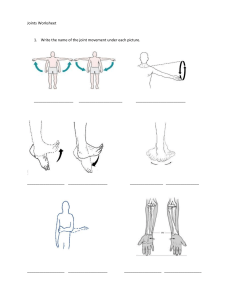
Lab Joints 1. What are the two general ways in which joints are classified? Joints are classified by structure and function. Structurally there are fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joint structures. Functionally joints are classified by the amount of movement they allow. There are synarthroses which are immovable, amphiarthroses which are slightly movable, and diarthroses which are freely movable. 2. Why is the coxal joint more stable than the shoulder joint? The shoulder joint gives up stability to provide the most freely movable joint of the body. The head of the humerus fits in the small glenoid cavity like a golf ball sitting on a tee. The coxal joint is a ball and socket joint like the shoulder but the head of the femur fits with the deeply cupped acetabulum of the hip bone. These two bones fit together in a much deeper socket limiting range of motion for stability. 3. For each of the following exercises, name two joints involved and one type of movement that occurs at each joint: a. Chin-ups: _Hinge joint- Flexion of arm to pull the body up to the bar. _______ __Pivot joint – Supination of the radioulnar joint to have the palms facing your face to get them in he right position to perform the chin up. b. Squats: _Hinge joint – Flexion of the knee to lower the body and extension to raise the body back up. Ball and Socket – Flexion of femur to lower body, extension of femur to raise body to upright position. 4. Match each of the following joints with its structural classification(s). ___2__ a. atlantoaxial joint 1. suture __11__ b. intervertebral joint 2. pivot joint ___3__ c. glenohumeral joint 3. ball-and-socket joint ___6__ d. interphalangeal joint 4. saddle joint __8___ e. dentoalveolar joint 5. syndesmosis 11. plane joint ___11__ f. sacroiliac joint 6. hinge joint ___1__ g. frontonasal joint 7. synchondrosis __11__ h. intertarsal joint _10___ i. metacarpophalangeal joint 8. gomphosis 9. symphysis 10. condyloid joint Identifying and classifying Joints 1. Using the list of structures provided, and a diagram, sketch a synovial joint in the space provided and identify the structures. synovial cavity articular cartilage periosteum fibrous outer layer articular (joint) capsule inner synovial membrane ligaments 2. Match each of the following joint structures with its description/function: ____2__ a. syndesmosis 1. contains periodontal ligament ____4__ b. suture 2. organized into a bad or sheet ____3__ c. synovial joint 3. contains joint cavity ____1__ d. gomphosis 4. is found only in the skull ____5__ e. synchondrosis 5. epiphyseal plate