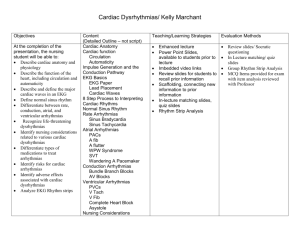
Heart Failure Types: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Management Chart
advertisement

LeftSided/Systo lic HF Leftsided/Diast olic HF Left-Sided/ Mixed HF Path/Etiolog y -HFrEF with reduced EF less than 45% as low as 5-10% -Results from inability of left ventricle to empty adequately during systole and fill adequately during diastole -Weakened dilated enlarged heart muscle cannot generate adequate stroke volume which decreased cardiac output HFpEF- EF is still 60% however the ventricles have impaired ability to relax and fill during diastole, resulting in decreased stroke volume and cardiac output Risk factor HTN is primary cause results in hypertrophy (heart muscle thickens makes LV chamber smaller preserving EF but not enough blood) other risk factors: older age, female, obesity, diabetes, aortic stenosis, cardiomyopa thy S/S same as HF Pulmonary edema, SOB, orthopnea, coughing up fluid, weight gain (1) signs and symptoms of HF (2) normal EF (3) evidence of LV diastolic dysfunction by echocardiogra phy or cardiac catheterization . EKG, ECHO, BNP Diastolic and Systolic HF, Poor EF <35%, high pulmonary pressures, Biventricular failure, both MI, chronically worsened cardiomyopa thy or hypertension Low BP, low cardiac output, poor renal perfusion, poor exercise tolerance, heart EKG, ECHO, BNP HTN (modifiable risk should be aggressively treated and managed reduces the incidence of HF by 50%), CAD, MI, DM, valvular disease, metabolic syndrome, advanced age, tobacco use, vascular disease, arrhythmias Signs/Sympto ms Fatigue, decreased urine production, tachycardia, Diagnostics EKG, ECHO, BNP Managemen t Monitor I&Os, Vital signs, Assess for signs and symptoms of SOB, dyspnea, High fowler’s position, Monitor ABGs and electrolytes, support, administer meds as ordered, Patient education: smoking cessation, maintain a healthy weight, exercise, reduce stress, control hypertension Meds Monitor I&Os, Vital signs, Assess for signs and symptoms of SOB, dyspnea, High fowler’s position, Monitor ABGs and electrolytes, support, administer meds as ordered, Patient education: smoking cessation, maintain a healthy weight, exercise, reduce stress, control hypertension Monitor I&Os, Vital signs, Assess for signs and symptoms of SOB, dyspnea, Administer O2 as ordered per provider Administer O2 as ordered per provider Complicatio ns Kidney Failure, heart valve problems, arrhythmias ACE inhibitors, ARBs, Calcium Channel blockers Kidney Failure, heart valve problems, arrhythmias ACE inhibitors, ARBs, Calcium Channel blockers Administer O2 as ordered per provider ACE inhibitors, ARBs, Kidney Failure, heart valve problems, arrhythmias left and right ventricles are dialated and have poor filling and emptying which means decreased Cardiac output Right-sided HF ADHF dysrhythmias, edema, fatigue Right ventricle fails to pump effectively, which causes fluid to back up into the venous system which means it backs up into tissues and organs Left sided HF, cor pulmonale (RV dilation and hypertrophy causing pulmonary disease), right ventricular MI, PE JVD, Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, N/V, anorexia, ascites, dependent edema 3+ or 4+, sudden weight gain due to fluid, swelling in hands and fingers, increased PVP EKG, ECHO, BNP Sudden onset of S/S of HF. REQUIRES IMMEDIATE MEDICAL CARE!!! Pulmonary and systemic congestion due to elevated left sided and right sided filling Dependent edema, Pulmonary edema, cough, blood tinged sputum, sudden weight gain of Check BNP if under 100 it is normal 100500 HF, over 500 severe HF, hemodynamic assessment, High fowler’s position, Monitor ABGs and electrolytes, support, administer meds as ordered, Patient education: smoking cessation, maintain a healthy weight, exercise, reduce stress, control hypertension Teach patient to take daily weights and report a sudden increase in weight ASAP. Monitor I&Os, Vital signs, High fowler’s position, Monitor ABGs and electrolytes, patient Education, support, administer meds as ordered, elevate edematous extremities, fluid and sodium restriction, Patient education: smoking cessation, maintain a healthy weight, exercise, reduce stress, control hypertension Determine underlying cause, Give Oxygen or BiPAP, High fowler’s position, Calcium Channel blockers Administer O2 as ordered per provider ACE inhibitors, ARBs, Calcium Channel blockers Morphine sulfate, Give IV furosemide Nitroglycerin IV, If these therapies fail give Liver damage heart valve problems, arrhythmias pressure by failure of the LV. CHF Progressive worsening of ventricular function and chronic neurohormo nal activation that results in ventricular remodeling. 3> in 2 days or overnight, nocturia(due to decreased renal perfusion), Physical findings: Orthopnea, dyspnea, tachypnea& use of accessory muscles, PE, crackles, wheezing, rhonchi, tachycardia, hypotension or hypertension, cool and clammy skin, cyanosis FACES: Fatigueearliest onset, pt may feel fatigue after doing usual activities even limits them from completing usual activities Limitations of Activity, Chest congestion/cou gh, Edema- 3 lbs of weight gain in 2 days or 3 to 5 in 1 week, SOB, Dyspnea at rest or with activity, orthopnea if patient is sleeping with more than 2 pillows to aid breathing, Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspneapatient wakes up in the middle of the night with sensation of suffocation, tachycardia due to increase in cardiac output, nocturiawaking up more than 2 times at night to pee EKG, TTE, TEE shows info on EF, heart valves and heart chambers, stress test, cardiac catherization vital sign assessment, provide antianxiety medications if non contraindicat ed such as lorazepam Digoxin, dopamine, milrinone Check BNP if under 100 it is normal 100500 HF, over 500 severe HF, EKG provides info about EF, heart valves and heart chambers, chest X-rayshows heart and fluid, 6 minute walk test, MUGA scan, stress test, heart catherizationcan be done in acutely ill patients who develop unexplained new onset of HF Treat the underlying cause and contributing factors, maximize CO, reduce symptoms, improve ventricular function, improve quality of life, preserve target organ function, improve mortality and morbidity, control HTN, encourage patient to stop smoking Give Furosemide IV, monitor potassium levels, Spironolacto ne is potassium sparring diuretic may cause hyperkalemi a, ACE inhibitors improve quality and reduce mortality, If side effect to ACE then can prescribe ARB, vasodialator s are used to open up the vessels more beneficial if patient having active MI, Digoxin increases cardiac output give IV for acute, Entresto is good medication for patient to be sent home on, First: GIVE OXYGEN to relieve dyspnea and fatigue, if administerin g IV diuretic make sure that urinal/bedsid e commode is near patient’s bed, STRICT I&O, monitor potassium DIET: low sodium dietrestricted sodium to 2g/day, Pleural effusion, Afib(most common), S/S: Dyspnea, cough, chest pain, crackle at base of lungs. Vtach, cardiac death, PE which increases risk for stroke, Renal failure, Hepatomeg aly Physical changes: skin is dusky, cool, damp to touch, absent hair growth, venous stasis, Restlessness, confusion, decreased memory due to reduced cerebral circulation, depression, anxiety, Chest pain (angina), anorexia, nausea Teach: -Get a scale for patient, calendar to record, teach how to assess themselves DASH dietemphasizes fruits, veggies, fat free or low fat milk and milk products, whole grains, fish, poultry, beans, seeds, nuts, obtain a detailed diet history, fluid restriction, daily weights