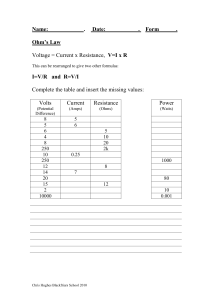
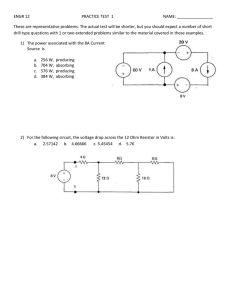
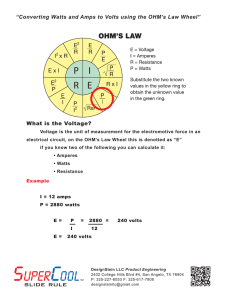
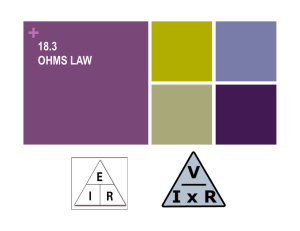
• Voltage: the charge (electron) “pusher.” Voltage causes current to flow/move. • Voltage sources: • Battery • Generator • Outlets • Symbol for voltage = V • Unit for voltage = Volts (V) • Italian physicist • known especially for the invention of the electrochemical cell, aka the battery in 1800. • Power utilities use large generators to provide the 120V that is delivered to your home outlets. • When you plug in something to the outlet (lamp, blow dryer, TV, etc) the voltage is applied across the circuit, allowing the charge to flow (electric current). • Current: flow of charge (electrons) within a conductor or how fast charge is moving. • Charge will only flow if there is a voltage source (potential difference). • Symbol for Current = I • Unit for Current = Amps (A) • French physicist and mathematician. • One of the main discoverers of electromagnetism. • SI unit of measurement of electric current, the ampere, is named after him. Current in Amps Effect on A Person 0.001 Amps Can be felt 0.005 Amps Painful 0.010 Amps Involuntary muscle spasms Loss of muscle control 0.015 Amps 0.070 Amps If through heart, serious injury, likely fatal if it lasts more than 1 second • Resistance: opposes the push from the voltage source. Resistance affects the speed of the current. • Symbol for Resistance = R • Unit for Resistance = Ohms (Ώ) • German physicist • Ohm determined that there is a direct proportionality between the voltage applied across a conductor and the electric current. • This relationship is known as Ohm's law. • If the voltage in a circuit increases, the current will increase. • If the voltage in a circuit decreases, the current will decrease. • This is a direct/proportional relationship. • If the resistance in a circuit increases, the current will decrease. • If the resistance in a circuit decreases, the current will increase. • This is an inversely proportional relationship. • State the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. • German physicist George Ohm had the law named after him, because of his extensive research. Voltage is equal to the current multiplied by the resistance. Voltage, measured in Volts, V Current, measured in Amps, A V=IR Resistance, measured in Ohms, Ω • If you want to find Voltage in Volts: V = IR If I= 2 A and R = 5 Ohms Then, V= (2A)(5Ω) = 10 V • If you want to find Resistance in Ohm’s: R=V/I If V = 9 Volts and I = 4 A Then R = 9 V/ 4A = 2.25 Ω • If you want to find Current in Amps: I=V/R If V= 140 V and R = 2Ω Then, I = 140V/ 2Ω = 70 A