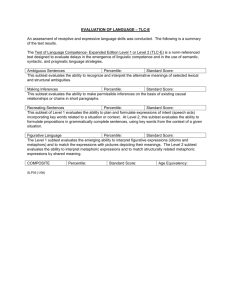
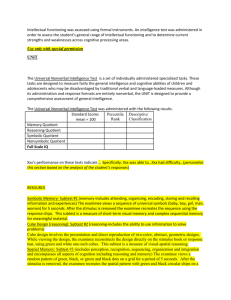
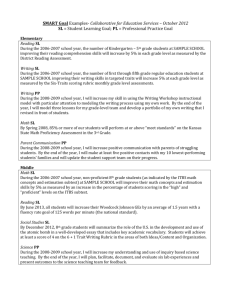
Form 8.2b Wechsler Individual Achievement Test, Fourth Edition (WIAT–4) (Kindergarten–12th Grade) WIAT–4, Grades K–12: Table 1 Total Achievement and Core Composite Standard Score Summary Composite Standard 95% CIa score* PRb Descriptive category Measured skills Total Achievement 000* [000, 000] < 0.00 Reading --* [--, --] -- Extremely high Very high High average Average Written Expression --* [--, --] -- Low average Very low Mathematics --* [--, --] -- Extremely low General proficiency in basic academic skills, including reading, written expression, and mathematics. Balance of word-level and text-level word reading and reading comprehension skills. Age-expected written language skills; letter and word writing, spelling, and sentence and essay composition. Application of quantitative principles to real-life situations; numerical computation skills. Note. Standard score mean = 100, standard deviation = 15, range = 40–160. Lower scores indicate greater impairment in achievement. PK = pre-kindergarten; CI = confidence interval; PR = percentile rank. Total Achievement data are in boldface. * denotes the presence of a specific learning disorder (i.e., standard score ≤ 78, PR ≤ 7). Source: American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: Author, p. 69. -- denotes not computed due to being out of grade range, or invalid due to incorrect administration or incomplete raw data. a 95% CI = the range within which the examinee’s true score falls with 95% certainty. bPR = the percentage of individuals in the norm reference sample (i.e., the population of same aged peers) that the examinee scores equal to or higher than. Interpretation: The Total Achievement standard score (SS) indicates that Mr./Ms. ….. is functioning within the ….. range of broad academic proficiency relative to individuals of the same age. The confidence interval (CI) indicates that it can be stated with 95% certainty that the true Total Achievement score falls somewhere between ….. and ….., which is well-within the aforementioned range of functioning, hence providing greater confidence in this conclusion/which shows an overlap with the ….. range of functioning. This means that the overall score can fall into either of these descriptive categories. The percentile rank (PR) means that Mr./Ms.’s overall achievement is equal to or greater than ….. percent of the population of same aged peers. Finally, the Total Achievement SS and PR are not/sufficiently low to indicate the presence of a specific learning disorder (SLD)/in one or more of the other academic areas that are measured by this test. Hence, further scrutiny of the various academic areas measured by this test will be done to determine the nature and extent of learning problems in this case. Remarkably low functioning is found among the following composite scales: …..; …..; …… Concerning ….., the SS is at/below the marker of 78, with an accompanying PR equal to/below 7, which effectively indicates the presence of a SLD in this academic area./Concerning ….., the SS is above the marker of 78, with an accompanying PR above 7, which effectively rules out the presence of a SLD in this academic area. The remaining/composite scales are measured to be within normal limits or above, hence effectively ruling out the presence of SLDs. No further subtest analysis is indicated by these results. Other reasons for the presence of low academic performance must be pursued. Analysis of the composite scale CIs indicates consistent performance as evidenced by a remarkable degree of overlap among them./Analysis of the composite scale CIs shows a lack of overlap, which indicates likely differential performance among the following composite scales: …..; …..; …… Because they do not/carry diagnostic and treatment implications, formal pairwise comparisons with hypothesis testing for any significant differences will not/be done. Table 2 Total Achievement and Core Composite Standard Score Difference Summary K–12 composite scale level standard score difference Total Achievement – Reading 1st standard score 000 2nd standard score 000 Difference (1st – 2nd)a +/–00* Critical value .05 0.00 Base rateb Total Achievement – Written Expression Total Achievement – Mathematics 000 000 +/–00* 0.00 ≥ 00.0%††† 000 000 +/–00* 0.00 < 00.0%††† Reading – Written Expression 000 000 +/–00* 0.00 > 00.0%††† Reading – Mathematics 000 000 +/–00* 0.00 ≤ 00.0%††† Written Expression – Mathematics 000 000 +/–00* 0.00 ≥ 00.0%††† ≤ 00.0%††† Note. K = kindergarten. Base rate = percentage of the population (i.e., as represented by the norm-reference sample) who obtained the 1st – 2nd listed standard score difference. -- denotes not reported due to missing data or statistically nonsignificant difference. No asterisk denotes that the 1st – 2nd standard score difference occurs by chance more than 5 times in 100 and is therefore statistically nonsignificant (i.e., the difference is merely due to chance or error); * denotes that the 1st – 2nd standard score difference occurs by chance less than 5 times in 100 and is therefore statistically significant (i.e., it is a true or real difference). bNo cross denotes that the base rate is typical (n > 15%); † denotes that the base rate is unusual (n ≤ 15%); †† denotes that the base rate is abnormal (n ≤ 10%); ††† denotes that the base rate is rare and profoundly abnormal (n ≤ 5%). a Interpretation: Of the pairwise comparisons done due to possible differential performance, none are statistically significant. Therefore no further analysis of base rate data are needed or required. Of the pairwise comparisons done due to possible differential performance, the following are statistically significant, with the first-listed composite scale showing significantly higher functioning and the base rate result in parentheses: (a) ….. versus ….. (typical/unusual); (b) ….. versus ….. (typical/unusual); (c) ….. versus ….... Table 3 Reading Composite Subtest Standard Score Summary Subtest Standard score* 95% CIa PRb Descriptive category Measured skills Word Reading 000* [000, 000] < 0.00 [--, --] -- Very high Average Low average Very low Extremely low Speed and accuracy of decontextualized word recognition; reading aloud a list of words of increasing difficulty. Understanding written passages after reading them (i.e., fictional stories; informational text; advertisements). Reading --* Comprehension Note. Standard score mean = 100, standard deviation = 15, range = 40–160. Lower scores indicate greater impairment in achievement. CI = confidence interval; PR = percentile rank. * denotes the presence of significant impairment in a specific skill (i.e., subskill) that may be contributing to a specific learning disorder (i.e., standard score ≤ 78, PR ≤ 7). Source: American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: Author, p. 69. -- denotes not computed due to being out of grade range, or invalid due to incorrect administration or incomplete raw data. a 95% CI = the range within which the examinee’s true score falls with 95% certainty. bPR = the percentage of individuals in the norm reference sample (i.e., the population of same aged peers) that that the examinee scores equal to or higher than. Interpretation: Concerning the ….. subtest, the SS is at/below the marker of 78, with an accompanying PR equal to/below 7, which effectively indicates the presence of a clinically significant impairment in this subskill./Concerning ….. subtest, the SS is above the marker of 78, with an accompanying PR above 7, which effectively rules out a clinically significant impairment in this subskill. The remaining subtest scales are measured to be within normal limits or above, hence effectively ruling out clinically significant impairment in these subskills. Analysis of the subtest CIs indicates consistent performance as evidenced by a remarkable degree of overlap among them./Analysis of the subtest CIs shows a lack of overlap, which indicates likely differential performance among the following subskills: …..; …..; …… Table 4 Written Expression Composite Subtest Standard Score Summary Subtest Standard 95% CIa score* PRb Descriptive category Measured skills Spelling (Grades K–12) 000* [000, 000] < 0.00 Written spelling of letter sounds and single words. [--, --] -- Extremely high Very high High average Average [--, --] -- Low average Very low [--, --] -- Extremely low Alphabet --* Writing Fluency (K–1) Sentence --* Composition (Grades 2–12) Essay --* Composition (Grades 4–12) Writing all the letters of the alphabet accurately (i.e., upper or lower case; print or cursive) within a 30-second time limit. Sentence formulation and written syntactic ability (i.e., sentence combining and building). Spontaneous compositional writing of maximum 10 minutes duration. Note. Standard score mean = 100, standard deviation = 15, range = 40–160. Lower scores indicate greater impairment in achievement. CI = confidence interval; PR = percentile rank; K = kindergarten. * denotes the presence of significant impairment in a specific skill (i.e., subskill) that may be contributing to a specific learning disorder (i.e., standard score ≤ 78, PR ≤ 7). Source: American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: Author, p. 69. -- denotes not computed due to being out of grade range, or invalid due to incorrect administration or incomplete raw data. a 95% CI = the range within which the examinee’s true score falls with 95% certainty. bPR = the percentage of individuals in the norm reference sample (i.e., the population of same aged peers) that that the examinee scores equal to or higher than. Interpretation: Concerning the ….. subtest, the SS is at/below the marker of 78, with an accompanying PR equal to/below 7, which effectively indicates the presence of a clinically significant impairment in this subskill./Concerning ….. subtest, the SS is above the marker of 78, with an accompanying PR above 7, which effectively rules out a clinically significant impairment in this subskill. The remaining subtest scales are measured to be within normal limits or above, hence effectively ruling out clinically significant impairment in these subskills. Analysis of the subtest CIs indicates consistent performance as evidenced by a remarkable degree of overlap among them./Analysis of the subtest CIs shows a lack of overlap, which indicates likely differential performance among the following subskills: …..; …..; …… Table 5 Mathematics Composite Subtest Standard Score Summary Subtest Standard score* 95% CIa PRb Descriptive category Measured skills Math Problem Solving 000* [000, 000] < 00.0 Basic math concepts; everyday math applications; geometry; algebra. Numerical Operations --* [--, --] -- Extremely low Very low High average Average Low average Written math computations in basic skills, basic operations with integers, geometry, algebra, and calculus. Note. Standard score mean = 100, standard deviation = 15, range = 40–160. Lower scores indicate greater impairment in achievement. CI = confidence interval; PR = percentile rank; K = kindergarten. * denotes the presence of significant impairment in a specific skill (i.e., subskill) that may be contributing to a specific learning disorder (i.e., standard score ≤ 78, PR ≤ 7). Source: American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: Author, p. 69. -- denotes not reported because invalid due to incorrect administration or incomplete raw data. a 95% CI = the range within which the examinee’s true score falls with 95% certainty. bPR = the percentage of individuals in the norm reference sample (i.e., the population of same aged peers) that that the examinee scores equal to or higher than. Interpretation: Concerning the ….. subtest, the SS is at/below the marker of 78, with an accompanying PR equal to/below 7, which effectively indicates the presence of a clinically significant impairment in this subskill./Concerning ….. subtest, the SS is above the marker of 78, with an accompanying PR above 7, which effectively rules out a clinically significant impairment in this subskill. The remaining subtest scales are measured to be within normal limits or above, hence effectively ruling out clinically significant impairment in these subskills. Analysis of the subtest CIs indicates consistent performance as evidenced by a remarkable degree of overlap among them./Analysis of the subtest CIs shows a lack of overlap, which indicates likely differential performance among the following subskills: …..; …..; …… Table 6 Dyslexia Index Composite and Subtest Level Standard Score Summary (Grades K–3) Composite/ Subtest Standard score 95% CIb PRc Descriptive category Measured skills Dyslexia Indexc 000* [000, 000] < 00.0 Word Reading --* [--, --] -- Ability to learn to read and interpret words, letters, and other symbols. Letter and letter-sound knowledge; single word reading. Phonemic Proficiency --* [--, --] -- Extremely high Very high High average Average Low average Very low Extremely low Ability to instantly and accurately analyze and manipulate the sounds within words. Note. Standard score (SS) mean = 100, standard deviation = 15, range = 40–160. Lower scores indicate greater impairment in achievement. PK = pre-kindergarten; CI = confidence interval; PR = percentile rank. a 95% CI = the range within which the examinee’s true score falls with 95% certainty. bPR = the percentage of individuals in the norm reference sample (i.e., the population of same aged peers) that that the examinee scores equal to or higher than. cRisk for dyslexia: SS (40–69) = very high; SS (70–76 = high; SS (77–84) = moderate; SS (85–89) = elevated; SS (90–97) = low; SS (98–160) = very low. Interpretation: Dyslexia Index Composite: The Dyslexia Index (DI) composite standard score (SS) indicates that …..’s risk of having this disorder is …… This is due to the overall score falling into the ….. descriptive category. The percentile rank (PR) means that Mr./Ms …..’s overall ability to learn to read and interpret words is equal to or greater than ….. percent of the population of same aged peers. Subtest Level: Both subtests that contributed to the DI are measured to fall within normal limits/above the marker of a standard score (SS) of 78, which also indicates that there is no current evidence of dyslexia. Both subtests that contributed to the DI are measured to fall equal to/below the marker of a standard score (SS) of 78, which also indicates evidence of dyslexia. Table 7 Dyslexia Index Composite and Subtest Level Standard Score Summary (Grades 4–12) Composite/ Subtest Standard score 95% CIb PRc Descriptive category Measured skills Dyslexia Indexc 000* [000, 000] < 00.0 Word Reading --* [--, --] -- Ability to learn to read and interpret words, letters, and other symbols. Letter and letter-sound knowledge; single word reading. Pseudoword Decoding --* [--, --] -- Orthographic Fluency --* [--, --] -- Extremely high Very high High average Average Low average Very low Extremely low Very low Extremely low Phonic decoding and knowledge of regular spelling-sound correspondence rules. Word recognition facility; size of orthographic lexicon or sight vocabulary. Note. Standard score (SS) mean = 100, standard deviation = 15, range = 40–160. Lower scores indicate greater impairment in achievement. PK = pre-kindergarten; CI = confidence interval; PR = percentile rank. a 95% CI = the range within which the examinee’s true score falls with 95% certainty. bPR = the percentage of individuals in the norm reference sample (i.e., the population of same aged peers) that that the examinee scores equal to or higher than. cRisk for dyslexia: SS (40–69) = very high; SS (70–76 = high; SS (77–84) = moderate; SS (85–89) = elevated; SS (90–97) = low; SS (98–160) = very low. Interpretation: Dyslexia Index Composite: The Dyslexia Index (DI) composite standard score (SS) indicates that …..’s risk of having this disorder is …… This is due to the overall score falling into the ….. descriptive category. The percentile rank (PR) means that …..’s overall ability to learn to read and interpret words is equal to or greater than ….. percent of the population of same aged peers. Subtest Level: The subtests that contributed to the DI are measured to fall within normal limits/above the marker of a standard score (SS) of 78, which also indicates that there is no current evidence of dyslexia. The ….. and …../All three subtests that contributed to the DI are measured to fall equal to/below the marker of a standard score (SS) of 78, which also indicates evidence of dyslexia. Table 8 Oral Language Composite and Subtest Level Standard Score Summary Composite/ Subtest Standard 95% CIa score* PRb Descriptive category Measured skills Oral Language 000* [000, 000] < 00.0 Listening Comprehension --* [--, --] -- Oral Expression --* [--, --] -- Extremely high Very high High average Average Low average Very low Extremely low General proficiency in listening and speaking vocabulary that form the basis for reading and writing. Listening vocabulary; inferring and remembering details from oral sentences and discourse. Speaking vocabulary; word retrieval; word retrieval efficiency; flexibility of thought process; syntactic knowledge. Note. Standard score mean = 100, standard deviation = 15, range = 40–160. Lower scores indicate greater impairment in achievement. PK = pre-kindergarten; CI = confidence interval; PR = percentile rank. Oral Language data are in boldface. * denotes the presence of a specific learning disorder (i.e., standard score ≤ 78, PR ≤ 7). Source: American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: Author, p. 69. -- denotes not reported because invalid due to incorrect administration or incomplete raw data. a 95% CI = the range within which the examinee’s true score falls with 95% certainty. bPR = the percentage of individuals in the norm reference sample (i.e., the population of same aged peers) that the examinee scores equal to or higher than. Interpretation: Oral Language Composite: The Oral Language (OL) composite standard score (SS) indicates that ….. is functioning within the ….. range of proficiency relative to individuals of the same age. The confidence interval (CI) indicates that it can be stated with 95% certainty that the true OL SS falls somewhere between ….. and ….., which is well-within the aforementioned range of functioning, hence providing greater confidence in this conclusion/which shows an overlap with the ….. range of functioning. This means that the overall score can fall into either of these descriptive categories. The percentile rank (PR) means that …..’s overall OL is equal to or greater than ….. percent of the population of same aged peers. Finally, the OL SS and PR are not/sufficiently low to indicate the presence of a specific learning disorder (SLD)/in one or more of the other academic areas that are measured by this test. Hence, further scrutiny of the various academic areas measured by this test will be done to determine the nature and extent of learning problems in this case. Subtest Level: Both OL subtests are measured to fall within normal limits/above the marker of a standard score (SS) of 78, which indicates that there is no current evidence of a language disorder, including both receptive and expressive speech. Concerning the ….. subtest, the SS is at/below the marker of 78, with an accompanying PR equal to/below 7, which effectively indicates the presence of a clinically significant impairment in this language subskill./Concerning ….. subtest, the SS is above the marker of 78, with an accompanying PR above 7, which effectively rules out a clinically significant impairment in this language subskill. The remaining subtest scale is measured to be within normal limits or above, hence effectively ruling out clinically significant impairment in this language subskill. Analysis of the subtest CIs indicates consistent performance as evidenced by a remarkable degree of overlap among them./Analysis of the subtest CIs shows a lack of overlap, which indicates likely differential performance among the measured language subskills, with ….. appearing to be significantly lower or more impaired than ……