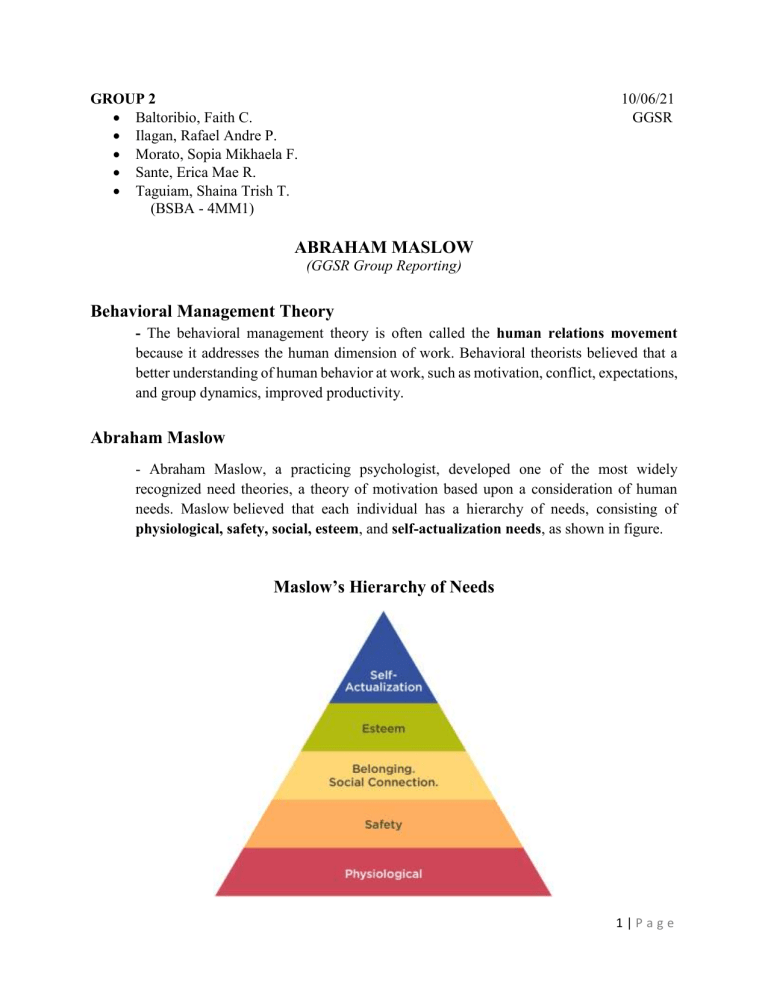
GROUP 2 Baltoribio, Faith C. Ilagan, Rafael Andre P. Morato, Sopia Mikhaela F. Sante, Erica Mae R. Taguiam, Shaina Trish T. (BSBA - 4MM1) 10/06/21 GGSR ABRAHAM MASLOW (GGSR Group Reporting) Behavioral Management Theory - The behavioral management theory is often called the human relations movement because it addresses the human dimension of work. Behavioral theorists believed that a better understanding of human behavior at work, such as motivation, conflict, expectations, and group dynamics, improved productivity. Abraham Maslow - Abraham Maslow, a practicing psychologist, developed one of the most widely recognized need theories, a theory of motivation based upon a consideration of human needs. Maslow believed that each individual has a hierarchy of needs, consisting of physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization needs, as shown in figure. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 1|Page His theory of human needs had three assumptions: 1. Human needs are never completely satisfied. 2. Human behavior is purposeful and is motivated by the need for satisfaction. 3. Needs can be classified according to a hierarchical structure of importance, from the lowest to highest. Maslow broke down the needs hierarchy into five specific areas: 1. Physiological needs - Maslow grouped all physical ends necessary for maintaining basic human well-being, such as food, drink, shelter, and clothing, into this category. After the need is satisfied, however, it is no longer a motivator. 2. Safety needs - These needs include the need for basic security, stability, protection, and freedom from fear. A normal state exists for an individual to have all these needs generally satisfied. Otherwise, they become primary motivators. 3. Belonging and love needs - After the physical and safety needs are satisfied and are no longer motivators, the need for belonging and love emerges as a primary motivator. The individual strives to establish meaningful relationships with significant others. 4. Esteem needs - An individual must develop self-confidence and wants to achieve status, reputation, fame, and glory. 5. Self-actualization needs - Assuming that all the previous needs in the hierarchy are satisfied, an individual feels a need to find himself. Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory helped managers visualize employee motivation. How Abraham Maslow’s Theory contributed to Corporate Good Governance? Managers who accept Maslow's ideas attempt to increase employee motivation by modifying organizational and managerial practices to increase the likelihood that employees will meet all levels of needs. Maslow's theory has also helped managers understand that it is hard to motivate people by appealing to already-satisfied needs. For employees to grow and reach their fullest potential, their basic needs must be prioritized. The hierarchy of needs also apply to business. We can apply Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs to show how employees can be supported to reach the highest levels of self-actualization— enabling businesses to achieve excellence and financial success. 2|Page Business Application of Maslow’s Hierarchy 1. Maslow's Need: Physiological Business Application: Safe work environment. Proper lighting. Clean facilities. Airflow. Heat. The correct tools to do the best job. Example: Google has bicycles and electric cars to get staff to meetings, gaming centers, organic gardens, and eco-friendly furnishings. They also provide free food, free fitness classes and facilities, massage therapists, onsite medical staff, gaming room and a lot more. The company wants to make its employees' lives more comfortable, and they are continually searching for ways to improve the health, well-being, and morale of its Googlers. 2. Maslow's Need: Safety Business Application: Treat coworkers with respect. Allow them the freedom to take risks and not be harshly criticized or humiliated. Example: The fact that the CEO of Facebook, one of the world's most dynamic and fastest growing companies, is meeting with entry-level employees says a lot about the way Mark Zuckerberg does business. Rather than slotting people into roles based on age and experience, Facebook values everyone's ideas in clear and distinct ways. 3|Page 3. Maslow's need: Belonging Business Application: Give everyone the opportunity to be heard. Create a sense of community. Coworkers are part of something bigger than themselves. They have a clear understanding of a value-centered mission. Example: HBO’s Corporate Social Responsibility team unites HBO employees, talent and non-profit partners to make a difference on social issues, connected to their industry, and their communities. Employees are inspired from their top-down leadership to educate, take action and help make the world a better place. (team building, organizing sports, trips, team outings, cultural events to build stronger relationship with the other employees/team members/managers; to create friendly environment.) 4. Maslow's need: Esteem Business Application: Empowerment. Public praise. Employee recognition programs. Understanding that each person's job contributes to the ultimate success of the company. Making everyone feel valued and important. Example: Southwest gives employees “permission” to go the extra mile to make customers happy, empowering them to do whatever is necessary to meet that vision. (appraisals, motivations, recognition, bonuses, rewards, promotions) 5. Maslow's need: Self-Actualization Business Application: Give employees the opportunity to think big, to be creative, to have a vision for the future, to reinvent, and provide direct input to senior leadership. Example: Google offers its employees one of the most innovative work environments. The company cares so much about innovation that it has set forth nine principles of innovation. One of their tenets encourages Google employees to spend 20% of their time pursuing innovative ideas about which they are passionate—resulting in products and applications like Google News, Google Alerts and Google Maps Street View. Companies who are adopting Abraham Maslow’s Theory Apple Google Facebook Southwest Airlines HBO 4|Page Maslow's model is a reminder that leaders and their businesses are served best when they look at the world with an “outward mindset,” from the perspective of their stakeholders—demonstrating authentic empathy, concern, and compassion, while establishing, articulating, and modeling clear and measurable values, standards and expectations. An effort to understand the physiological, safety, belonging, and esteem needs of those stakeholders is essential to creating an environment where people are trusted and supported in their pursuit of excellence. Establishing a model of “participatory management,” where employees are involved in the decision-making process, where their input is sought and valued. When they feel like they are as important as what they do, it will result in the true dedication that all leaders need to maximize their company’s performance. Leaders always espouse a desire for teamwork, but they often forget their own role in establishing a collaborative team feeling that drives performance and results. They need to recognize and respond proactively to the physiological, safety, belonging and esteem needs of their stakeholders. The best companies create workforces treated with respect and dignity, where each person feels heard and empowered, where everyone understands their role and how it contributes to something bigger than themselves, where there is no fear of taking risks, and where there is a feeling of ownership. Working to satisfy these needs helps empower people to become their best selves and enables businesses and brands to excel. References: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/business-application-maslows-hierarchy-needs-suzy-jurist https://www.slideshare.net/MahnoorBaqai1/behavioral-management-theory 5|Page




