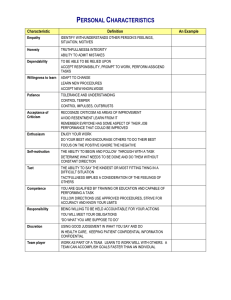
Conflict Management Skills What triggers conflict? Criticism Feeling entitled Perceived lack of fairness More perceived costs than rewards Different perspectives Stress and lack of rest Dialectical tension Criticism Young people are not pleased by criticism from their elders. Some male have a heightened sensitivity to what they perceive as criticism from women. They are insecure about the relationship. Feeling entitled If we believe we’re entitled to something and we’re denied getting what we think is ours, then conflict is a likely result. Perceived lack of fairness If we believe we have not been treated fairly conflict is likely. “It’s mine, not yours!” These sentiments fuel conflict between adults as well as nations. More perceived costs than rewards One person feels that he or she is getting less out of the relationship than the other person. Different perspectives Power Social issues Personal flaws Distrust Intimacy Personal distance Stress and lack of rest When you are not at your physical best, what you thought was a casual remark can quickly escalate into conflict. Beginning of vacations, the end of a long work week etc. Dialectical tension People’s need for two things at the same time. Results in uncertainty and discomfort with the relationship. For example, being separated and connected, feelings of being open and closed. Myths or Truth? Conflict is always a sign of a poor interpersonal relationship. Conflict can always be avoided. Conflict always occur because of misunderstandings Conflict can always be resolved. Pseudo conflict Simple conflict Ego conflict CONFLICT TYPES Pseudo conflict Pseudo means false. Occurs when we simply miss the meaning in a message. Unless we clear up the misunderstanding or a real conflict might ensue. How can you avoid pseudo conflict? Check your perceptions Listen between the lines Establish a supportive rather than a defensive climate for conversation. Simple conflict Differences in ideas, definitions, perceptions or goals. Keep the conversation focused on the issues at hand so that the expression of differences does not deteriorate into a battle focusing on personalities. To keep simple conflict from escalating: Clarify yours and your partner’s understanding of issues and your partner’s understanding of the source of the disagreement. Keep the discussion focused on facts and the issue at hand. Look for more than just the initial solutions. Don’t try to tackle too many issues at once. Find the kernel of truth in what your partner is saying. If tempers begin to flare and conflict is escalating, cool off. Ego conflict When you launch a personal attack, you are picking a fight. As each person becomes more defensive about their position, the issues become more tangled. When you are under stress, you are more likely to be verbally aggressive. Refrain from hurling personal attacks and emotional epithets. Take turns expressing your feelings without interrupting each other. Stay focus on issues rather than personalities. Make the issue a problem to be solved rather than a battle to be won. Write down what you want to say. When things get personal, make a vow not to reciprocate. Avoid contempt. CONFLICT MANAGEMENT STYLES Conflict Management Styles Avoidance Accommodation Competition Compromise Collaboration Avoidance To back off and try to side-step the conflict. Typical responses: “I don’t want to talk about it.” Indicate that a person has low concern for others as well as for themselves. Lose-lose approach. Wishes the problem would go away by itself and appears uninterested in managing the conflict. Unassertive and unable to stand up for one’s own rights. People might also avoid conflict because they don’t want to hurt the feelings of others. Demand-withdrawal pattern of conflict management. Advantages: Provides time for each person in the conflict to think about the issues. Allow each person to save face. Disadvantages: Sending a message that you really don’t care. Make things worse. Issues remain unresolved. Accommodation To give in to the demands of others. Fear rejection. Lose-win approach. Sacrifice your own needs so that someone else can win the argument. Advantages: You are reasonable and want to help. Gain credibility. Disadvantages: Give the accommodator a false sense of security. Diminish your power. Short-circuit the possibility of finding a solution that is to everyone’s liking Competition People who have a competition conflict management style have a win-lose philosophy. Want to win at the expense of the other person. Often resort to blaming a scapegoat. May try treats and warnings. Collaboration To have a high concern for yourself and others. More likely to view conflict as a set of problems. Best used when: All sides of the conflict need fresh ideas. Enhanced commitment to a solution is important. To establish rapport. Emotional feelings are intense. Affirm the value of the interpersonal relationship. Disadvantages: Time, skill, patience and energy required. Organisational Techniques for Preventing Conflict. Creating a culture of openness. Involves employees in decisions that affect them. Ensuring alignment of organisational systems. Offering team training and team building. Providing diversity training. Offering conflict management and negotiation training. The Language of Managing Conflict and Difficult Situations What are some factors or symptoms of conflict? Lack of communication Lack of trust Opposing agendas Steps in Managing Conflict (that does not involve you) Open the discussion. Identify the issue. Acknowledge and explore the issue. Generate solutions and options. Make agreements. Open the discussion. I sense/feel that there might be some issues/areas at work that you are not 100% satisfied with, and I just want to sit down with you informally and talk things out. I have a feeling that there might be some issues we need to deal with, so I was hoping we can sit down and discuss…. Identify the issue. "I have noticed...." "I feel...." "There appears to be...." I have noticed that you and your co-workers seem to be arguing a lot recently. I was just wondering if I could perhaps get a clearer picture of exactly what is going on. It seems to me recently that you have been coming quite late to work... Acknowledge and explore the issue. Summarise or repeat and confirm each party's presenting issues after they have spoken. Refer to the examples. You have said......Is this correct? You have mentioned….Is that right? Yes, I see… (repeat the issue) Show understanding and sympathy using the following phrases: Ya, that could be frustrating. Generate Solutions and Options What are some steps that can be taken to resolve this for you? Well, what are your views? How do you think we should deal with this? What kind of solutions would you propose? I was wondering what your ideas are on this situation. Make agreements. Show agreement. Yes, that might be worth a try. Establish a specific agreement (who, what, when, where, how). Sure, ok. This is what we will do. We will…. Alright, here’s what we will do. Here’s a way we can move forward… Here’s what we can do to tackle the problem… Set a date to review progress of the agreement Let's meet again on [date] to review progress on this issue. Let’s try this out and meet again in a month’s time to take stock. Tutorial