AC Machinery Fundamentals: Generators, Transformers, Motors
advertisement

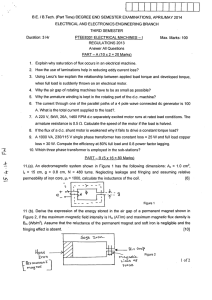
Electrical Machines 2 AC Machinery Fundamentals Electrical_Machines_2 1 Preview After the discussion, the students must be able to: 1. Understand and be familiar with the terms and ideas in AC Machinery. Electrical_Machines_2 2 Electrical Machines Machines used for converting energy from one form to another. [1] Table 1 Common Electrical Machines (AC) Machine From (Energy) To (Energy) Generator Mechanical Electrical Transformer Electrical (Voltage) Electrical (Voltage) Motor Electrical Mechanical Electrical_Machines_2 3 AC Generator Similar to a DC Generator, but has no rectifier (through commutator and brushes). [1] Note: To produce a sinusoidal magnetomotive force, the windings are distributed. [3] Figure 1 Single Loop AC Generator [2] Electrical_Machines_2 4 AC Generator Construction In practice, it is with a stationary armature and moving field [1]. 1. The armature winding is more complex than the field. 2. The armature winding can be braced more securely in a rigid frame. 3. The armature winding protected. (high-voltage ) can be insulated and Electrical_Machines_2 5 Transformer A passive electrical device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another. [4] Figure 2 Working principle of a Transformer [4] Electrical_Machines_2 6 AC Motors Induction Motor Synchronous Motor The rotor receives its power It operates at an absolutely average inductively in exactly the same constant speed regardless of the way as the secondary of a load. transformer. Electrical_Machines_2 7 AC Motor Power Flow Where: 𝑃 - Power input - Stator copper loss 𝑃 𝑃 - Core loss 𝑃 - Rotor power input Figure 3 Induction motor power flow - Rotor copper loss 𝑃 𝑃 - Mechanical loss 𝑃 - Friction and windage loss 𝑃 - Power output Electrical_Machines_2 8 AC Motors: Single-Phase Small motors built in a fractional-horsepower sizes, smaller than that having a continuous rating of 1 Hp at 1,700 rpm – 1,800 rpm, and connected to a single-phase source. [1] Ex. Universal Series Motor, Shaded-pole Motor, Reluctance Motor, Splitphase Motor, Repulsion Motor Electrical_Machines_2 9 References References [1] Electrical Machines: Direct and Alternating Current, Charles S. Siskind [2] AC Generator Handout - Physics 2, https://www.phys.ufl.edu/~phy3054/magnet/inductn/gens/achand/Welcome.html [3] Magnetomotive Force And Flux Distribution On AC Machines, https://www.theengineeringknowledge.com/magnetomotive-force-and-flux-distribution-on-ac-machines/ [4] Transformer: What is it? (Definition And Working Principle), https://www.electrical4u.com/what-is-transformerdefinition-working-principle-of-transformer/ Electrical_Machines_2 10