Uploaded by
adolfoariannejade
Brain Parts & Functions: A Middle School Module

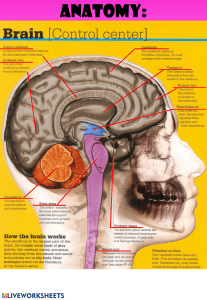
6 Module 9 Science and Health PARTS OF THE BRAIN AND THEIR FUNCTIONS A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development To the Learner The brain is responsible for issuing nerve impulses, processing nerve impulse data, and engaging in the higher order thought processes. It is the master control center over the body. Let’s Learn This Identify the parts of the nervous system and their functions. Let’s Try This HOW GOOD IS YOUR MEMORY? 1. Read the three columns for one minute. Try to remember the syllables and words in the three columns. Column 1 han shi phi cho aug fat gre pla Column 2 heating greater together function east ability party shop Column 3 Your Brain Can Easily Retain Short Understandable messages 2. Recall as many syllables and words as you can and write them down in your paper. 3. How many syllables in column 1 and words in column 2 & 3 do you remember correctly? ________________________________________________________________ 73 4. Which syllables and words in the three columns are difficult to recall? ________________________________________________________________ 5. Which column is the easiest to recall? ________________________________________________________________ 6. What do you think affects your ease of recall? ________________________________________________________________ Let’s Study This The brain is divided into three parts: the large cerebrum, the smaller cerebellum, and the brainstem leading to the spinal cord. I. The Cerebrum The cerebrum or forebrain forms the bulk of the brain. It is a large mass of white and gray neural fiber in the upper cranium. It is responsible for the higher thought processes such as memory, judgment, and reason. It also processes sensory data initiating willful motor processes, such as voluntary muscle bending. The cerebrum is composed of two lateral halves called the right and the left cerebral hemispheres. They feature a number of folds called gyri and furrows called sulci. They are connected in the middle at the medulla. 74 II. The Cerebellum and How It Functions The cerebellum is the second smaller division of the brain. It is located below the cerebrum and in the back part of the cerebrum. It consists of large mass folia. It also has a right and a left hemisphere, and a finger-like structure in the middle. The cerebellum is responsible for body balance, posture, and the coordination of movement. Nerve pathways connect the right half of the cerebellum with the left cerebral hemisphere and the right side of the body. Pathways from the left half connect with the right cerebral hemisphere and the left side of the body. The cerebellum receives, coordinates, and modifies orders from the cerebrum. For example, to be able to maintain precise muscular coordination, this is what happens. First, the cerebellum receives information about body balance and equilibrium from nerve endings in the inner ear. Then, the cerebellum adjusts and fine tunes these actions by passing the regulating signals to the motor neurons of the brain and spinal cord. Thus, the person moves and acts normally. If the cerebellum is damaged, the person will have loss of ability to maintain precise muscular coordination and fine cooperative actions of the motor processes. This disease is called ataxia. 75 III. The Brain Stem and Other Structures The brain stem is located behind the cerebellum. It is a stalklike structure that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. The bottom part of the brain stem is called the medulla oblongata. Just above the medulla is the pons. Above the pons lies the midbrain. The pons connects the two hemispheres of the cerebellum. Its nerve fibers link the cerebellum and the cerebrum. Nerve centers in the midbrain help control movements of the eyes and the size of the pupils. Thalamus, Hypothalamus, and Reticular Formation At the upper end of the brain stem are the hypothalamus and the thalamus. One thalamus is on the left side of the brain stem. Another thalamus is on the right side. Each thalamus receives nerve impulses from various parts of the body and redirect them to the appropriate areas of cerebrum. They also relay impulses from one part of the brain to another. The hypothalamus regulates internal conditions of the body such as temperature, hunger, pain, pressure, etc. Beside the hypothalamus is the pituitary gland which is the master gland of the body. It is the hypothalamus which controls the activity of the pituitary gland. The reticular formation is a network of nerve fibers. It lies deep within the brain stem. It helps regulate and maintain the brain’s level of awareness. It is stimulated by the sensory messages that pass through the brain stem. The reticular formation stimulates alertness ad activity throughout the cerebral cortex. 76 Let’s Do This 1. Observe and take note of what the members of your family are doing for about 5-10 minutes. 2. Write your observations in your paper. Identify the parts of the brain responsible for each of the actions they do. 3. Your chart should look like this. Members of the Family Actions Parts of the brain responsible 1. ______________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ 2. ______________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ 3. ______________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ 4. ______________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ 4. What part of the brain do they commonly use? 77 Let’s Do More Answer the following: Parts of the brain Functions of each part Parts of the Brain 78 Let’s Remember This The brain is the master organ of the nervous system and the control center of the body. It receives information about the outside world from your senses and sends out messages to tell your body what to do. Its main parts are: cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. The cerebrum enables you to think, memorize, recognize and be aware of the things happening in your surroundings. It receives and interprets the messages of the five senses. The cerebellum coordinates voluntary muscular actions. It is responsible for the ability to learn habits and develop skills. It also maintains balance in the body. The brainstem controls involuntary actions such as breathing, alertness, and eye movement. It conveys messages between the spinal cord and the brain. It also takes care of the reflex actions such as coughing and blinking. Let’s Test Ourselves Choose the letter of the correct answer. 1. What controls the involuntary actions of the body? A. nerves B. cerebrum C. cerebellum D. brainstem 2. Which is the largest part of the brain and it controls mental processes such as thinking, memorizing, and decision-making? A. pons B. cerebellum 79 C. cerebrum D. spinal cord 3. What coordinates voluntary muscular actions and maintains balance in the body? A. cerebrum B. cerebellum C. brainstem D. spinal cord 4. Why is the brain enclosed in the skull? A. for B. for C. for D. for design protection a better look sound proofing 5. What will happen if a person injures part of his brain? The person ______________. A. will die B. brain decays C. actions will continue to be coordinated D. cannot integrate and coordinate his movements Science Fact File The hypothalamus forms the main link between the body’s endocrine system and nervous system. However, some endocrine glands are not controlled by the pituitary gland or by the nervous system. These are the glands that help maintain the normal chemical composition of the blood and respond to changes in the amounts of various chemicals. 80 Answer Key Let’s Try This Answer depends on the learner’s memory Let’s Do This Answers depend on the actions of the different members of the family Let’s Do More Parts of the Brain Cerebrum Enables us to: think, memorize and recognize. Cerebellum Coordinates voluntary muscular actions. Ability to learn habits and developed skills. 81 Brain Stem Controls involuntary actions such as breathing, alertness and eye movement.