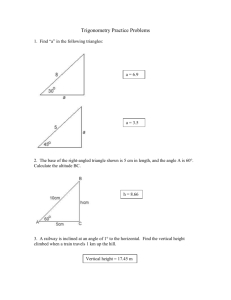
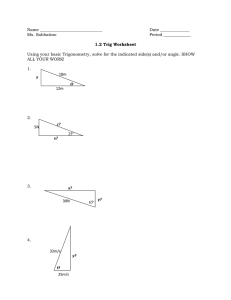
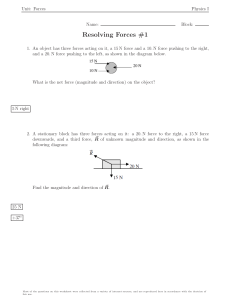
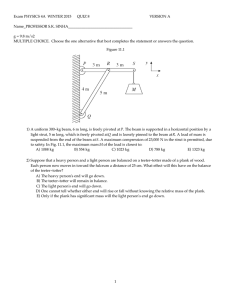
4 Worksheet (AS) Data needed to answer questions can be found in the Data, formulae and relationships sheet. 1 Two forces, each of magnitude 8 N, act on an object. The angle between the two forces is 60º. What is the magnitude of the resultant force acting on the object? A B C D 2 The object in the diagram is in equilibrium. Which equation is correct about the forces? A B C D 3 [1] F θ 15 = 20 cos θ 20 = F cos θ F = 15 sin θ F = 15 tan θ 15 N 0.5 m 100 N 200 N 300 N 400 N A uniform square block is pushed along a rough surface at constant speed by a force of 100 N. A horizontal force of friction acts between the surface and the block. What is the moment of the force of friction about the centre of gravity? [1] A B C D [1] 2N 4N 6N 12 N A man of weight 600 N stands at the end of a uniform wooden plank, which is pivoted as shown in the diagram. What is the weight of the wooden plank? [1] A B C D 5 20 N A force of 10 N is resolved into two components at right angles to each other. One of the components is 8 N. What is the other component? A B C D 4 4N 7N 8N 14 N [1] 80 N m clockwise 80 N m anticlockwise 160 N m clockwise 160 N m anticlockwise AS and A Level Physics 3.0 m direction of movement centre of gravity ● 1.6 m Original material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1 4 Worksheet (AS) 6 Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force in each case below. a b [3] [2] 7 In each case below, resolve the vector into two perpendicular components in the x and y directions. a b [2] [2] 8 a Define the moment of a force. b State two conditions that must be met for the equilibrium of an extended object. [1] [2] 9 The diagram shows a uniform beam of length 1.5 m and weight 60 N resting horizontally on two supports. a By taking moments about the support A, determine the force RB at the support B. b Use your answer to a to calculate the force RA at support A. [3] [1] 10 A child of mass 35 kg on a swing is pulled to one side. The diagram shows the forces acting on the seat of the swing when it is in equilibrium. a What is the net force on the seat? [1] b Draw a triangle of forces. Hence determine: i the tension T in the rope ii the angle θ made by the rope with the vertical. AS and A Level Physics [4] [2] Original material © Cambridge University Press 2010 2 4 Worksheet (AS) 11 A gardener pulls a 50 kg roller along level ground, as shown in the diagram. The roller moves at a steady speed along the level ground when the handle makes an angle of 30° to the horizontal ground and the gardener pulls with a force of 300 N along the handle. a Calculate the horizontal component of the force 300 N. b What is the net force in the horizontal direction? Hence determine the magnitude of the resistive force acting on the roller. c Determine the vertical contact force acting on the roller due to the ground. [2] [2] [3] 12 A ladder of mass 32 kg rests at an angle against a smooth wall as shown in the diagram. The centre of gravity of the ladder is at its mid-point. a Determine the force R exerted by the wall on the ladder by taking moments about the base of the ladder. [3] b Explain why the force at the base of the ladder was not included when doing the calculation in a. [1] 13 A 62 kg person lies flat on a uniform plank of mass 15 kg. The plank, with the person lying on it, is placed on a brick and some bathroom scales, as shown in the diagram below. The person’s toe-to-head distance is 1.56 m. The length of the plank is also 1.56 m. a Sketch the diagram above. On your sketch, show all the forces acting on the plank. b The reading on the bathroom scales is 30 kg. Use this information to determine how far the centre of gravity of the person is from the toes. Total: AS and A Level Physics 45 Score: Original material © Cambridge University Press 2010 [2] [4] % 3