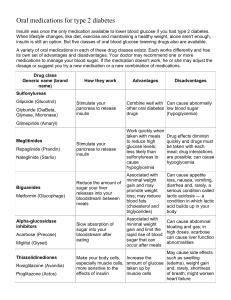
Pharm 2 Final Medications: Psych Barbiturates: • • • medications phenobarbital CNS depressant Can be used to help with insomnia Not first choice of anti-anxiety med Benzodiazepines: diazepam (valium) ** antidoteà flumazenil ** • Used for acute agitation or insomnia--- SHORT ACTING drug • Can also be used for seizures & nausea • Kicks in right away! • Low dose for anxiety, high dose for sedation/hypnosis Antidepressants o serotonin syndrome: can occur 2-72 hours after treatment… altered mental status, agitation, confusion, hyperreflexia, incoordination, sweating, tremors, fever o do NOT mix any antidepressants together bc can cause inc. serotonin in body o serotonin withdrawal: abrupt stops of serotonin in body... dizziness, headaches, N/V, dysphoria— can be avoided by tapering off the drug ® SSRI: fluoxetine • Selectively inhibits the reuptake of serotonin (allows more to stay in the synapse) • 4-6 weeks for therapeutic effects • Causes sexual dysfunction ® SNRI: venlafaxine • Can be used for depression and chronic pain in fibromyalgia and diabetic neuropathy ® Tricyclics: imipramine ** antidoteà physostigmine (cholinesterase inhibitor) ** • reduces uptake of serotonin and norepinephrine • sedative effects and helpful for chronic pain • can cause anticholinergic effects and cardiac toxicity ® MAOI: phenelzine • Very last drug used • Hypertensive crisis if mixed with foods with tyramine (aged meats, aged cheeses, beer, wine, yeast) ® Mood stabilizers: lithium • Low therapeutic index must check blood levels regularly • 0.4-1.5 mEq/L **over = toxic à shaky, thirsty, freq. urination, diarrhea, vomiting, drowsiness, blurred vision, seizures • Patients must balance fluid and sodium intake • Diuretics, anticholinergics, NSAIDS are not recommended • Treat hand tremors with betablocker ** Bupropion (Wellbutrin) helps smoking cessation** Antipsychotics o Extrapyramidal symptoms: dystonia (muscle spasms), parkinsonism’s, tardive dyskinesia (lip smacking), akathisia (restless) o Neuro malignant syndrome: fever, lead pipe rigidity * must notify PCP * o Metabolic triad: weight gain, heart disease, high cholesterol o Agranulocytosis: monitor WBCs (can cause decrease in wbc, less than 3500) ® First generation “conventional”: chlorpromazine, haloperidol • Strong dopamine blockage • Haldol can cause dysrhythmias • EPS, tardive dyskinesia ® Second generation “atypical”: clozapine, risperidone • Moderate dopamine blockage • Less risk for EPS, but high risk for agranulocytosis and metabolic triad (big risk for noncompliance) Medications affecting the o Cardiovascular system© RAS system is activated by kidneys and causes vasoconstriction Antihypertensives ® ACE inhibitors (-pril): captopril • First line of antihypertensives • Orthostatic hypotension • Not as effective for African Americans (must use additional med) • Cough** angioedema** • Patient at risk for HYPER-kalemia ® Angiotensin II Receptor blockers (-artan): Losartan • Like ACE inhibitors, but does not cause **hacking cough • Lowers BP in patients with HF • Monitor renal function ® Renin inhibitors: aliskiren ® Calcium channel blockers (-pine/-zem): diltiazem, nifedipine, and verapamil • First like for African Americans • Like beta blockers • Decreases heart rate and BP, lowering workload of the heart • Causes vasodilationà peripheral edema and hot facial flushing Antiadrenergic ® Alpha 2 agonists: Clonidine • Acts within the CNS to decrease sympathetic outflow resulting in decreased stimulation of adrenergic receptors • Lowers HR and vasodilates ® Beta blocker: -olol • Propranololà both beta1 and beta2 blocks beta receptors of CNS § CONTRAINDICATED in patients with asthma due to B2 (lungs) • Metoprololà beta1 only, affects AV node and heart rate/pressure • B1= HEART B2= LUNGS Diuretics: o NA+ levels: 135-145 o K+ levels: 3.5-5.0 ® Thiazides: hydrochlorothiazide • Non-sparing diuretic • Eat potassium rich foods • First line of therapy ® Potassium sparing: spironolactone • Potassium sparing • Avoid potassium rich foods ® Loop diuretics: furosemide • used for chronic kidney disease and edema associated w CHF • lowers potassium, Na+ and fluids • can cause severe hypotension ® Osmotic diuretics: mannitol • Used to decrease intracranial or intraocular pressure • Drains fluid from cells into the blood vessels—can cause heart failure symptoms • Cannot be give PO • Side effectà edema Hypertensive emergencies ® Vasodilators: nitroprusside • Used only in crisis • Big fall risk and causes headaches • NO Viagra (-afil) Shock o Impaired perfusion to vital organs: oliguria, HF, confusion, cool extremities, low BP weak rapid HR o Maintain patent airway and maintain SBP >90, give IV fluids!! o Goalà prevent hypoxia and increase cardiac output ® Adrenergic Drugs (vasopressors): Dobutamine, Dopamine, Epinephrine***, Norepinephrine • Vasoconstriction!!!! • Do not give if patient has cardiac problems (dysrhythmias/angina/HTN) ® Inotropic: Milrinone • Increases heart effective contractility (increases cardiac output) and dilates arteries and veins (decreases BP) ® EpiPen • First line drug for anaphylaxis • Relieves bronchospasm, laryngeal edema and hypotension Digoxin • Increases force of hearts contractions, used for AFIB and CHF • Levels: 0.5-2 ng/ml, anything over 2 is TOXIC • Dig toxicityà nausea/vomiting, visual disturbances • Watch potassium levels (seesaw—when one is elevated the other in low) Blood coagulations Anticoagulants—prevents/delays coagulation, only given prophylactically, big risk for bleeding – report to PCP severe and recurrent bleeding ® Heparin **antidoteà Protamine Sulfate** • Turns off coagulation pathway and prevents clots from forming • Contraindicated in GI bleeding, hemorrhagic stokes ® Heparin derivatives: enoxaparin ® Warfarin **antidoteà vitamin K** • Normal INR: 0.8-1.2 • Therapeutic levels: 2-3 • High INR thins the blood, low INR thickens the blood • Green leafy vegetables can decrease INR, alcohol, NSAIDS can increase INR • Watch for PT and INR levels ® Direct Factor Xa inhibitors: Xaretto and Elilquis **antidoteà andexxa** • Used for DVT prophylaxis, prevention of stroke for AFIB, rapid onset, very $$ ® Direct Thrombin Inhibitors: Pradaxa **antidoteàpraxbind** • Alternative to heparin, watch for petechiae (red spots) Antiplatelet—inhibits platelet function ® Antiplatelet: acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) • Risk for GI bleeds, drug lasts as long as platelet (90 days) ® Adenosine Diphosphate Receptor antagonists (P2Y): clopidogrel • Used if patient is allergic to aspirin • Plavix can be combined with aspirin to keep stents open, prophylaxis for previous stroke ® Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor: Cilostazol (pletal) • Increases blood flow for ** intermittent claudication Thrombolytic Therapy ® Alteplase/TPA • Given to patients post MI, place on cardiac monitor Antihyperlipidemics ® Psyllium preparations Fiber, can add to juice and water, like oats/fruits/veggies ® Bild Acid Sequestrants: cholestyramine Helps trap fats in the gut and prevents them from being absorbed--- later poops them out ® Statins HMG-CoA reductase: Atorvastin Lowers lipids—LDL, cholesterol and tryglycerides!! Hard on the liver (monitor LFTs), side effects à muscle pain (give CoQ10 enzyme), dark urine, rhabdo (check RENAL labs) NO grapefruit, and do not give in pregnancy – take at bedtime for best effects ® PCSK9 inhibitors: Praluent/Repatha Lowers LDL in patients, injections given 2x monthly, can be used if patients have ADSR to statins ® Fibrates: Gemfibrozil Increased risk of rhabdo if given with statins, increased risk of bleeding ® Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor: Ezetimibe / Zetia Decreases cholesterol absorption in the small intestine, very hard on the liver Anti-Cancer o o o o o o o medications Cytotoxic drugs: attacks rapid-prolifering cells (WBC, RBC, platelets, GI, hair) Patients can have neutropenia (nadir is lowest point), anemia, thrombocytopenia Bone- marrow suppression is a dose-limiting symptom Can stop treatment is patient have severe peripheral neuropathy (cold packs to fingers and head) Anaplasia: when cells lose their function Vaccines to prevent cancer? HPV Vesicant drugs: potential to cause extravasation à if occurs: STOP infusion, notify provider, wait for instructions before removing cannula, sometimes we can aspirate any possible chemo out of tissue ® Colony stimulating factors: Neulasta o Used to stimulate WBCs o Can cause boney pain – treat with Motrin o Wait 24 hours after chemo ® Epogen o Used to stimulate RBCs ® Cytotoxic Agents: doxorubicin o Very bad for peripheral nerves and cardiac!!! o Myelosuppression, N/V, sperm banking or egg retrieval Hormone modulators ® Prostate Cancer o androgen blockers: Lupron ® Breast cancer o Herceptinà treats HER2+ breast cancer, cardiotoxic!! o SERM: Tamoxifenà Favorable for breast cancer/bones/cholesterol, Unfavorable for increased risk of uterine cancer, blood clots/ DVT/ Pulmonary Embolism, DO NOT give to patients with unfavorable symptoms already. Can cause hot flashes and red urine but not dose limiting side effects o Aromatase Inhibitors: anastrozoleà for post-menopausal women who have had breast CA ® Immune Stimulators: interferon alpha o Stimulates immune system to attack cancer o Can cause flu-like symptoms à give Tylenol prophylactically o Can cause depression à usually put on an antidepressant o Patient at risk for suicide ® Interleukins o Uses our immune system to fight off cancer, used mainly for viral cancers ® Steroids: corticosteroids o Immune suppressant for cancers affecting lymphatic system o Helps with allergic reactions associated with chemo o Used for autoimmune disorders Medications affecting the Thyroid: endocrine system ® Hypothyroid: levothyroxine (Synthroid) Thyroid supplementation used in hypothyroidism, promotes gluconeogenesis, watch for hyperthyroidism synthetic form of thyroid--- minimal symptoms unless given high doses monitor TSH and T3 / T4 – dose is adjusted according to labs lifelong treatment: not a cure first thing in the morning with water before breakfast ® Hyperthyroid: propylthiouracil (PTU/Tapazole) treats grave’s disease: blocks the synthesis of thyroid hormones ☆watch for agranulocytosis—increased risk of infx., hepatotoxic☆ high doses can cause symptoms of hypothyroidism Parathyroid: We need vitamin D to absorb calcium After menopause, give calcitonin – if it doesn’t work then add PTH Used for osteoporosis – check bone density studies All treatments must be used with calcium supplementation and vitamin D recommended to walk daily in sun Osteoporosis: treat with calcium supplements ® Bisphosphonates: alendronate o First line of drug for osteoporosis!!!!! o Must be taken first thing in the morning and sit upright with 6-8oz of water o Esophagitis: causes esophageal irritation/ulcers and heart burn ® Calcitonin: calcimar o Lowers serum calcium o Helps deposit it into the bone o Spray is irritating to noses ® Parathyroid hormone o Helps absorb calcium, must consume more calcium o Never on this without another agent o HELPS keep calcium that we ingest from out diet o Added on to calcitonin if it doesn’t work ® Selective estrogen receptor modulators: raloxifene o Like tamoxifen o Do not give if have history of blood clots and risk for uterine cancers Pancreas: Diabetes Type 1à genetics, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2à lifestyle, insulin receptor sites are worn out and develop resistance, risk factorà metabolic syndrome: high BP, high blood sugar, obesity, high lipids Insulin o o Pancreas releases insulin when eating from BETA cells Insulin is the key for glucose and potassium to ENTER the cell… without insulin, glucose cannot enter cell and stays in the blood Pituitary: o Acromegaly/giantism: excess growth hormones in body, can cause cardiac, pancreatic and musculoskeletal issues, increase in Serum Somatotropin (growth hormone) ® GH antagonist: octreotide (sandostatin) o Blocks growth hormone, used for acromegaly and giantism: can be due to tumor on pituitary gland o Stops inappropriate growth ® GH agonist: somatotropin o Stimulates growth of body tissues ** potential for abuse** o Given to children daily if child is not growing according to the growth curved o Dangerous to give to patients with closed epithesis (adults)—can cause boney pain o can be considered a performance enhancing drug Female Sex hormones ® Estrogens ® Progestins ® Birth control pills Posterior Pituitary: ® Antidiuretic: desmopressin o Used in bleeding and rhinitis Adrenal Cortex: ® Adrenal insufficiency: Glucocorticoids o Corticosteroids o Adrenocorticoids o Corticoids o Androgens Medications affecting the GI system Agents used in mineral/electrolyte imbalances ® Kayexalate treats high level of potassium ® Lactulose treats high ammonia ® Ferrous sulfate prevent iron deficiency ® Magnesium oxide laxative effects, treats low magnesium ® Potassium chloride prevent or treat low potassium levels ® Zinc sulfate treats zinc deficiency Peptic Ulcer Disease/GERD ® Antacid: sodium bi carbonate, TUMS, milk of mag neutralizes stomach acid, do not take with other medications do not give to heart failure patients (contains sodium) ☆short term relief☆ ® H2 Blockers: [-dine] ranitidine/ famotidine blocks H2 receptors of acid producing parietal cells, reduces hydrogen ion secretions to increase pH of stomach (less acidic) USED FOR PEPTIC ULCERS, given 30mins before meals ☆ can cause mental confusion, libido ☆ ® Proton Pump Inhibitors: omeprazole/protonix reduces acid produced by stomach lining, turn offs protein pump, used for peptic ulcer prophylaxes!!! long term effects à MI, osteoporosis, decrease in Ca absorption ☆watch for FRACTURES (regular bone density tests), HYPOMAGNESUEM ☆ short term use recommended!! give before first meal, often prophylactic for NSAIDS ® Prostaglandin: misoprostol not given for pregnancy, protects gastric ulcers, given to patients with long term NSAID therapy ® Sucralfate: Carafate mucosal protectant, take on empty stomach!!! do not take with other meds ® Antibiotics for H. Pylori: Laxatives ® Bulk forming: psyllium **BOTH for diarrhea and constipation** ® Surfactant: docusate (COLACE) causes fluids to be pulled into the colon to keep stool soft ® Saline: magnesium citrate pulls fluid into colon and causes diarrhea used prior procedure to empty out colon not give for significant renal impairment ® Lubricant: mineral oil drink, inserted as suppository, enema hard stool slides out ® Lactulose & Sorbitol (sweetener) known side effects are diarrhea Antidiarrheals ® Opiates: Lomotil and Imodium o low gastric motility, decreases gastric motility to decrease liquid stool o TOO MUCH: can cause stop in motility ® Bulk forming: psyllium **BOTH** ® Antibacterial treats bacterial that is causing diarrhea ® Pepto-Bismol o Don’t give to patients who are not supposed to have aspirin (reyes syndrome, peptic ulcer, cardiac problems) Anti-emetics ® H1 receptor blocking agents: dimenhydrinate (Dramamine) H1 blocks acetylcholine in the brain for motion sickness/vertigo causes drowsiness ® Promethazine Give for nausea in pregnancy Can cause urinary retention ® Compazine Given to people who can’t stop throwing up ® Corticosteroids: dexamethasone, methylprednisone Unknown mechanism long term use can cause Cushing’s like syndromes ® Can use benzos ® Prokinetic: metoclopramide Reglan Promotes peristalsis—relieves N/V associated with gastroparesis increases GI motility ® Serotonin receptor antagonist: ondansetron Zofran blocks serotonin receptors, treats chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting and post op N/V, approved used for pregnancy ® Dietary: ginger and lemon—helps nausea GI weight loss ® Normal BMI ranges (BMI over 30 for medication, BMI over 40 for surgery) ® GLP-1s used for weight loss ® Amphetamines (anorexiants) à phentermine: used for appetite suppression • Cardiac side effects, screen patients before • Potential for abuse ® Lipase inhibitor: Xenical, Alli (OTC) • block absorption of GI tract, patient is not absorbing % of fat • lowers LDL, most people don’t tolerate drug though • Fatty stools, flatulence with oily discharge Oral Diabetic Meds → Decreases blood glucose, helps pancreas → Only used after diet and exercise is ineffective → Used for type 2 diabetics only, can be used with insulin Sulfonylureas Prototype: Glyburide (Diabeta) “Squeezes pancreas” to release more insulin Bad for the heart Only effective if Beta cells are functioning Take with food to decrease GI symptoms Watch for hypoglycemic events and weight gain Photosensitivity and toxic in elderly Glitazones aka TZDs Prototype: Rosiglitazone (Avandia) Decreases insulin resistance Heart and liver toxic – risk for heart failure Watch for edema and rapid weight gain • Can take up to 12 weeks for effects Biguanides Prototype: Metformin (Glucophage) Increases use of glucose by muscles and fat cells Major treatment for insulin sensitivity/ decrease insulin resistance Titrate the dose to subside GI symptoms Does NOT cause hypoglycemia Massive weight gain Major liver and kidney TOXIC Hold 48 hours before contrast and start 48 hours after due to kidney toxicity (creatine over 1.3 = kidney dysfunction) -- Deadly Lactic Acidosis Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors Prototype: Acarbose (Precose) Always take with first bite of meal Delays glucose absorption causing smaller increase in post prandial blood glucose Interferes with the absorption of carbohydrates Meglitinides Prototype: Prandin Stimulates secretion of insulin Must have functioning beta cells Take with meals, “skip a meal skip a dose” DPP-4 inhibitors Prototype: Sitagliptin (Januvia) Stimulates insulin secretions Must have functioning beta cells Beta cell neogenesis Do NOT use with insulin and CHF patients Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Prototype: Canagliflozin (Invokana) Pulls glucose out of bloodstream into urine Decreases microvascular changes Can cause hypoglycemia or DKA Urinary tract infx – vulvavag candidas Dopamine receptor Agonists Prototype: Bromocriptine (Clycoset) Uses dopamine receptors in CNS to control blood glucose Low risk of hypoglycemia Incretine Mimetic Helper hormone Prototype: Exenatide (Byetta) Stimulates amount of hormone “Natural helper hormone” Can cause nausea (1x week injection) Helpful in weight reduction Amylin Analog Regulation of glucose in postprandial period Slows gastric emptying to give insulin time to respond “full feeling (satiety)” secondary hormone may cause severe hypoglycemia GLP-1 receptor agonist Prototype: Trulicity (dulaglutide) weekly Injections Stimulates insulin resistance and slows gastric emptying Risk of thyroid CA and pancreatitis Can cause hypoglycemia (must have something to eat at all times) Diabetic ketoacidosis → Not enough insulin and build-up of ketones making blood acidic → Nausea, vomiting, dehydration, fruity breath, dry mouth, Kuusmauls respirations, change in LOC → Treatment: ICU, IV drip, treat cause, 1-1 patient ratio, check glucose every hour o Potassiumsupplements May give sodium bicarbonate Peri-operative patient: hold insulin or oral agents Hypoglycemia Conscious: give candy, glucose paste Unconscious: never give anything in mouth, SubQ or IV 0.5-1mg, IV glucose 50% Glucagon: 1mg IV/IM/SQ repeat 15 minutes, must reconstitute the fluid!!!!!!!!! à give 15 grams of carbs (2-3 candy, 8lifesavers, 4oz juice) and check every 15 minutes follow w protein snack Medications affecting the Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic Adrenergic (fight or flight) / Muscarinic Antagonists Anti-cholinergic symptomsà HIGH & DRYY § Pupil dilation § Urinary retention § Decrease peristalsis § Decrease secretions § bronchodilation § High HR and high BP § Vasoconstriction Norepinephrine Epinephrine Alpha-1à AGONISTS-- treats nasal congestion, vasoconstriction Alpha-2: Tamsulosin/Clonidine à BLOCKERS-causes low BP, blocks epi, vasodilates Beta-1: à increases contraction of heart, treats cardiac arrest and heart failure Beta-2: albuterolà treats asthma, bronchoconstriction Drugs: ® Atropine: used for bradycardia ® Ipratropium Bromide: used in COPD to slow excess mucus secretions à bronchodilation ® Oxybutynin: used for overactive bladder ® Succinylcholine: causes paralysis before intubation or mechanical ventilation!! ® Epinephrine: causes fight or flight symptoms **used for Cardiac Arrest** ® Clozapine: antipsychotics Parasympathetic Cholinergic (rest and digest) / Muscarinic Agonists Cholinergic symptoms à LOW & WETTT • Pupil constriction (blurred vision) • Wet secretions • Low HR and low BP • Vasodilation • Urination and diarrhea • bronchoconstriction ACh: primary cholinergic neurotransmitters Nicotinic receptors: skeletal muscles Muscarinic receptors: lows HR and produces secretions Cholinesterase inhibitors BLOCKS the reuptake of acetylcholine Acetylcholine is needed to produce cholinergic effects Drugs: ® Bethanechol: used for urinary retention ® Neostigmine: Myasthenia Gravis ® Pilocarpine: Glaucoma ® donepezil (Aricept): Alzheimer’s ® Sarin: dangerous nerve gas ® Organophosphates: used for pesticides ® Betablockers à bronchoconstriction ® Alpha-blockers Antidote: ATROPINE Overdose: HOT AS A HARE, MAD AS A HATTER, RED AS A BEET, DDRY AS A BONE Antidote: PHYOSTIGMINE cholinesterase inhibitors Myasthenia Gravis: neuromuscular condition where this is not enough acetylcholine transmitters causing extreme muscle weakness and paralysis of respiratory muscles à ptosis, dysphagia and weakness – anticholinergic effects • Tensilon test: cholinesterase inhibitor (pro-cholinergic) used to treat patients with suspicion of M.G only used for DIAGNOSIS of myasthenia gravis. If symptoms don’t improve then patient does not have M.G and have some other cholinergic crisis Seizures • Partial or focal • Problem is due to aberrant electrical activity in brain • Drugs are not cure only lowers seizure threshold • • Drugs • • • Providers choose medications based off what part of the brain is causing the issue during EEG ALWAYS USE PARENTAL MEDICATION NOT P.O – if no IV available, give rectal o Best medà Ativan/Valium IV push to stop acute seizure o Narrow therapeutic drug levels—always consistently check labs o Gabapentin: can also be used for pain (peripheral pain, neuropathy) o Dilantin: give Cerebyx if cannot be give P.O o Phenytoin: narrow therapeutic index, 10-20 is therapeutic range ROUTINE blood tests, can cause ataxia (trouble speaking/trouble walking)—call provider, hold tube feedings 1hr before administration for Multiple Sclerosis Treat MS by manipulating immune system Immune system modulators: Avonex, Tysabri, Aubagio Flu-like symptoms, premedicate with Tylenol Drug for ALS: Riluzole (Rilutek) à prolongs life, delays trach, HEPATOTOXIC, take on empty stomach Drug for hemorrhagic stroke: Nimodipine (Nimotop) à calcium channel blocker, prevents cerebral arterial vasospasms that results in neurological injury Drug for spinal cord injury: give multiple medications to help blood pressure, manage every function of their bladder Drugs for Parkinson’s: Blocks dopamine givers Parkinson’s like symptoms, lose neuromuscular control (muscle rigidity, tremors, shuffling gait) Use drugs that REPLACE dopamine and block acetylcholine—very strict schedule Effective is client can start ambulating more efficiently Levodopa à try to increase dopamine (dopamine agonist) nursing considerations is to keep strict schedule!!!! Can cause orthostatic hypertension, red/brown urine is normal, MAOI enhances drug Amantadine à antiviral medication inhibits dopamine reuptake **Anticholinergic medications** Dantrolene à central nervous system relaxer, can be used for malignant hyperthermia (reaction to anesthesia) Medications affecting the CNS system CNS Stimulants ® Amphetamines: dextroamphetamine-amphetamine (Adderall), methamphetamine used for add/adhd and narcolepsy, act on norephedrine and dopamine with higher doses to stimulate attention, wakefulness, alertness act on norepinephrine ☆HIGH ABUSE POTENTIAL—TAKE ONLY WHEN NEEDED☆ ® Amphetamine like drugs: methylphenidate used for add/adhd, when wear off – high abuse – let down period appetite suppression overdose or overtaking can lead to psychosis, high HR, high BP ® Methylxanthines: caffeine, theophylline smooth muscle relaxation, bronchodilation, effect, teratogenic monitor levels – narrow therapeutic range ® Non-stimulant (SNRI): atomoxetine must be taken daily, don’t see results right away ☆NO ABUSE POTENTIAL☆ suicide risk Drug of abuse in recovery or right out of rehab = highest risk for overdose because tolerance is much lower cocaine/crack: High vital signs, dilated pupils, nosebleeds, nasal congestion, impaired movements, skinny/lose weight, agitation o ecstasy, flunitrazepam (date rape), ketamine o inhalants (nitrites, benzenes, anesthetics) alcohol withdrawal: librium, disulfiram (antabuse), buprenorphine abruptly stopping can cause death or severe illness, seizures can lead to brain damage/unconscious due to loss of O2 delirium tremens: acute alcohol withdrawal • benzodiazepines → librium, ativan, haldol can prevent seizures - often put on drip • CIWA scale → less than 8-10 is minimal, 15 or more is severe • disulfiram (antabuse) → help people 18 or older remain sober, stays in body up to 2 weeks • if they do drink alcohol, they get very sick • watch for cardiac symptoms (no nitroglycerin or metronidazole) • must be alcohol free for at least 12 hours, pt must be 100% on board Opioid withdrawal: Buprenorphine, methadone, naloxone block the high from opioid like drugs can become addicted to methadone, liquid, or pill - a part of supervised rehab program o o naloxone (Narcan) - ONLY opioids!! will not hurt anyone, give Narcan ask questions later *** IV push, IM, SQ, Nasally Naltrexone - vivitrol *** can be given a shot, will not have effects of alcohol or drugs (no feeling of high, can still overdose) risk for hepatotoxicity Benzo flumazenil (romazicon) overdose, help respiratory depression Nicotine addiction transdermal patches, chewing gum, lozenges, nasal spray, oral inhaler bupropion (Wellbutrin) - atypical antidepressants can cause insomnia