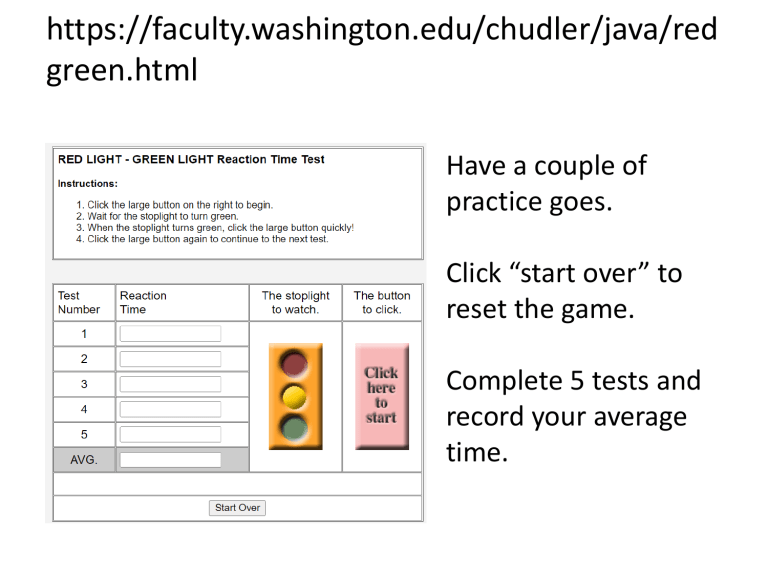
https://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/java/red green.html Have a couple of practice goes. Click “start over” to reset the game. Complete 5 tests and record your average time. Forces and Motion You will find out about Thinking, Braking and Stopping Distances Which factors affect Thinking, Braking and Stopping Distances Why we should all know about this and how this helps us to stay safe on the road Stopping Distance When a driver presses hard on the brakes the car does not stop instantly. It is the same when you press the brakes on your bike – you don’t just stop suddenly. Stopping Distance is made up of two elements. The first is the Thinking Distance. The second is the Braking Distance. The equation to work out Stopping Distance is: Stopping Distance = Thinking Distance + Braking Distance Stopping Distance is the total DISTANCE the car travels until it stops. REMEMBER: These are DISTANCES we are dealing with… not times. Thinking and Braking Distance When someone walks out in front of a car the driver does not instantly press down on the brake pedal. An element of thinking is involved – the information the eye sees need to be sent by the brain down to the muscle in your foot to press the brake. All the while you are THINKING about pressing the brake the car is travelling a DISTANCE. Once the brake has been pressed the car will slow down until it has stopped. All the while you are BRAKING the car is travelling a DISTANCE. THINKING DISTANCE: The DISTANCE the car travels between the driver seeing a danger and acting upon it (e.g. press the brakes). BRAKING DISTANCE: The DISTANCE the car travels until it stops once the brakes have been applied. You can see here in the table that the faster a car travels the larger the THINKING and BRAKING DISTANCES are. At 70 miles/h the car will travel 21m whilst you THINK about pressing the brakes and a further 75m once the brakes have been pressed… that’s a long way! Factors affecting Thinking and Braking Distance Being tired, under the influence of drugs or alcohol, or being distracted INCREASE the THINKING DISTANCE. Drinking stimulants (caffeine – coffee or energy drinks), being fully rested and wide awake, and distraction free REDUCE the THINKING DISTANCE. Difficult Concept: If the driver is driving really fast their thinking TIME will be the SAME. However, their THINKING DISTANCE could change due to any of the conditions mentioned above. Driving on icy or wet roads, having bald tyres or poor brakes, or driving too fast INCREASE the BRAKING DISTANCE. Driving on good dry roads, having new brakes and tyres and driving slower REDUCE the BRAKING DISTANCE. As before Thinking Distance, Braking Distance and Stopping Distance are all DISTANCES. Remember to discuss DISTANCE in your answer! Safe Driving It is very important that drivers drive safely and know the limits of their cars. They can do this by slowing down when it is wet or windy or when road conditions are really bad. They can also drive at the speed limits appropriate to particular roads. Outside schools 20 is plenty, you would not drive at Motorway speeds there. Think about the Stopping Distance if a driver did. Drivers can also keep an appropriate distance from the car in front – the faster they drive the bigger the gap between them. This should be at the very least the thinking distance. More about the factors that affect Braking Distance Recall that F=ma. This means that a vehicle that has a greater mass or a greater acceleration needs a greater force to slow it down. Therefore the BRAKING DISTANCE is increased if mass or speed is high. This graph shows that as the speed of a vehicle increases: Two brake pads push on to a disc when the brake pedal is applied. Friction is used to slow the car down. If brakes are worn then there is less friction force to slow down the car. This then INCREASES the BRAKING DISTANCE. Similarly, worn, balding tyres reduce the friction on the road. So again this increases the BRAKING DISTANCE. Thinking Distance increases linearly (double speed = double Thinking Distance) and That the Braking Distance increases as a square relationship (if speed doubles then Braking Distance increases x4, if speed trebles then Braking Distance x9). Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. A cyclist sees the traffic lights ahead of him turn red. Why does he not brake straight away? James knows that at his current speed his Thinking Distance is 15m. How fast is he going? If he doubled the Thinking Distance how fast would he then be going? Why are most urban roads limited to 30 miles per hour? Two cars are driving along a 30 mile/h road. What should be their minimum distance between them? Why do you think tractors have tyres with such thick treads? Joanne is a mum with a new born baby. She wants to drive as safely as possible and avoid a crash. Name three ways she can reduce her thinking and braking distance. Margaret says that the Stopping Distance of a car is about how long it takes for the car to stop. Is she right? Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. A cyclist sees the traffic lights ahead of him turn red. Why does he not brake straight away? He needs to think about pressing the brake and as he does his bike is still travelling. His reaction may be quick at about 0.5 seconds but the bike will still move a distance over that period of time. James knows that at his current speed his Thinking Distance is 15m. How fast is he going? If he doubled the Thinking Distance how fast would he then be going? 15m corresponds to 50 miles/h. If doubled then speed doubles too. So he would travel at 100 miles/h which would be breaking any speed limit! Why are most urban roads limited to 30 miles per hour? Stopping Distance is shorter so more likely to stop in time. Also less Force required to slow the car down. Less chance of skidding. Two cars are driving along a 30 mile/h road. What should be their minimum distance between them? This should be their Thinking Distance – 9m. The Government advises more than this. Why do you think tractors have tyres with such thick treads? Mud and fields are more slippery than roads so they need tyres with larger tread to increase the friction force between tyre and muddy field. Small tyre treads will not cause as much friction force so would probably slip more easily. Joanne is a mum with a new born baby. She wants to drive as safely as possible and avoid a crash. Name three ways she can reduce her thinking and three ways she can reduce her braking distance. Thinking Distance reduced by – be alert, drink coffee/stimulant, no distractions, lots of sleep, no alcohol or drugs in her system. Braking Distance reduced by – good tyre tread, good brakes, no icy or wet roads, drive slowly. Margaret says that the Stopping Distance of a car is about how long it takes for the car to stop. Is she right? No. Stopping Distance is all about Distance. It is the Distance the car travels whilst the driver is thinking about pressing the brakes AND the Distance the car travels once the brakes have been pressed and the car stops.