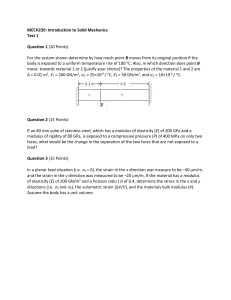
COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH OF WOOD PARALLEL TO GRAIN • ASTM D143 contains the standard test methods for testing small clear timber specimens. The data from ASTM D143 test methods can be used to compare the mechanical properties of various species, establish allowable stresses, and determine the influence of density, locality of growth, height, and treatment of chemicals on the mechanical properties. • This standard contains test methods for determining the various strength and elastic properties of wood one of it is compression parallel to grain • By means of our timber testing expertise and modular product design, we will help find the testing solution that is right for you. Give one of our application engineers a call today for help with creating the best budget and testing plan according to ASTM D143. COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH OF WOOD PARALLEL TO GRAIN • Per ASTM D143: "These test methods cover the determination of various strength and related properties of wood by testing small clear specimens.“ • Applicable Products: Wood specimens APPARATUS • 500 KN universal testing machine, to load the sample in compression till its rupture • Wooden cubes • Deflection dial gauges, to determine the corresponding value of strain with each load increment • Vernier caliper, to measure the dimensions of wooden cubes, including their length, breadth, and height. TEST PROCEDURE • • Measure the dimensions of the wooden sample using a vernier caliper. • • • • Attach the deflection dial gauges to the sample. • • Using the peak load and contact area, calculate the compressive strength of the wooden cube. • Repeat the above procedure by orienting the sample in such a way that the grain fibers are perpendicular to the applied load. Place the wooden sample in the universal testing machine such that the grain fibers are parallel to the applied compressive load. Start loading the sample in compression. Note down the deflection reading from the dial gauges for each regular load increment. When cracks begin to appear, remove the deflection gauges and load the sample to failure. Note down the peak or crushing load. Calculate the stress and strain values and plot a graph between them to determine the modulus of elasticity and modulus of stiffness. CALCULATIONS • When grains are parallel to the applied load • Compressive Strength, = MPa • Modulus of Elasticity, E = MPa = • Modulus of Stiffness, k = N/mm • When grains are perpendicular to the applied load • Compressive Strength = MPa • Modulus of Elasticity, E = MPa • Modulus of Stiffness, k = N/mm THANK YOU!