Simple Shearing Stress: Mechanics of Deformable Bodies
advertisement

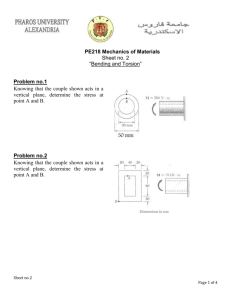
Simple Stress: Shearing Stress ES205 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Engr. GG Ancog Shearing Stress Forces parallel to the area resisting the force cause shearing stress. Shearing stress is also known as tangential stress. Shear stress arises whenever the applied loads cause one section of a body to slide past its adjacent section. where V is the resultant shearing force which passes through the centroid of the area Av being sheared (parallel area). Force Area Force Force Force Examples of Direct Shear a) Single Shear in a Rivet b) Double Shear in a bolt a) Shear in a metal sheet produced by a punch Resisting Area Sample Problem 1 What force is required to punch a 20-mm-diameter hole in a plate that is 25 mm thick? The shear strength of the plate is 350 MPa. Solution P 350 25 mm = ( P = 549,778.71 N P = 549.78 KN 20 mm )( ) Sample Problem 2 The bell crank, which is in equilibrium under the forces shown in the figure, is supported by a 20mm-diameter pin at D that is in double shear. Determine: (a) the required diameter of the connecting rod AB, given that its tensile working stress is 100 MPa; (b) the shear stress in the pin. Solution RDX 15KN 25.98KN RDY (a) Solve for the diameter of the connecting rod AB ∑MD = 0 + PAB(200) – 25.98(240) = 0 PAB = 31.177 KN (T) 100 = . d = 19.924 mm ~ 20 mm Solution 31.177KN RDX 15KN 25.98KN RDY (b) Shear stress in the pin ∑FY = 0 + ∑FX = 0 + RDX – 15 – 31.177 = 0 RDY – 25.98 = 0 RDX = 46.177 KN RD = RDY = 25.98 KN 52.98 KN τ = 84.32 MPa Sample Problem 3 Two wooden planks, each 22mm thick and 160mm wide, are joined by the glued mortise joint shown. Knowing that the joint will fail when the average shearing stress in the glue reached 820 KPa, determine the smallest allowable length d of the cuts if the joint is to withstand an axial load of magnitude P = 7.6 kN. Solution Given: τ = 820 KPA P = 7.6 KN Req’d: d = ? Identify the resisting area: A = 7[d(22 mm)] d = 60.20 mm Surfaces that will have sliding P.S. Please check Google Classroom for your Assignment No. 2. Have a good day!