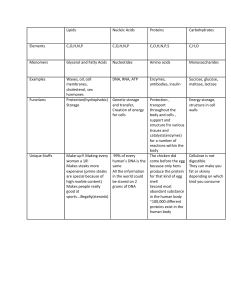
Foundations of Biology Notes Organic Molecules I. Organic molecules Name: _______________________ Block: ________ Date: _________________ A. Organic molecules are molecules that contain a ________________________________ and are made by or found inside living things. 1. Organic chemistry is the ______________________________________. 2. Organic molecules are centered on ________. B. There are 4 types of organic molecules. 1. ___________________ 2. ___________________ 3. ___________________ 4. ___________________ C. Most of the organic molecules are _____________________________________ formed by bonding many small molecules called ___________ together. D. Carbohydrates 1. Carbohydrates are used by living things for _______________. 2. Carbohydrates exist as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides. a. ___________________________; the monomers of the disaccharides and polysaccharides. (1) The most common monosaccharides are _________________________________. (2) Glucose – ________________________________________________. Glucose molecule (C6H12O6) (3) Fructose – ______________________________ Fructose molecule (C6H12O6) Glucose and fructose are isomers. They have the ______________________________ _______________________________________________________________________. b. Disaccharides – _______________________________________________. Sucrose is a disaccharide made when a glucose molecule is bonded to a fructose molecule. Sucrose molecule (C11H22O11) b. Polysaccharides large, complex carbohydrate polymers made up of many _______________________________. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are 3 examples of polysaccharides. (1) Starch – a _______________________________________________. Starch is used as food storage in the seeds, bulbs, and roots of many plants. (2) Glycogen – a highly branched chain of glucose monomers. Glycogen is used by mammals to store food in the liver. (3) Cellulose – the most complex glucose polymer that ____________________________________. Cellulose gives plants their structural support. Humans cannot digest cellulose- but it is necessary in the human diet because it provides _____________ that keeps the digestive system healthy and working properly. 3. We get carbs from eating foods such as ____________________________________. 4. Carbohydrates are made of C,H,and O in a ___________. (CH2O) . 5. Digestion breaks carbs down into individual ______________. The monosaccharides are then used by the cells for energy. E. Lipids (fats) 1. _____________________________________________________. 2. Lipids are very large, ______________ molecules that will not bond with water or dissolve in water. 3. There are 5 types of lipids: _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ Phospholipids a. Fats – are ______________________________________ and are usually associated with animals. Fats are used to _________________. Excess carbohydrate in the body is converted to fat to be stored. Fats are often associated with heart disease because excess fat in the diet can clog the arteries. _______________________ is a type of fat that is made of a glycerol molecule bonded to 3 fatty acids. 3 fatty acids Glycerol molecule b. Oils – are _______________________________ and are usually associated with plants. Oils are often found in seeds and are a source of energy for sprouting seeds. c. Waxes – a type of lipid that is ____________________. In plants waxes form a waterproof coating on the outer surfaces of the leaves. In animals waxes form ____________________; earwax forms a barrier to keep microorganisms from entering the middle ear. d. Steroids – are considered lipids because they ______________________________. Steroids act like chemical messengers inside of the body. __________ is a type of steroid. A small amount of cholesterol is needed for the proper _______________________. High amounts of cholesterol leads to clogged arteries and other forms of heart disease. Steroids are a major component of _________________________________ ________________________________________________________________. e. Phospholipids- make up the cell membrane. Two parts make up a phospholipid. Heads: ____________________- meaning water-loving Tails: ______________________- meaning water-hating 4. The functions of lipids: a. ______________________________________________ b. ______________________________________________ c. ______________________________________________ d. ______________________________________________ 5. We get lipids from eating fried foods, hamburger meat, bacon, lard, whole dairy products, and cheese. F. Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) 1. Nucleic acids are _______________________ that store cellular information in the form of a code “__________________________”. 2. Nucleic acids are polymers made of smaller subunits called ____________________. 3. Nucleotides have 3 parts: a. ______________________________________ b. ______________________________________ c. ______________________________________ 4. DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid a___________________________ of all organisms. It contains all of the ________________ about the organism. b. DNA instructions are held in the ________________ of every living thing. c. DNA is copied every time a cell divides so that all cells will have the genetic information needed for life. d. DNA is in the shape of a _________________________________ and is found in the nucleus of all cells. d. DNA contains the 5-carbon sugar _______. f. The 4 nitrogen bases found in DNA are adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. These bases pair up in a very specific way: (1) ____________________________________________ (2) ____________________________________________ DNA Molecule 5. RNA – _____________________. a. RNA is actually a copy of DNA that can ___________________________ and carry instructions to other parts of the body. b. RNA is a ___________ straight strand. c. RNA has the 5-carbon sugar ____________. d. In RNA, the nitrogen base _________________________________. 6. Both DNA and RNA are necessary for the process of protein synthesis – ________________________________________________________. RNA Molecule F. Proteins 1. Proteins are organic compounds that contain _______________________________________________________. 2. Proteins are more complex than carbohydrates. 3. Proteins are chains of ______________________. a. Amino acids are the _____________________________________ _____________________________________________________________. b. There are 20 amino acids used to make proteins. The ___________________ of amino acids determines the type of protein. c. The amino acids in a protein are linked together by special covalent bonds called _____________________. d. Proteins are also called ____________. Protein (polypeptide) structure There are 20 different R groups because there are 20 different types of amino acids. The remaining structure (Amino group, H, and acidic carboxyl group are identical in all amino acids. 4. Proteins provide structure for cells and tissues, are important in the __________ of muscle tissue, transport O2 in the blood, provide ________, regulate other proteins, and carry out chemical reactions. ** Digestion breaks ____________________________________________that make it up. The amino acids are then used by the cells to build the new proteins that the organism needs. 5. Enzymes – enzymes are special proteins that change the ________ of a chemical reaction. a. Enzymes cause reactions to happen _________ because they __________________________________ needed for the reaction to occur. b. Enzymes are also called ______________________________. c. Enzymes are involved in nearly all metabolic reactions. d. Enzymes work because of _________________. They fit to certain molecules called _____________ like a key fits in a lock. e. If the shape of the enzyme is changed then the enzyme will not function. ____________________________________ can alter the shape of an enzyme. f. Enzymes are _________ to their reaction and will not work in other reactions. g. The enzyme is _________________________________________; it simply causes the reaction to happen. h. We get proteins from eating __________________________________________. i. ____________________: (EA) is the amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to begin (initiate) or proceed.