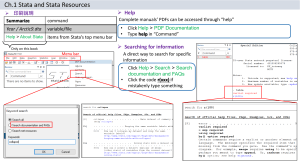
8/11/10 1:41:33 PM Stata Cheat Sheet Command Keeping Stata up to date update all update swap Set Stata Preferences window manage prefs default In "User" Menu Useful for what? N/A This tells Stata to update itself to the newest version. N/A This needs to be issued if Stata downloaded a new "exe" file during the "update all" command. Stata will tell you when it is needed. Failure to do so will create problems with several commands. "Set Stata Preferences" "Restore Default Window Layout (window manage)" Additional Options More info Stata help under "update" Stata help under "update" This restores the default window arrangement of Stata. Use if your windows are messed up or if you canʼt see the Command Window. "Stata Tutorial" "Clear Memory (clear)", then "Set Memory for Data (set memory)" This allocate <X> MB of memory to Stata. To figure out how much to allocate, look at how big the data set it on the hard drive and double the number. "Stata Tutorial" "Clear Memory (clear)", then "Set Memory in Procedures (set matsize)" This specifies that Stata can use up to <X> variables in a regression. Usually 200 is plenty. Use the option "permanently" if you want the matsize command to stick after you quit Stata. permanently "Stata Tutorial" Opens a "Results log" file that records everything in the Results window in Stata. This file can be later opened in any text editor to cut and paste into MS Word or another word processor. If you use the option "replace" then if a log file of the same name already exists it will be overwritten. If you use the option "append" then if a log file of the same name already exists what you do next will be appended to that file. replace; append "Stata Tutorial" Ex: window manage prefs default clear set memory <X>m, permanently Ex: clear set memory 20m, permanently clear set matsize <X> Ex: clear set matsize 200 Recording your work log using <filename.log> "Record your work" "Open Results Log (log using)" Ex: log using "C:\data\BBB_analysis.log", replace log close Open/Save data use <filename> "Close Results Log (log close)" "Open/Save Data" "Open Stata Dataset (use)" or use Toolbar This closes the Results log file. Opens a Stata data file. Make sure to specify the full path. Often it is easier to read the data in using the Toolbar. clear "Stata Tutorial" "Save Stata Dataset (save)" or use Toolbar Save data in memory as a Stata data file. Make sure to specify the full path. Often it is easier to save the data in using the Toolbar. clear "Stata Tutorial" "Import From Spreadsheet (insheet)" This allows you to import data from Excel very easily. Just make sure you have exported the data in tab-delimited format in Excel and that the first row of the spreadsheet contains the variable name you want. Often it is easier to read the data in using the dialog box from the "User" menu instead of typing the command. Ex: use "C:\data\BBB-v1.dta", clear save <filename> Ex: save "C:\data\BBB-v1.dta", replace insheet using <filename> "Stata Tutorial" Stata help under "insheet" Ex: insheet using "C:\data\mydata.txt" outsheet using <filename> "Export To Spreadsheet (outsheet)" This allows you to export data to Excel very easily. Often it is easier to read the data in using the dialog box from the "User" menu instead of typing the command. Stata help under "outsheet" Ex: outsheet using "C:\data\mydata.txt" Viewing data as spreadsheet browse browse <var1> <var2> ... "View Data as Spreadsheet" "Browse Data (browse)" or use Toolbar N/A Shows a spreadsheet with all the data in it. Great to get an overview of the data. This works just like browse but it only show the listed variables. This works very well when you have many variables but you are only interested in a few of them. "Stata Tutorial" "Edit/Modify Data (edit)" or use Toolbar N/A Same as browse, but with the ability to edit/modify the data. Same as browse <var1> <var2> ... , but with the ability to edit/modify the data. "Stata Tutorial" "Sort Data (gsort)" N/A Sorts variables by ascending (+) or descending (-) order Sorts variables by ascending (+) or descending (-) order "Stata Tutorial" "Stata Tutorial" "Order variables" (order)" N/A Orders the variables in the desired sequence Orders <var1> first and <var2> second "Stata Tutorial" "Stata Tutorial" "Move variables" (move)" N/A Moves the location of a variable Moves <var1> to where <var2> is currently located, pushing <var2> to the right. "Stata Tutorial" "Stata Tutorial" Get a listing of all variables in the dataset and see whether they are numerical or string variables. This also tells you how much free memory you have. Some variables are displayed with string labels although they are actually coded as numbers. This allows you to see what numbers correspond to what labels. "Stata Tutorial" Stata help under "browse" Ex: browse buyer acctnum edit edit <var1> <var2> ... "Stata Tutorial" Ex: edit buyer acctnum gsort gsort <-var1> <+var2> ... Ex: gsort -purch +child order order <var1> <var2> ... Ex: order purch child move move <var1> <var2> ... Ex: move purch child Summarize and describe data describe labelbook <var1> "Summarize and Describe Data" "Describe Data in Memory (describe)" "View Data Labels (labelbook)" "Stata Tutorial" Ex: labelbook buyer summarize <var1> <var2> ... "Simple Summary Statistics (summarize)" This is the standard command to get summary statistics (mean, standard deviation, min, max) for a variable. This works well for continuous variables or binary 0-1 variables (the mean of a variable whose only outcomes are 0 or 1 is the proportion of "1"s in the whole sample) by(<var3>) "Stata Tutorial" "Complex Summary Statistics (tabstat)" This is a much more powerful version of the summarize by(<var3>) command. You can ask for many type of summary statistics <st1> <st2> ..., including the "median", the "sum" of the values of the variables, a "count" of the number of observations, etc. "Stata Tutorial" "Tabulate (tabulate)" Shows all the values of categorical variables and how many observations have that value "Stata Tutorial" "Cross-Tabulate (tabulate)" Performs a cross tab between var1 and var2. Allows you to row; column; see whether two categorical variables are associated. chi2 When used with the "chi2" option after the comma then you can test whether the two variables are associated. "Stata Tutorial" This is a good command to get a graphic depiction of how two continuous variables <var1> and <var2> are associated. by(<var3>) "Stata Tutorial" "Draw Bar Graph (graph bar)" This create a bar graph of <var1> over <var2> where the Y axis depicts of mean, the sum, or whatever statistic of <var1> is specified in <st>. by(<var3>) "Stata Tutorial" "Draw Histogram (histogram)" This displays the distribution of <var1>. This is very useful by(<var2>) to get a feel for what values the data have and how often discrete they occur. If your data is discrete and you want one bar for each value, use the option discrete "Stata Tutorial" "Manipulate Variables and Obs" "Generate New Variable (generate)" Generates a new variable with the name <var1> from other variables and manipulations thereof. "Stata Tutorial" "Replace/Change Existing Variable (replace)" Replaces the value of <var1> with what is on the right hand side of the "=" sign. "Stata Tutorial" "Extended Generate New Variables (egen)" This creates a new variable <newvar> that contains the sum of <var1> for each different value of <var2>. Instead of the sum one can also use "mean", "max", "min", "count", and many other statistics that are calculated from <var1> for each category of <var2> separately. "Stata Tutorial" and Stata help under "egen" Ex: summarize purch last tabstat <var1> <var2> ..., statistics(<st1> <st2> ...) Ex: tabstat total_ purch, statistics(count mean sd median) by(gender) tabulate <var1> by(<var3>) Ex: tabulate gender tabulate <var1> <var2> Ex: tabulate gender buyer, chi2 Graph data scatter <var1> <var2> "Graph Data" "Draw Scatter Plot (scatter)" Ex: scatter geog art graph bar (<st>) <var1>, over(<var2>) Ex: graph bar (mean) buyer, over(region) histogram <var1>, frequency Ex: histogram total_, frequency Manipulate Variables and Observations generate <var1>=... Ex: generate ordersize=total_/purch replace <var1>=... Ex: replace female=0 if female==. egen <newvar>=mean(<var1>), by(<var2>) Ex: egen res_prob=total(buyer), by(zip3) This study source was downloaded by 100000791708149 from CourseHero.com on 05-25-2022 20:19:49 GMT -05:00 1 https://www.coursehero.com/file/31295758/Stata-Cheat-Sheet-v2pdf/ Manipulate Variables and Observations "Manipulate Variables and Obs" 8/11/10 1:41:33 PM Stata Cheat Sheet egen <newvar>=mean(<var1>), by(<var2>) Command "Extended Generate New Variables (egen)" This creates a new variable <newvar> that contains the sum of <var1> for each different value of <var2>. Instead of Useful for what? the sum one can also use "mean", "max", "min", "count", and many other statistics that are calculated from <var1> for each category of <var2> separately. "Drop Variables (drop / keep)" Deletes <var1>, <var2>, etc. Careful, you can't get the variables back! "Stata Tutorial" Drop Observations (drop if / keep if)" Deletes observations (not variables) for which <var1> equals <X>. The if-command works as described below. "Stata Tutorial" see separate tab in all dialog boxes This can be used after nearly every command (just before the comma, if there are any options) to have that command be executed only for the observations for which <var1> equals <X>. If <var1> is a continuous variable one can also use ">", "<", "<=", ">=", or "~=" (not equal). If <var1> is a string variables, <X> needs to be in double quotes (e.g. gender=="F"). "Stata Tutorial" see separate tab in all dialog boxes This can be used after nearly every command to have that command be executed only if <var1> has missing values. Instead of "==" one can also ask for not equal by using "~=". Stata help under "op_logical" see separate tab in all dialog boxes You can string together logical statements using an "&" for a logical "and" Stata help under "op_logical" see separate tab in all dialog boxes ... and a "|" for a logical "or" Stata help under "op_logical" Creates a new variable <ntile_var> containing the value of the N-tile based on the values of <var1>. <N> specifies whether one gets quintiles (N=5) or deciles (N=10) or any other desired number of categories. To cover later "Extended Generate New Variables (egen)" Used to calculate response rates per N-title <ntile_var>. This create a new variable <newvar> that contains the mean of <var1> for each different value of < ntile_var>. Instead of the mean one can also use "sum", "max", "min", "count", and many other statistics that are calculated from <var1> for each value of < ntile_var> separately. To cover later "Replace/Change Existing Variable (replace)" This "flips" the values of the N-tile to make sure that the "best" customers are always in the first N-tile. For example, for deciles this becomes: "replace <ntile_var>=11<ntile_var>. To cover later In "User" Menu Additional Options "Stata Tutorial" and Stata help under More info "egen" Ex: egen res_prob=total(buyer), by(zip3) drop <var1> <var2> ... Ex: drop zip zip3 drop if <var1> == <X> Logical statements if <var1> == <X> Ex: if age==40; if age <40; if gender=="F" if <var1> ==. Ex: if age==. if <logical statement1> & < logical statement2> Ex: if age>20 & age<=40 if <logical statement1> | < logical statement2> Ex: if age<20 | age>40 USEFUL COMMANDS FOR FUTURE CLASSES Manipulate N-Tiles, e.g. deciles or quintiles xtile <ntile_var>=<var1>, nquantiles(<N>) "Manipulate N-Tiles" "Create N-Tiles (xtile)" Ex: xtile purch_dec=purch, nquantiles(10) egen <newvar>=mean(<var1>), by(<ntile_var>) Ex: egen res_prob=mean(buyer), by(purch_dec) replace <ntile_var>=<N>+1-<ntile_var> Ex: replace monet_dec=11-monet_dec Simple tests of association tabulate <var1> <var2>, chi2 "Simple Tests of Association" "Cross-Tabulate (tabulate)" Performs a cross tab between var1 and var2. Allows you to see whether two categorical variables are associated. Use the "chi2" option after the comma to test whether the two variables are associated. row; column; chi2 To cover later Ex: tabulate gender buyer, chi2 ttest <var1>, by(<var2>) "Test of Means (ttest)" Performs a test to check whether the means <var1> for two groups are the same. The groups are described by <var2> which should have exactly two value. To cover later "Correlation Between Variables (pwporr)" Calculates the correlation between any set of variables, two at a time. To cover later Performs a "regular", i.e. OLS regression. Works best when you have a continuous dependent variables. "To cover later "Generate Predicted Values (predict)" Creates predicted values for the dependent variables based on the coefficients of the regression you performed. The predicted values are stored in <newvar>. Always use right after the regression command. The predict command uses the coefficient estimates of the last regression that you ran. To cover later "Test Significance of Coefficients (test)" Performs a test of whether the coefficients of two variables are the same. You can also use "test <var1>==X" where X is any number. This tells you whether <var1> is statistically different from that number. To cover later Ex: ttest total_, by(female) pwcorr <var1> <var2> ..., sig Ex: pwcorr total_ purch last, sig Regular regression (OLS) regress <depvar> <var1> <var2> ... "Regular Regression (OLS)" "Run Regression (regress)" Ex: regress salary female mba experience predict <newvar> Ex: predict salary_predict test <var1>==<var2> Ex: test female==4500 Logistic regression logistic <depvar> <var1> <var2> ... "Logistic Regression" "Run Logistic Regression (logistic)" Performs a logistic regression. Works only when you have a binary (0/1) dependent variable. coef To cover later Ex: logistic buyer total_ last purch predict <newvar> "Generate Predicted Values (predict)" Same as for regular regression, see above. To cover later "Test Significance of Coefficients (test)" Performs a test of whether the odds ratios of two variables are the same. To cover later Ex: predict purch_prob test <var1>==<var2> Ex: test art==geog This study source was downloaded by 100000791708149 from CourseHero.com on 05-25-2022 20:19:49 GMT -05:00 2 https://www.coursehero.com/file/31295758/Stata-Cheat-Sheet-v2pdf/ Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)