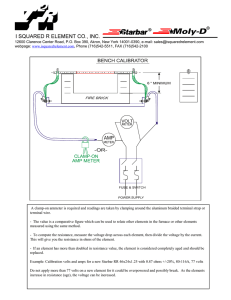
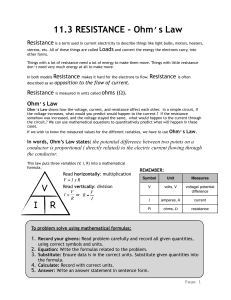
Electric Current and Ohm`s Law
advertisement

Electric Current and Ohm’s Law www.sengpielaudio.com Conductors • Electric conductor is a material through which charge flows easily. • What types of things would be good conductors? • Ex. Copper and silver Superconductor = a material that has almost no resistance when it is cooled to low temperatures Uses: MRI, Maglev trains (levitate train above magnetic rails) http://www.superconductors.org/tc_graph.gif Insulators • Electrical insulators are materials through which charge does not flow easily. • What are types of materials that would be good insulators? • Ex. Wood, plastic, rubber, air Resistance • When electrons flow, they collide with ions and other electrons, so lose some energy • Less energy = less current • Resistance - “R”= opposition to the flow of electrons in a material • Measured in Ohms - “Ω” = symbol What affects resistance? • Thickness – higher thickness = less resistance lower thickness = more resistance • Length – shorter wire = less resistance longer wire = more resistance • Temperature – as temperature increase, resistance increases due to more collisions Ohm’s Law • 1826 – Georg Simon Ohm • Discovered relationship between voltage, current and resistance • the amount of current is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance of a circuit. V=IxR where V = voltage (volts) I = current (amps) R = resistance (ohms) So: - if you double the voltage, then you will double the current - If you double the resistance, the current will be half of what it was What is the voltage of a circuit that has a current of 12 amps and a resistance of 10 ohms? What is the current of a circuit that has a voltage of 9 volts and a resistance of 5 ohms? What is the resistance of a circuit that has a voltage of 12 volts and a current of 3 amps?