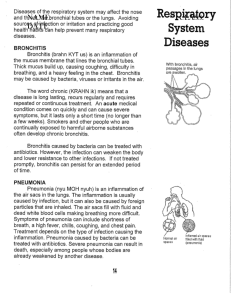
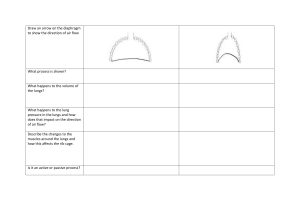
F.4 Biology 1st Term Mock Exam Answers Part A: Multiple-Choice Questions DBBDB CDDAB CAADB CDABB DCAAA CDBCC DA Part B: Structured Questions 1. (a) D (b) B (c) A (d) C 2. (a) W: cell wall X: nucleus Y: cytoplasm Z: cell membrane (b) cellulose (c) It protects / supports the cell / gives shape to the cell. (d) W is fully permeable while Z is differentially permeable. (e) 100x/10x = 10x 3. Anaemia: Eat more beef / liver / beans / cabbage / spinach / raisins to increase the intake of iron. Iron is essential for the production of haemoglobin in red blood cells. Constipation: Drink more water so that faeces are soft and can be passed out of the body more easily. OR Eat more fruits / vegetables / wholemeal products to increase the intake of dietary fibre. Dietary fibre adds bulk to food to stimulate peristalsis / Dietary fibre holds a lot of water so that faeces can be passed out of the body more easily. Obesity: Eat a balanced diet / Choose low-fat food to reduce the energy intake. There will be no more weight gain if the energy intake is less than the energy output. OR Eat more fruits / vegetables to increase the intake of dietary fibre. High-fibre food is filling and can help control body weight. 4. (a) Each enzyme has its unique active site. OR Enzymes are specific in action. Molecules of proteins in meat and gluten in wheat are different in shape. Proteins in meat can fit into the active sites of the proteases but gluten cannot. (b) As less digested food is absorbed into the villi, there is more digested food present ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ in the lumen of the small intestine. The water potential in the lumen becomes lower. ⠀⠀This causes water to move from the epithelial cells of the villi to the lumen by ⠀⠀⠀ osmosis. The intestine cannot absorb so much water, thus watery faeces are produced. 5. (a) *Ribosome (b) *Protease. to ensure that the enzymes produced will not digest the glandular cells while it is ⠀ still within the cells. (c) The portion of the polypeptide formed after cleavage undergoes conformational ⠀ ⠀ change, ⠀ exposing the active site, thus making the enzyme functional. 6. (a) The mucus traps dust particles and bacteria. The cilia beat to sweep the mucus towards the nasal cavity. The mucus is then ⠀ ⠀ removed. (b) The mucus trapped in the sinuses may contain bacteria. These bacteria cause ⠀ ⠀ ⠀ sinusitis. (c) Sore throat. ⠀ Mucus containing bacteria is drained into the back of the throat from the sinuses ⠀ ⠀ and the pathogens cause an infection. ⠀ (or other reasonable answers) 7. (a) ⠀ ⠀ (b) ⠀ ⠀ ⠀ (c) ⠀ ⠀ (d) ⠀ ⠀ (e) ⠀ ⠀ ⠀ ⠀ ⠀ ⠀ ⠀ ⠀ ⠀ ⠀ The walls of the arteriole and venule are impermeable. No exchange of materials occurs there. The content of the blood and hence the water potential remains unchanged. At the arteriole end of the capillary, high blood pressure forces some ⠀ ⠀ ⠀ components of the plasma like water, minerals, sugar, lipids and hormones out of the capillary wall. This leads to a decrease in the water potential of the blood in the capillary. 1m Plasma proteins are too large to pass through the capillary wall. They remain ⠀ in the blood.1m At the venule end, the water potential of the blood is lower than that of the ⠀ tissue fluid due to the presence of plasma proteins. Water in the tissue fluid is drawn into the capillary, causing the water potential to increase. Lymph is kept flowing by the contraction of skeletal muscles which surround the lymph vessels. Valves are present in the lymph vessels to prevent the backflow of lymph. Collects and returns excess tissue fluid to the blood circulation. / Protects us against disease by filtering out germs from the lymph at the lymph nodes. / Transports lipids from the lacteals in the small intestine to the blood. 8. (a) (i) *Diaphragm ⠀ (ii) *Lungs ⠀ (iii) *Thoracic wall / *rib cage ⠀ (iv) *Trachea / *mouth / *nose (b) (i) The balloons inflate / increase in volume. ⠀ (ii) This represents inhalation / breathing in. ⠀ (iii) During inhalation, the diaphragm muscles contract and the diaphragm ⠀ ⠀ becomes flattened. The volume of the thoracic cavity (space Y) increases and hence the air pressure inside decreases. The volume of the lungs increases and the air pressure inside becomes lower than the atmospheric pressure. Air rushes into the lungs. (c) The small space between the lungs and the wall of thoracic cavity is filled with ⠀ pleural fluid instead of air. / ⠀ When at rest, the diaphragm is dome-shaped while the bottom of the plunger is ⠀ ⠀ flat. / The movement of the diaphragm is controlled by muscle contraction and relaxation while that of the plunger is controlled by hand. / ⠀ The size of the thoracic cavity can be changed by movement of the rib cage while the syringe barrel is rigid. ⠀ ⠀ (d) The pressure inside the thoracic cavity (space Y) will be the same as the ⠀ ⠀ atmospheric pressure even when the diaphragm becomes flattened. No pressure difference will exist between the lungs and the atmosphere and thus ⠀ air will not rush into the lungs. 9. (a) The rate of digestion of lipids It was measured by the time required for the solution to change from red to ⠀ yellow. (b) When lipids in the milk were digested by lipase, fatty acids and glycerol were ⠀ ⠀ produced. ⠀ The fatty acids lowered the pH of the solution from above 8.2 to below 6.8, thus ⠀ phenol red in the solution changed from red to yellow. ⠀ ⠀ ⠀ (c) Bile salts alone could not digest lipids into fatty acids and glycerol. / ⠀ In the presence of lipase, the larger the amount of bile salts, the higher the rate of digestion of lipids into fatty acids and glycerol. / Lipase alone could digest lipids into fatty acids and glycerol. / In the presence of 2 cm3 of the lipase solution, the amount of lipase was not a ⠀ limiting factor of the rate of digestion of lipids into fatty acids and glycerol. (any 3) (d) Bile salts emulsify lipids into small droplets ⠀ to increase the surface area for the lipase to act on. 10. (a) (i) 615.8 / 1436.8 = 0.4 (ii) The ratio becomes smaller as the size of the sphere increases. (b) (i) Unicellular organisms have a larger surface area to volume ratio. Exchange of gases by diffusion through their body surface is fast enough to meet their requirements. Large organisms like humans have a much smaller surface area to volume ratio. Exchange of gases by diffusion through their body surface is not fast enough to meet their requirements. (ii) *Mitochondrion