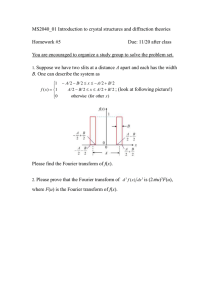
RIPHAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY Signals And Systems Engr. M.S. Orakzai Review of the Fourier Series Review of Fourier Series • Deal with continuous-time periodic signals. A Periodic Signal f(t) t T 2T 3T Two Forms for Fourier Series Sinusoidal Form ∞ 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝑎0 + 𝑎𝑛 cos 𝑛𝜔0 𝑡 + 𝑏𝑛 s𝑖𝑛 𝑛𝜔0 𝑡 𝑛=1 2 T /2 a0 = f (t )dt − T / 2 T Complex Form: ∞ 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝐶𝑛 𝑒 𝑛=−∞ 𝑗𝑛𝜔0 𝑡 2 T /2 an = f (t ) cos n0tdt − T / 2 T 2 T /2 bn = f (t ) sin n0tdt − T / 2 T 1 cn = T T /2 −T / 2 f (t )e − jn0t dt How to deal with Aperiodic Signals? How to Deal with Aperiodic Signal? A Periodic Signal f(t) t T If T→, what happens? • The Fourier series expansion reveals the frequency content of the periodic signal. • It is also possible to analyze the frequency content of nonperiodic signals. The tool that enables us to do this is the Fourier transform • The transform assumes that a nonperiodic (or aperiodic) signal is a periodic signal with an infinite period Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Fourier Integral derivation 2 0 = T Let 1 0 = T 2 2 = 0 = T T → d = 0 Fourier Transform Pair Fourier Transform: ∞ 𝑋 𝜔 = න 𝑥(𝑡)𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 −∞ Inverse Fourier Transform: 1 ∞ න 𝑋(𝜔)𝑒 𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝜔 𝑥 𝑡 = 2𝜋 −∞ 𝑥 𝑡 is time domain signal 𝑋 𝜔 is frequency domain signal Fourier Transform and Inverse Fourier transform are used convert between time and frequency domain Note: some books write 𝑋 𝜔 as 𝑋 𝑗𝜔 , its just a notation, don’t be confused Example-1: FT of Exponential Signal • Find the Fourier transform of 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝑒 −𝑎𝑡 𝑢 𝑡 𝑎>0 Solution ∞ 𝑋 𝜔 = න 𝑥(𝑡)𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 −∞ ∞ 1 − 𝑎+𝑗𝜔 𝑡 𝑋 𝜔 =− .𝑒 ቚ 𝑎 + 𝑗𝜔 0 ∞ 𝑋 𝜔 = න 𝑒 −𝑎𝑡 𝑢 𝑡 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 𝑋 𝜔 =− −∞ 1 . 𝑒 −∞ − 𝑒 0 𝑎 + 𝑗𝜔 ∞ 𝑋 𝜔 = න 𝑒 −𝑎𝑡 . 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 𝑋 𝜔 = 0 1 𝑎 + 𝑗𝜔 ∞ 𝑋 𝜔 = න 𝑒− 0 𝑎+𝑗𝜔 𝑡 𝑑𝑡 𝑒 −𝑎𝑡 𝑢 𝑡 𝐹𝑇 1 𝑎 + 𝑗𝜔 Example-2: FT of Rectangular Pulse • Find the Fourier transform of 1 −𝑇 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 𝑇 𝑥 𝑡 =ቊ 0 𝑡 >𝑇 Solution ∞ 𝑋 𝜔 =න 𝑥(𝑡)𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 −∞ 𝑇 𝑋 𝜔 = න 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 −𝑇 1 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑇 𝑋 𝜔 = − .𝑒 ቚ 𝑗𝜔 −𝑇 𝑋 𝜔 =− 1 −𝑗𝜔𝑇 𝑒 − 𝑒 𝑗𝜔𝑇 𝑗𝜔 2 𝑒 𝑗𝜔𝑇 − 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑇 𝑋 𝜔 = 𝜔 2𝑗 2 𝑋 𝜔 = sin(𝜔𝑇) 𝜔 𝑋 𝜔 = 2𝑇. sin 𝜔𝑇 𝜔𝑇 𝑋 𝜔 = 2𝑇. sin𝑐 𝜔𝑇 Example-2: Cont… 𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑡 2𝑇 𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑡 𝑇 𝐹𝑇 2𝑇𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑐(𝜔𝑇) or 𝐹𝑇 𝑇𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑐(𝜔 𝑇/2) Example-2: Cont… 𝑡 𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑇 𝐹𝑇 𝑇𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑐(𝜔 𝑇/2) X a () 2 −2 𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑡 2 𝐹𝑇 2 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑐(𝜔) − 2 Example-2: Cont… 𝑡 𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑇 𝑋 𝜔 = 4𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑐 2𝜔 𝐹𝑇 𝑇𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑐(𝜔 𝑇/2) Example-3: IFT of Rectangular Pulse • Find the Inverse FT of rectangular spectrum 1 −𝑊 ≤ 𝜔 ≤ 𝑊 𝑋(𝜔) = ቊ 0 𝜔 >𝑊 Solution: 1 ∞ 𝑥 𝑡 = න 𝑋(𝑗𝜔)𝑒 𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝜔 2𝜋 −∞ 1 𝑒 𝑗𝑊𝑡 − 𝑒 −𝑗𝑊𝑡 = 𝜋𝑡 2𝑗 1 𝑊 𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑥 𝑡 = න 𝑒 𝑑𝜔 2𝜋 −𝑊 1 = sin(𝑊𝑡) 𝜋𝑡 𝑊 1 𝑗𝜔𝑡 = .𝑒 ቚ 2𝑗𝜋𝑡 −𝑊 1 = 𝑒 𝑗𝑊𝑡 − 𝑒 −𝑗𝑊𝑡 2𝑗𝜋𝑡 𝑊 sin 𝑊𝑡 = . 𝜋 𝑊𝑡 = 𝑊 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑐(𝑊𝑡) 𝜋 Example-3: cont… Example-4: FT of Impulse Unit Impulse 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝛿(𝑡) Solution: ∞ 𝑋 𝜔 = න 𝛿(𝑡) 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 −∞ ∞ 𝑋 𝜔 = න 1. 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 −∞ 𝑋 𝜔 = 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 ቚ 𝛿(𝑡) 𝐹𝑇 𝑡=0 1 Example-5: IFT of Impulse • Find the Inverse FT of 𝑋 𝜔 = 2𝜋𝛿(𝜔) 1 ∞ 𝑥 𝑡 = න 𝑋(𝑗𝜔)𝑒 𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝜔 2𝜋 −∞ 1 ∞ 𝑥 𝑡 = න 2𝜋𝛿(𝜔)𝑒 𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝜔 2𝜋 −∞ 𝑥 𝑡 =1 1 𝐹𝑇 2𝜋𝛿(𝜔) Example-6: FT of 𝑒 𝑗𝜔0𝑡 • Find the Fourier Transform of 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝑒 𝑗𝜔0 𝑡 Solution: We know that 1 𝐹𝑇 2𝜋𝛿(𝜔) ∞ න 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 = 2𝜋𝛿(𝜔) −∞ ∞ ℱ 𝑒 𝑗𝜔0 𝑡 = න 𝑒 𝑗𝜔0 𝑡 . 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 ∞ −∞ = න 𝑒 −𝑗(𝜔−𝜔0 )𝑡 𝑑𝑡 −∞ = 2𝜋𝛿 𝜔 − 𝜔0 Example-6: FT of 𝑒 𝑗𝜔0𝑡 • Find the Fourier Transform of 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝑒 𝑗𝜔0 𝑡 Solution: We know that 𝛿(𝑡) 𝛿 𝑡 = ∞ 𝐹𝑇 ℱ −1 1 1 1 ∞ 𝛿 𝑡 = න 1. 𝑒 𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝜔 2𝜋 −∞ ℱ 𝑒 𝑗𝜔0 𝑡 = න 𝑒 𝑗𝜔0 𝑡 . 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 ∞ −∞ = න 𝑒 𝑗(𝜔0 −𝜔)𝑡 𝑑𝑡 −∞ = 2𝜋𝛿 𝜔0 − 𝜔 or ∞ න 𝑒 𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝜔 = 2𝜋𝛿 𝑡 −∞ Since the impulse function is an even function, 𝛿 𝜔0 − 𝜔 = 𝛿(𝜔 − 𝜔0 ), Interchanging variables t and ω results in ∞ න 𝑒 𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 = 2𝜋𝛿 𝜔 −∞ ℱ 𝑒 𝑗𝜔0 𝑡 = 2𝜋𝛿 𝜔 − 𝜔0 Example-7: FT of 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔0𝑡 • Find the Fourier Transform of 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔0 𝑡 Solution: ∞ ℱ 𝑒 𝑗𝜔0 𝑡 = න 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔0 𝑡 . 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 −∞ ∞ = න 𝑒 −𝑗(𝜔+𝜔0 )𝑡 𝑑𝑡 −∞ = 2𝜋𝛿 𝜔 + 𝜔0 Example-8: FT of cos signals • Find the Fourier Transform of 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝜔0 𝑡 Solution: ∞ 𝑋 𝜔 = න cos 𝜔0 𝑡 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 −∞ ∞ 𝑋 𝜔 =න −∞ 𝑒 𝑗𝜔0𝑡 + 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔0 𝑡 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 .𝑒 𝑑𝑡 2 1 ∞ −𝑗(𝜔−𝜔 )𝑡 1 ∞ −𝑗(𝜔+𝜔 )𝑡 0 𝑑𝑡 + 0 𝑑𝑡 = න 𝑒 න 𝑒 2 −∞ 2 −∞ = 1 2𝜋𝛿 𝜔 − 𝜔0 2 + 1 2𝜋𝛿 𝜔 + 𝜔0 2 = 𝜋𝛿 𝜔 − 𝜔0 + 𝜋𝛿(𝜔 + 𝜔0 ) Example-9: FT of sin signal • Find the Fourier Transform of 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝜔0 𝑡 Solution: ∞ 𝑋 𝜔 = න 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝜔0 𝑡 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝑡 −∞ ∞ 𝑋 𝜔 =න −∞ 𝑒 𝑗𝜔0𝑡 − 𝑒 −𝑗𝜔0𝑡 −𝑗𝜔𝑡 .𝑒 𝑑𝑡 2𝑗 1 ∞ −𝑗(𝜔−𝜔 )𝑡 1 ∞ −𝑗(𝜔+𝜔 )𝑡 0 𝑑𝑡 + 0 𝑑𝑡 = න 𝑒 න 𝑒 2𝑗 −∞ 2𝑗 −∞ = 1 2𝜋𝛿 𝜔 − 𝜔0 2𝑗 + 1 2𝜋𝛿 𝜔 + 𝜔0 2𝑗 = −𝑗𝜋𝛿 𝜔 − 𝜔0 + 𝑗𝜋𝛿(𝜔 + 𝜔0 ) = 𝑗𝜋 𝛿 𝜔 + 𝜔0 + 𝛿(𝜔 − 𝜔0 ) Example-10: Find the FT of given Signal Obtain the Fourier transform of the signal shown in Figure Solution: Example-11: Find the FT of given Signal Solution: Practice Problem-1 • Find the Fourier Transform of Practice Problem-2 Practice Problem-3 • Find the Fourier Transform of 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝑒 𝑎𝑡 𝑢 −𝑡 Answer: 𝑋 𝑗𝜔 = 1 𝑎−𝑗𝜔 Practice Problem-4 • Find the Fourier Transform of Exam Question • Determine the Fourier Transform of the following Signal 𝑥(𝑡) −4 −1 0 1 4 Table of Fourier Transform Fourier Transform Pairs Fourier Transform Pairs