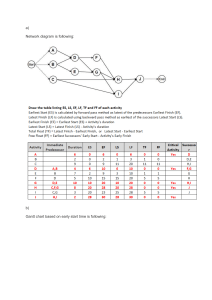
HISTOGRAM A histogram is a graphical representation that organizes a group of data points into user specified ranges. Similar in appearance to a bar graph, the histogram condenses a data series into an easily interpreted visual by taking many data points and grouping them into logical ranges or bin. Histogram is the data representation in terms of frequency. It uses binning and is a popular form of data reduction. PARTS OF HISTOGRAM • The Title = The title describes the information included in the histogram. • X-axis = The X-axis are intervals that show the scale of values which the measurement falls under. • Y-axis = The Y-axis shows the number of times that the values occur within the intervals set by the X-axis. FREQUENCY HISTOGRAM ▪︎ A frequency histogram is a histogram that shows the frequencies ( the number of occurrences ) of the given data items. For example, in a hospital, there are 20 newborn babies whose ages in increasing order are as follows: 1,1,1,1, 2,2,2,2,2, 3,3,3,3,3,3,3, 4,4, 5 What Shape is a histogram? • Histogram is bell shaped of is resembles a bell curve and has one single peak in the middle of the distribution. HISTOGRAM SHAPES • The histogram can be classified into different types based on the frequency distribution of the data. There are different types of distributions, such as normal distribution, skewed distribution, bimodal distribution, multimodal distribution, comb distribution, edge peak distribution, etc. We have mainly 5 types of histogram shapes. • Bell Shaped Histogram • Bimodal Histogram • Skewed Right Histogram • Skewed Left Histogram • Uniform Histogram BELL SHAPED HISTOGRAM • A bell shaped histogram has a single peak. The histogram has just one peak at this time interval and hence it is a bell shaped histogram. For example, the following histograms shows the number of children visiting a park at different time intervals. The histogram has only one peak. The maximum number of children who visit the park is between 5:30pm to 6:00pm. BIMODAL HISTOGRAM • A bimodal histogram has two peaks. For example, the following histogram shows the marks obtained by the 48 students of class 8 of St. Mary’s School. The maximum number of student’s have scored either between 40 to 50 marks OR between 60 to 70 marks. SKEWED RIGHT HISTOGRAM • A skewed right histogram is a histogram that is skewed to the right. For example, the following histogram shows the number of people corresponding to different wage ranges. The histogram is skewed to the right. For the maximum number of people, wages ranges from 10-20 ( thousands ). SKEWED LEFT HISTOGRAM • A skewed left histogram is a histogram that is skewed to the left side. For example, the following histogram shows the number of students of Class 10 of Greenwood High School according to the amount of time they spent on their studies on a daily basis. The maximum number of students study 5.5-5 ( hours ) on daily basis. UNIFORM HISTOGRAM • A uniform histogram is a histogram where all the bars are more or less of the same height. For example, Ma’am Lucy, the Principal of Little Lily Play School, wanted to record the heights of her student. The height of the students ranges between 30 inches to 50 inches. RANDOMNESS • Is a quality or state of being or seeming random ( as in lacking or seeming to lack a definite plan, purpose, or pattern ) the metaphor of a coin flip for randomness remains a questioned. • An example of a simple random sample would be the names of 25 employees being chosen out of a hat from a company of 250 employees. Individual random events are by definition, unpredictable but if the probability distribution is known, the frequency of different outcomes over different trials is predictable. For example, when throwing two dice, the outcome of any particular roll is unpredictable, but the sum of 7 will tend to occur twice as often as 4. Run Test of Randomness • Is a statistical test that is used to know the randomness in data. Run test of randomness is sometimes called the Geary tests, and it is non parametric tests. Run tests of randomness is an alternative tests to tests autocorrelation in data. Run is basically a sequence of one symbol such as + or - . ASSUMPTIONS IN RUN TEST OF RANDOMNESS 1. DATA LEVEL: it is assumed that the data is recorded in order and not in a group. 2. DATA SCALE: It is assumed that data is in numeric form. 3. DISTRIBUTION: It is a nonparametric tests. 4. In run tests of randomness, the probability of run is independent. UNCERTAINTY • Is the quantitative estimation of error present in data; all measurements contain some uncertainty generated through systematic error and or random error. • Any measurement made will have some uncertainty associated with it, no matter the precision of the measuring tool. • For example if you are trying to use a ruler to measure the diameter of a tennis ball, the uncertainty might be +-5mm, but if you use Vernier caliper, the uncertainty could be reduced to maybe +-2mm.


![Lou Recamara enrichment activity 6[1]](http://s1.studylib.net/store/data/025605296_1-bd1a147feb25973f22130b5288f16857-300x300.png)