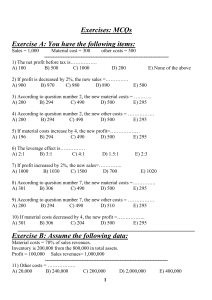
Welcome to MGTA01 Introduction to Business Today’s Lecture: Agenda 1. Course Intro & Overview Break (10 minutes) 2. “Business Enterprise” MGTA01: Introduction MGTA01 background and overview: - “business” defined - economic systems -measuring performance - entrepreneurs - forms of organization - strategy - factors of production - markets/competition - small businesses - business plans - raising capital Please read the textbook Course Textbook Introduction to Canadian Business Chris Bovaird Second Edition McGraw Hill Education 2019 Available in the UTSC Bookstore Professor Toor • Teaches courses in business, entrepreneurship, marketing and operations • Runs his own business • Believes in participatory style of teaching Arif Toor – Contact Info e-Mail: Office: Hours: a.toor@utoronto.ca BB Collaborate Wed 11 – 1 (By appointment only) Most other afternoons: shoot me an email Course Evaluation Type Probable Date Weight Format 1st Midterm Oct 20th, 2021 20% 20-40 MCQs 1 – 3 SAQs 2nd Midterm Nov 17th, 2021 30% 30-50 MCQs 1-3 SAQs Final Exam Somewhere in Dec 50% 40-60 MCQs; 3-6 SAQs Note Takers I am asking for volunteer note takers If: You attend class regularly Take fairly detailed notes Have decent handwriting or Type your notes Please consider volunteering er… that’s it MGTA01 – Intro to Business – Key Points Main points of today’s lecture: Definition of “business” Characteristics of business Revenues and expenses Profit and Loss The Profit Motive Risk and Return What is a BUSINESS? • Any activity undertaken for the sake of profit is known as business “Business” Defined as per the textbook Business: an organised effort, to create or provide something, that people want and will pay for, in order to make a profit. Your Turn • Think of a profession whose practitioners make a lot of money (in your opinion). • Share the profession and the estimated annual earnings with the class.. Business and Wealth Maximization • Businesses are a means to wealth maximization This is a business So is this… .. Business: Characteristics This business exists… Because people might be hungry Business: Characteristics This business exists… Because people might be thirsty Business: Characteristics Customers need and want things and they will pay for them Why do businesses exist? • Businesses exist to satisfy customer needs and acquire benefits from this activity • Business ideas can come from: Entrepreneurs Environment Experts Government Legislation Evolution of Business • http://www.bain.com/publications/articles/3000years-of-business-history-in-two-minutes-video.aspx Business: Some Basics A business must make enough money to continue serving its customers The $$$ that comes in: “Revenues” or “Sales” Business: Characteristics Customers pay, get something in return. The business must provide a pizza. Dough = 50 ¢ Cheese = 50 ¢ Mushrooms = 40 ¢ Green Pepper = 40 ¢ Onion = 15 ¢ Paper Plate = 5 ¢ Profit Profit - The difference between: $$$ in (revenues or sales) $$$ out (costs or expenses) Profit: Simple Example Business sells small, plain pizza Revenue (sales) = $6.00 less Expenses (costs) = - $5.00 Profit = $1.00 Profit versus Loss Profit When revenues are more than costs business owners become wealthier Profit versus Loss Loss When revenues are less than costs Business owners become poorer. Profit Key reason for a business to exist Not all organisations are businesses Hospitals, universities, churches: provide services but not intended for profit These are “not for profit” organisations Not for Profit Organisations This is not a business Not for Profit Organisations Nor is this Businesses vs. Not for Profits A business tries to make a profit Churches and universities do not U of T is not a business Tuition fees pay for less than 40% of the cost of running the university 11% 3% 19% 38% 14% 26% tuition fees government grants research grants investments donations other The Profit Motive People give up their time, energy and money if there is incentive to do so. Profit – the chance for owners to create wealth – is the incentive The Profit Motive He liked the idea. Adam Smith The Profit Motive He didn’t. Karl Marx Businesses Can and Do Fail New Entries Exits Net Change 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 -20 -40 -60 -80 -100 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 Businesses Can and Do Fail 2002-2009: Canadians started 95,000 businesses per year (260 per day) 88,000 closed (240 per day) 2008-2009: Number of businesses fell by ~ 40,000 Businesses Can and Do Fail • Running a business is difficult • Running a business is complicated • Businesses must anticipate needs • Customers are unpredictable • Competition can enter at any time Businesses Can and Do Fail Another characteristic of business: “risk” Main points - Review Definition of “business” Profit and Loss The Profit Motive Risk • Thanks