What is Light? Properties, Spectrum, and Production Methods
advertisement

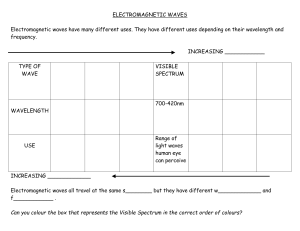
What Is Light? Light Sunlight- energy that makes life possible on Earth Nuclear reactions in the sun produce a lot of energyone form is light Earth captures only a small amount of the light, however it is enough to heat the Earth and allow photosynthesis to occur Properties of Light Travels at a high speed – so fast it can go around the Earth about 7.5 times in one second! 𝑐 A = 3 × 108 𝑚/𝑠 packet of light energy is called a PHOTON Light travels in a straight line Light – An Electromagnetic Wave What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance that transfers energy from one point to another without transferring matter. Light is… a particle AND a wave Most waves need a medium… Medium – any physical substance (air, water, dust) that acts as a carrier for the transmission of energy. Sound travels through air particles Water waves travel through water A rope or slinky can be a medium for waves How does light travel through space? Electromagnetic Waves The term electromagnetic waves is used to describe light because light is made up of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Colours-electromagnetic waves that the human eye can detect What distinguishes colours of light is the different wavelengths of light. COLOUR SPECTRUM These colours are called a SPECTRUM White light is made up of shades of Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo and Violet ROY G BIV is a mnemonic to help you remember the spectrum. We can only sense so much… When a dog whistle is blown, can you hear it? Some sounds are at such a high frequency, we can’t hear them. Our eyes can’t “see” some of the electromagnetic spectrum An example When you use a microwave, you can’t see the waves your food is absorbing. The waves used to heat your food is called Microwave radiation. ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Visible light spectrum is a very small portion of a much larger spectrum called the Electromagnetic Spectrum Sample Mnemonic: Rick’s Mother Is Visiting Uncle Xavier’s Garden Visible light provides only limited information about the universeThe Andromeda galaxy looks different using different parts of the EM spectrum How is light produced? Light production Luminousproduces its own light ex: the Sun Non-luminous – does not produce its own light, can only be seen using reflected light ex: book, tree, moon WAYS TO GAIN ENERGY & PRODUCE LIGHT Incandescence – production of light as a result of high temperature (ex. Burning candle) Only 5-10% of electricity is converted into visible lightinefficient WAYS TO GAIN ENERGY & PRODUCE LIGHT Electric Discharge – process of producing light by passing an electric current through a gas (ex. Neon lights or lightning) WAYS TO GAIN ENERGY & PRODUCE LIGHT Materials are coated with phosphors –material that gives off light Phosphorescence – process of producing light by the absorption of UV light resulting in the emission of visible light over an extended period of time (ex. Glow in the Dark) WAYS TO GAIN ENERGY & PRODUCE LIGHT Fluorescence – immediate emission of visible light as a result of the absorption of UV light (ex. Energy saving light bulbs) These bulbs are more energy efficient than incandescent bulbs however they contain mercury so need to be treated like hazardous waste Detergents have fluorescent dyes that absorb UV light and emit visible light Highlighters use the same principle WAYS TO GAIN ENERGY & PRODUCE LIGHT Chemiluminescence (“cold-light”)– direct production of light as the result of a chemical reaction with little or no heat produced (ex. Glow sticks) Glowstick experiment WAYS TO GAIN ENERGY & PRODUCE LIGHT Bioluminescence – production of light in living organisms as the result of a chemical reaction with little or no heat produced (ex. Fireflies) Bioluminescence WAYS TO GAIN ENERGY & PRODUCE LIGHT Triboluminescence – production of light from friction as a result of scratching, crushing, or rubbing certain crystals First noticed by Francis Bacon in 1620 WAYS TO GAIN ENERGY & PRODUCE LIGHT Light-Emitting Diode (LED) – light produced as a result of an electric current flowing in semi-conductors in one direction ex:silicon Regular conductors allow electrons to flow in either direction Benefits of LED – less heat produced, more efficient