
termined by precise leveling methods. Permanent PCGS
,lg2-
i,,if,i!:
mrll
lI,.Jl fl::
lllliltrll'r
}lltil
bnlltilrx