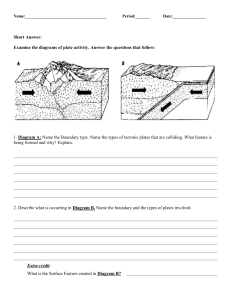
Plate Tectonics—Practice Test 1. What is the main idea Alfred Wegner proposed in the “Theory of Continental Drift” that he published in 1915? a. The continents float on a liquid layer that allows them to move. b. The continents were once a single landmass that drifted apart. c. The fossils found on Earth are all the same age. d. The seafloor has spread the continents into separate landmasses. 2. What observation did Alfred Wegener make that led him to develop the theory of continental drift? a. The seafloor has “magnetic stripes”. b. Continents appear to have once fit together. c. The ocean floor has long ridges of volcanic mountains. d. Earth’s magnetic poles have reversed polarity in geologic history. 3. How did Wegener explain dinosaur fossils that are now found in Antarctica? a. Heat from Earth’s interior made the climate warmer. b. The land they are on was once a single landmass. c. Earth was closer to the sun in ancient times. d. Animals migrated from continent to continent. 4. How was Alfred Wegener’s theory accepted in his time? a. Not at all, there was not a way to explain how the continents move. b. Poorly, most people thought the earthquake data was wrong. c. Reasonably well, some scientists questioned the rock types. d. Very well, scientists saw the fit of the continents. 5. How does Earth’s geologic record (rocks) support the continental drift theory? a. Identical rock patterns on different continents match up. b. Continents are all made of igneous rock. c. Sedimentary layers are always found in horizontal positions. d. Volcanic island chains on one continent match those on other continents. 6. How does the fossil record support the continental drift theory? a. Fossil plants and animals are found on all continents. b. Fossils were formed in the same way and at the same time. c. Fossils of the same type are found on continents that were once together. d. Fossils can be dated through radioactive decay to show age of sediments. Use the colored diagram to answer the following question: 7. How does continental drift explain the pattern of Glossopteris fossils? a. Glossopteris were marine animals that could swim the Atlantic Ocean. b. The Glossopteris were found on the coast of every continent on Earth. c. South American and Africa were once part of the same continent. d. South American and African animals are all descendants of Glossopteris. 8. What process is happening at oceanic trenches? a. The crust broken into 9 tectonic plates. b. The crust is destroyed by subduction. c. The crust is created. d. The crust gets thinner and warmer. Use the diagram of the sea floor below to answer the next 3 questions. 9. What explains the North-South-North-South pattern of magnetic minerals on either side of the mid-ocean ridges? a. Past earthquakes b. Past volcanic activity c. The spreading of the sea floor. d. The presence of many magnetic fields on Earth pointing in various directions B A 10. What does the “striping” of the sea floor indicate about Earth? a. The seafloor is uneven and bumpy. b. The rocks cooling from the magma have changed composition. c. The age of the rocks on the sea floor is the same at locations B and A. d. The magnetic pole has switched from north to south poles. 11. If letter “B” labels rocks oriented toward todays’ magnetic north pole, what orientation do the rocks at “A” contain? a. North c. South b. East d. West 12. Which type of tectonic plate interaction forms a mid-ocean ridge? a. Absorption of one plate by another b. Two plates colliding c. Two plates moving apart d. Two plates sliding past each other Use this diagram of an imaginary tectonic plate to answer the next four questions: 13. What direction would this plate move? a. From the west to the east b. From the east to the west c. From the south to the north d. From the north to the south 14. The volcanoes were formed over a mantle plume. Which is true of their ages? a. They are all the same age. b. Leonard is older than Penny c. Sheldon is older that Leonard d. Penny is older than Leonard Penny Oceanic Trench Leonard Sheldon Mid-Ocean Ridge 15. How is a hot-spot magma plume (such as the islands shown in the map above) an attribute of tectonic plate motion? a. Hot spots can push magma through the mantle and crust because of the high pressure b. Plates are at divergent boundaries, pulling surface material apart, allowing magma to escape c. Plates are at convergent boundaries in the mid-Pacific ridge, creating an opening for magma to escape d. Plates move over the mantle plume, creating a chain of volcanoes of different ages Plate Motion—Practice Test 1. How do scientists explain the movement of Earth’s tectonic plates? a. They are floating in the oceans and move randomly. b. They move when heat creates convection currents in Earth’s mantle c. They move when volcanoes erupt and earthquake faults slip. d. The spinning of Earth gives each plate the energy that moves the continents. 2. What is the movement of heated materials upward and the movement of cooled materials downward called? a. Coriolis Effect c. Convection b. Contraction d. Climate 3. What are the two types of tectonic plates? a. Crustal and Mantle b. Oceanic and Crustal c. Continental and Oceanic d. Lithospheric and Continental Use the map below to answer the following question: World Earthquakes and Volcanoes 4. The distribution of world earthquakes and volcanoes is an indication of… a. Tectonic plate boundaries c. Ancient climates b. Earth’s internal heat sources d. Doppler Effect 5. What type of energy is transferred to earth’s surface during an earthquake? a. Heat c. Mechanical b. Light d. Chemical 6. What conditions of temperature and density would allow a tectonic plate to SUBDUCT? Boundaries that are… a. cold and dense c. cold and less dense b. hot and dense d. hot and less dense Use the diagram below to answer the following questions: 7. Why does rock begin to sink at A and D? a. It has cooled and is more dense b. It has cooled and is less dense c. It has warmed and is more dense d. It has warmed and is less dense 8. Where would you expect to find the hottest rock? a. A b. B c. C d. D 9. What direction are the plates moving in relation to each other at point C? a. towards each other c. sideways to each other b. away from each other d. one up, the other down 10. What type of plate boundary would you expect to see at point D? a. Convergent c. Transform b. Divergent d. All of the above 11. What effect does a subducting plate boundary have on the rest of the plate? It would a. push the plate upward c. cool the plate b. compress the plate d. pull the plate downward 12. The collision of two continental plates results in which land feature? a. Valleys c. Volcanoes b. Mountains d. Trenches 13. Which feature can be created by a divergent plate boundary? a. Trench c. Earthquakes b. Rift Valley d. Island Arc 14. As Australia drifted away from Asia, what happened to its animal life? a. Australian animals became more like North American animals. b. It remained very similar to life on Asia c. Asian life forms changed dramatically. d. It evolved into different forms than Asia. 15. The movement of plate boundaries has created spectacular volcanoes. What effect do volcanoes have on living things over time? a. They do not allow for plant growth c. They are difficult to travel over b. They form hot gases d. They alter the weather and climate