Hematology Overview: Anemias, Neoplasms, and Blood Disorders
advertisement

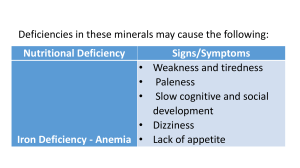
BLS overview GESHAN GUNAWARDANA -RBC life span – 120d -Plt life span – 7 – 10 d -Neutrophil life span – 2d (in inflammation – 6-8h) =early manifestation of BMF Haematology Deficiency anemia s (Fe, B12) Haemolytic anemias Pancytopenias Neoplasms in WBC (ALL, AML, CLL, CML, MM etc…) Platelet defects (reduced number or functional) and DIC Thrombophilia Defects in coagulation Transfusion medicine Pharm (deficiency anemias, anticoagulants) Haematology Deficiency anemia s (Fe, B12) Haemolytic anemias Pancytopenias Neoplasms in WBC (ALL, AML, CLL, CML, MM etc…) Platelet defects (reduced number or functional) and DIC Thrombophilia Defects in coagulation Transfusion medicine Pharm (deficiency anemias, anticoagulants) Point 1 – deficiency anemias Fe deficiency B12 and folate deficiency Point 2 – Haemolytic anemia Haemolytic profile Point 4 –neoplasms in WBC Lymphoid neoplasms Lymphoid neoplasms Precursor B cell leukaemia/lymphoma (Pre B ALL) Peripheral B cell neoplasia CLL/SLL Hairy cell leukaemia Burkitt s lymphoma Precursor T cell or NK cell neoplasia (pre T ALL or lymphoma) Peripheral T cell or NK cell neoplasia Hodgkin lymphoma Hodgkin vs non-hodgkin Non- Hodgekin(B cell) Multiple myeloma Myeloid neoplasms(AML/CML) Causes for AML, 1ry – de novo gene mutation (ionizing radiation, chemicals like benzene, viruses like HTLV 1, genetic sx like fanconi, down s) 2ry – From MDS, myeloproliferative diseases Myelo-proliferative disorders In PV, PMF, ET there s V617F mutation causing activation of JAK 2 kinase which stimulate erythropoietin & thrombopoietin Receptors causing increased RBC and plts. But GM-CSF (so not huge rise in WBC). CML has different gene mutations Myelodysplastic syndrome Point 4 - Pancytopenia Pancytopenia Reduced production Infiltration of BM AML/MF MDS(can progress from BMF) Increased consumption B12/FA deficiency MM Metastasis TB True BMF AA Inherited Fanconi anemia Dyskeratosis congenita Splenomegaly PNH Idiosyncratic SLE Infections(TB,AIDS Point 5 – Causes of Macrocytosis Physiological – pregnancy, neonates PathologicalWith megaloblastosis (anything which disrupts DNA synthesis) Without megaloblastosis B12/FA deficiency Alcohol (most common cause) Methotrexate (inhibit DHF reductase) Hypothyroidism (erythropoiesis becomes slow) 5-flurouracil Liver diseases (cirrhosis) macrocytosis with target cells Haemolytic anemias (due to reticulocytosis) In BM infiltrations (MM, Metastasis) Point 6 – Leuco-erythroblastic blood picture (megaloblastosis) M – Myelofibrosis M – megaloblastic anemia M – metastasis M – Multiple myeloma M – Marble bone disease(osteogenesis imperfecta) H – Haemorrage (severe) H – Severe haemolysis Point 7 – Different types of RBC Point 8 – causes of splenomegaly In aplastic anemia liver, spleen,LN are not enlarged (if pancytopenia present with organomegaly look for other cuases for BMF rather than AA like myelofibrosis Platelet disorders Thrombophilia Coagulation disorders Transfusion medicine THANK YOU & GOOD LUCK !!!