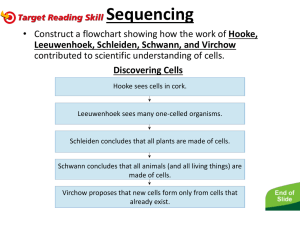
Name: Cell Theory Notes: Cell: ● Smallest structural and functional unit of an organism ● Usually ______________ ● Contains cytoplasm and a ___________ enclosed in a membrane ● Two main types of cells: ○ Prokaryotic (__________________) ○ Eukaryotic ( has a ____________) Robert Hooke (1665) ● Observed bark of cork trees under a ___________________ ● Thought the objects looked like individual rooms in a monastery (where monks lived), which were called cells ● Called his discovery, cells ● Did not know their true function 1. Were the cork cells observed by Robert Hooke living or not? Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1670) ● Developed the microscope lens to see greater magnification ● First person to observe __________________ and protozoa (singlecelled animal) ● Observed and described red ________ cells. Mathias Schleiden ● Concluded all plant tissues are composed of cells ● Declared that the cell is the basic ________________ block of all plant matter ● Sensed the importance of the nucleus of a cell 2. What type of cells did Mathias Schleiden study? Theodor Schwann ● Concluded that ______________ tissues are composed of cells too ● Worked with Schleiden to form a new theory in biology 3. What type of cells did Theodor Schwann study? 4. Schwann stated that all animals are made of cells, but animals are made of many different types of cells. For example, there are 3 different types of cells that make up muscle tissue in humans. How could you prove these were all “cells” even though they look different and make different tissues? Cell Theory: ● Schleiden and Schwann’s ideas became known as cell theory. ○ All organisms are made up of _________ ○ Cells are the _________ unit of life ● Rudolph Virchow proposed the third part of cell theory: ○ All cells result from the division of previously existing ___________ cells. 5. Think about what it would be like to go back in time and be one of the scientists working on the ideas that would become Cell Theory. Choose one of the three pieces of Cell Theory and describe an experiment that you could do that would support your piece of Cell Theory. Functions of Cells: ● ______________: chemical reactions inside the cell ● ______________: perceiving and responding to changes in the environment ● ______________: keeping conditions inside the organism within tolerable limits (balanced) ● ______________: increase in size ● ______________: producing offspring (sexually or asexually) ● ______________: obtaining food to provide energy for growth ● ______________: protection against enemies 6. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek created microscopes that could magnify objects 10 times better than anyone else at his time. In fact, his methods of grinding glass lenses were so precise, it would be 150 years before anyone outdid his work. Imagine, though, that microscopes never existed. What parts of Cell Theory would we still be able to figure out? Why? 7. What is a cell? 8. What are the three parts of Cell Theory? 1. 2. 3.