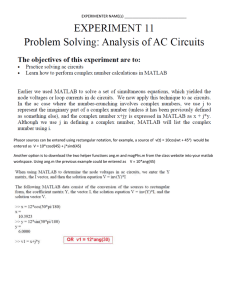
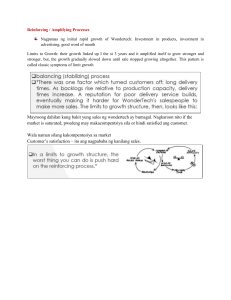
What is Behavior? What is Objectives? ◦The way one acts or conducts oneself, especially towards others. It is often a response to a particular situation or stimulus. ◦Objectives are precise actions or measurable steps individuals, and groups take to move closer to the goal. They are specific targets that typically have a time-bound schedule or timeline for completion. ◦ Also known as learning objectives and educational objectives, is a tool that teachers use to let students know at the beginning of the course or lesson what is expected of them. ◦It is a learning outcome stated in measurable terms, which gives direction to the learner’s experience and becomes the basis for student evaluation ◦ • The conditions part of an objective specify the circumstances, commands, materials, directions, etc., that the student is given to initiate the behavior. • All behavior relevant to intended student learning outcomes can best be understood within a context of the conditions under which the behavior is to be performed or demonstrated. • By end of the lesson, students will be able to • When presented with • Using the • Without the use of • The Behavior is a verb that describes an observable activity -- what the student will do. • It should be specific and measurable goals. ◦ Nakakikilala… (identify or recognize…), Naipapaliwanag (explain), Nailalarawan (describe) ◦ Nakibabahagi… sa… (share… with…), Napapahalagahan/Nakapagpapahalaga… (appreciate…) ◦ Naisasagawa… (execute…), Nakagagawa/Nakagaganap…( perform…) • Defines the level of performance and product, process or outcome. • Criterion is the standard that is used to measure whether or not the objective has been achieved. ◦ Speed - in under two hours, within fifteen minutes, before midnight ◦ Accuracy - with no more than two incorrect entries in the log ◦ Quality - follows APA format style (form), the presentation includes appropriate color combinations (aesthetics). Example of Behavioral Objectives Given a list of twenty countries (condition), the student will identify (behavior) at least fifteen of the corresponding capitals of each country (criteria). Given the names of 5 explorer, student will be able to correctly locate the specific countries they explored. Nang hindi gumagamit ng mapa, ang mga magaaral ay natutukoy ang iba’t ibang rehiyon sa Asya sa loob ng 5 minuto. Nailalapat ang kahulugan ng demand sa pang araw-araw na pamumuhay ng bawat pamilya. ◦ Gamit ang video, natutukoy ng mga mag-aaral ang kaugnayan ng demand sa pang-araw-araw na pamumuhay ng tao na walang mali. ◦ Ang mga mag-aaral ay nakagagawa ng isang demand schedule at nagragraph ito basi sa natutunang konsepto tungkol sa demand ng hindi gumagamit ng calculator sa loob ng 5 minuto. ◦ Pagkatapos ng diskusyon, ang mga mag-aaral ay napahahalagahan ang konsepto ng demand sa pamamagitan ng wastong pagba-budget ng allowance sa loob ng isang linggo. Refers to intellectual learning and problem solving Cognitive levels of learning includes; knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation Example of Cognitive Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student will be able to compare the battle strategies employed by Germany in World War I and World War II with 85% accuracy. In the presence of a seller, the students will be able to examine critically the different factors affecting the rising of prices in the market within 15 minutes. Pagkatapos ng aralin, ang mag-aaral ay naipaliliwanag ang iba’t ibang isyung may kaugnayan sa kasarian na hindi bababa sa 3 mula sa 5 isyu. Affective Domain Refers to the emotions and value system of a person Affective levels of learning includes; receiving, responding, valuing, organizing, and characterizing by a value ◦ ◦ Example of Affective Objectives Pagkatapos ng diskusyon, ang mga mag-aaral ay napahahalagahan ang konsepto ng demand sa pamamagitan ng wastong pagba-budget ng allowance sa loob ng isang linggo. Using the different pictures, the students will be able to recognized the importance of the different physical features of Asia within 5 minutes. Pagkatapos mapanood ang video, ang mga mag-aaral ay nakapagpapahayag ng paggalang at pagpapahalaga sa karapatan ng ibang tao sa pagpili ng kasarian na may 85% katumpakan. Psychomotor Domain Refers to physical movement characteristics and motor skill capabilities that involve behaviors requiring certain levels of physical dexterity and coordination These skills are developed through repetitive practice and measured in terms of speed, precision, distance, procedures, or execution techniques. ◦ Example of Psychomotor Objectives Gamit ang camera, ang mga mag-aaral ay nakabubuo ng isang dokyumentaryo na nagsusulong ng karapatan ng mga tao na mamili ng kasarian sa loob ng pitong (7) minuto. Ang mga mag-aaral ay nakagagawa ng isang demand schedule at nagragraph ito basi sa natutunang konsepto tungkol sa demand ng hindi gumagamit ng calculator sa loob ng 5 minuto.