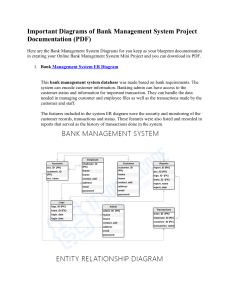
What will be covered: • • • • • • • What is DFD? Why DFD? How does DFD work? Who currently uses DFD? How can you use DFD? Resistance to DFD Summary What is DFD? (1/3) Design for Disassembly(DFD) is: • A type of green manufacturing • Products are designed to be taken apart, so that they can be used in later generations of products. • Also known as Design for Remanufacture or Reuse. What is DFD? (2/3) “The goal is to close the production loop, to conceive, develop, and build a product with a long-term view of how its components can be refurbished and reused--or disposed of safely--at the end of the product's life…..” What is DFD? (3/3) “…In a world where the costs of disposal are rising, ease of destruction becomes as important as ease of construction.” -Gene Bylinsky, Fortune Why DFD? • Unlike other green business programs, DFD has financial benefits as well as environmental ones. Why DFD? Why include recycling/reuse plans in the design process? • Thinking problems through beforehand can lower recycling costs dramatically and reduce environmental hazards. Why DFD? • New laws across Europe will soon require manufacturers to take back used product. • In Germany, manufacturers are already responsible for the final fate of their products' packaging. • Similar legislation is expected in the US in the notto-distant future. Why DFD? “The Germans have established a de facto global manufacturing standard. U.S. companies wishing to compete globally must start making products that will comply with the green dictates of the huge European market” -Gene Bylinsky, Fortune Green Product Design from a Environmental Perspective Design for Disassembly • Slows the depletion of Natural Mineral Resources • Lower Amounts of trash to already crowed landfills According to the National Academy of Sciences, 94% of the materials that are pulled out of the earth enter the waste stream within months. Green Product Design from a Business Perspective The main principles of DFD and green manufacturing also fit into modern efforts to make assembly more efficient, such as concurrent engineering and total quality control. Green Product Design from a Business Perspective (cont.) Used or refurbished parts sometimes work better than new ones. Among Integrated Circuits, 5% of new chips fail, but in comparison, used chips only fail 2% of the time How Does DFD work? Design for Disassembly/Green Design: • Emphasis on reducing parts • Rationalizing materials • Reusing components • Green Products more efficient to build and distribute than conventional ones How Does DFD work? Design for Disassembly/Green Design: • DFD experts fit into Concurrent Engineering teams easily • DFD reduces waste, which is an enemy of total quality management Examples of DFD • Eastman-Kodak • Hewlett Packard • Vehicle Recycling Development Center Eastman-Kodak • • • • • The Fling - first disposable camera Angered Environmentalists Funsaver Panoramic - very popular Name Wastemaker of the Year In 1990, Kodak had converted the disposable cameras to recyclable ones. • Now 87% of the Cameras are either reused or recycled. Hewlett-Packard • Depending on the model, hp is able to recycle up to 65% of the print cartridge by weight. The remaining parts that cannot be recycled are disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner. Hewlett-Packard • Each month, HP reuses or recycles more than 3.5 million pounds of material in their U.S. and European product-recovery centers. • • Recycled over 39 million hp LaserJet cartridges worldwide HP’s workstation designers’ new chassis reduces transport packaging by 30%, while disassembly time has been cut 90%. Vehicle Recycling Development Center • • • Established in 1994 Joint venture of GM, Chrysler, & Ford Goals of VRDC: 1. 2. Finding ways to recycle automobile "fluff"--the 25% or so of material remaining after recycling of the ferrous, nonferrous, and other readily recycled components. Finding ways to more cost-effectively disassemble cars, including removal of fluids. How to implement DFD • DFD is easily implemented in most Quality Strategies • DFD involves considering the products’ entire life cycle. How to implement DFD • DFD includes looking at the impact of design decisions not only as they relate to a specific product attribute, but in the broader sense of environmental impact over the entire product life from procured parts to disposal. Collecting Data for DFD 1. 2. 3. 4. Cost in the form of complexity and time Revenues provided in respect to the materials that can be liberated Environmental impact in the form of residual material disposal Technical difficulty in the form of special tools, material handling, material identification Resistance to DFD Xerox is one of the companies meeting some resistance to selling refurbished products. “There are pockets in the consumer base that keep saying, 'We only want 100% new products.’” -Jack C. Azar, Xerox • Summary • • • DFD involves examining a product’s entire life cycle DFD’s benefit, both financial and ecological, outweigh the costs DFD is important part of a firm’s quality strategy. Summary • • • (cont.) Many European Countries will soon require DFD by law Germany is the worldwide leader in DFD There is a resistance to DFD by United States consumers who want 100% new products Bibliography S. Thomas Foster, Managing Quality (Prentice Hall 2001) Bylinski, G., “Manufacture for Reuse,” Fortune (Feb 6, 1995) Hewlett Packard (http://www.hp.com) Eastman-Kodak (http://www.kodak.com) General Motors (http://www.gm.com) National Academy of Science (http://www4.nationalacademies.org/nas/)