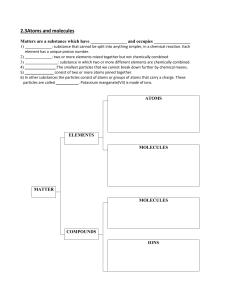
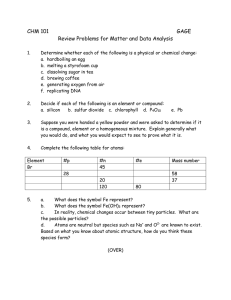
Cut and Paste Instructions: You must cut out and rearrange the terms to match their definitions. Paste these into your science book once you have correctly matched the terms with their definitions. Homogeneous - The same amount of element/s in a chemical formula. It does not change Molecule Heterogeneous - No fixed volume or shape - Can be measured or observed without changing chemical nature of substance Atom Matter Compound Fixed ratio - Particles are evenly distributed No new substance is made Fixed volume and shape Characteristic that can be observed during a chemical reaction Solid - Two or more atoms chemically bonded together Liquid - How tightly matter is packed into a substance Gas Physical change Chemical change Physical property Chemical Property Evidence of physical change Density - Mass - Bubbles or colour change Makes up everything How much matter is in a physical body Particles are not evenly distributed New substance is made No fixed shape but has fixed volume Smallest unit of matter Two or more atoms from different elements joined together Answers: Homogeneous: Particles are evenly distributed Molecule: Two or more atoms chemically bonded together Heterogeneous: Particles are not evenly distributed Atom: Smallest unit of matter Matter: Makes up everything Compound: Two or more atoms from different elements joined together Fixed ratio: The same amount of element/s in a chemical formula. It does not change Solid: Fixed volume and shape Liquid: No fixed shape but has fixed volume Gas: No fixed volume or shape Physical change: No new substance is made Chemical change: new substance is made Physical property: Can be measured or observed without changing chemical nature of substance Chemical Property: Characteristic that can be observed during a chemical reaction Evidence of physical change: Bubbles or colour change Density: How tightly matter is packed into a substance Mass: How much matter is in a physical body