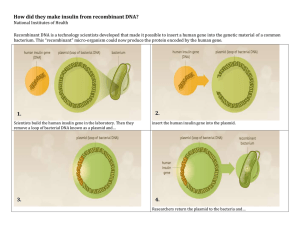
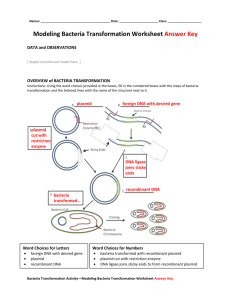
Gene Cloning Genetic Engineering • Genetic engineering can be defined as a modification of the genetic properties of an organism by the use of recombinant DNA technology. • Recombinant DNA technology is the joining together of DNA molecules from two different species. • Recombinant DNA technology has many benefits, such as the ability to improve health and improve the quality of food. • The three important applications are: (1) Applications in Crop Improvement (2) Applications in Medicines and (3) Industrial Applications. Gene cloning • A clone can be defined as an identical copy. • Gene cloning means making many copies of gene. • By definition, DNA cloning is a Molecular Biology technique that allows us to get multiple copies of identical DNA sequence or gene. For cloning, we need the following elements 1. A source of the DNA of interest: any DNA sequence which produces functional protein. For example, insulin gene, pest resistant gene, growth hormone. 2. Host Cells: We need host cells in which to introduce plasmids and amplify the gene of interest. Usually Escherichia coli is used. 2. Plasmids: Plasmids are circular double stranded DNA molecule present inside the bacteria. The structure of plasmid contain: a. Origin of replication (ORI): due to which it have the capability to self replicate itself. b. Restriction enzyme site: at this site restriction enzyme can cut the DNA strands thus allow to insert any foreign DNA. c. Ampicillin resistant gene: used to separate non recombinant bacteria from recombinant bacteria. Restriction enzymes: these are molecular scissors which have the capability to cut specific DNA sequences. Steps involved in cloning • Step I: Gene of interest, is inserted into a circular DNA molecule called a vector, to produce a recombinant DNA molecule. • For this purpose, plasmids are used as vector. Plasmid is cut from restriction site with the help of restriction enzyme. Then gene of interest is joined inside plasmid with the help of ligase enzyme. The plasmid containing foreign gene is called recombinant plasmid. • Step II: The recombinant plasmid is then introduced into bacteria (E.coli). This process is called transformation. • For this purpose, bacteria is treated with chemicals and heat which will create pores in the cell membrane. Recombinant plasmid enter through these pores inside the bacteria. • Step III: then bacteria containing recombinant plasmid is grown on media to make many copies of gene. • As after transformation some recombinant plasmid enter the bacteria, while in some bacteria plasmid donor enter. The select recombinant bacteria ampicillin resistance is used. For this purpose, bacteria is grown on media containing antibiotic ampicillin. Those bacteria which contain recombinant plasmid will grow as they have the capability to resist to antibiotic while all other bacteria die. • Step IV: Within the host cell the plasmid multiplies, producing numerous identical copies, not only of itself but also of the gene that it carries. • When the host cell divides, copies of the recombinant DNA molecule are passed to the next generation and further vector replication takes place. • After a large number of cell divisions, a colony, or clone, of identical host cells is produced. Each cell in the clone contains one or more copies of the recombinant DNA molecule; the gene carried by the recombinant molecule is now said to be cloned. Application • Through recombinant DNA techniques, bacteria have been created that are capable of synthesizing human insulin, human growth hormone and hepatitis B vaccine, and other medically useful substances.