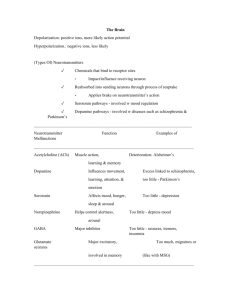
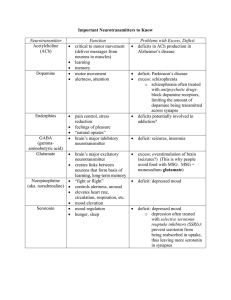
Exam revision paper Foundation of Mental Health and Distress 2022 (correct answers are displayed at the end of the paper) 1) The work of Ronald Laing is part of… A. B. C. D. The neo-Kraepelian movement The anti-psychiatry movement The psychoanalytic movement None of the above 2) Which of the following statements about Psychiatry is incorrect? A. All psychiatrists exclusively endorse categorical and biomedical models of mental health difficulties B. Relatively to Clinical Psychology, Psychiatry places more emphasis on biological to explain mental health difficulties C. Relatively to Clinical Psychology, Psychiatry places more emphasis on biological interventions for mental health difficulties D. All of the above 3) One of the possible side effects of antipsychotic medication is tardive dyskinesia, what does this term refer to? A. Repetitive, involuntary, purposeless movement B. Increased appetite and weight gain C. Stiffness in the arms and legs D. Flat facial expressions 4) The “fight or flight” response is a physiological reaction which mirrors/explains the bodily symptoms associated with… A. Low mood B. Mania C. Anxiety D. All of the above 5) Which of the following statements about trauma-related symptoms is incorrect? A. Trauma-related symptoms (e.g. nightmares, flashbacks, dissociation etc) are very common in the immediate aftermath of a traumatic event B. When people experience trauma-related symptoms, therapy and/or medications are always required C. Only a minority of people who have experienced potentially traumatic events develop symptoms severe enough to meet criteria for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder D. None of the above 6) Bipolar Type II is the diagnostic label used to describe… A. Individual who experience pervasive low mood B. Individual with mood-swings with both episodes of depression and episodes of mania C. Individuals with mood swings with episodes of depression and hypomania (but not full blown manic episodes) D. Individuals with mood swings who experience manic episodes but no episodes of intense low mood 7) Which of the following risk factors has been linked to increased risk of developing psychosis? A. B. C. D. Childhood trauma Experiences of social inequality and disadvantage Belonging to a minority group All of the above 8) The most researched and widely used psychological approach is: A. B. C. D. Cognitive Therapy Behaviour Therapy Psychoanalysis Cognitive Behaviour Therapy 9) Possible ‘negative symptoms’ of psychosis include: A. B. C. D. E. Thought disorder, Anhedonia, Asociality Alogia, Anhedonia, Hallucinations Blunted affect, Alogia, Avolition Blunted after, Thought disorder, Anhedonia None of the above 10) Which of the following statements about the Rosenhan’s experiment is incorrect? A. All participants received diagnoses of severe mental illness (schizophrenia and manic depression) B. Despite reporting that their symptoms had disappeared, participants were prevented from leaving the hospital C. Many were discharged after receiving a diagnosis of “remitted paranoid schizophrenia” D. None of the above 11) The acronym SSRI stands for: A. B. C. D. Selective synaptic reuptake inhibitors Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors Selective serotonin reabsorption inhibitors Selective synaptic reabsorption inhibitors 12) Biological theories of schizophrenia/psychosis have assumed that: A. Schizophrenia is caused by abnormal serotonin functioning B. Schizophrenia is characterised by increased levels of dopamine due to abnormalities in pre-synaptic cell reuptake C. Patients with diagnosis of schizophrenia are “supersensitive” to dopamine as they have more dopamine receptors in the post-synaptic cell. D. Both B. and C. 13) The “cognitive paradigm shift” in psychotherapy was heavily influenced by the work of… A. B. C. D. Aaron Beck Carl Rogers Albert Ellis Both A. and C. 14) Psychodynamic therapies are therapies influenced by the work of… A. B. C. D. Carl Rogers Sigmund Freud Aaron Beck Hans Eysenck Answers 1) The anti-psychiatry movement 2) All psychiatrists exclusively endorse categorical and biomedical models of mental health difficulties 3) Repetitive, involuntary, purposeless movement 4) Anxiety 5) When people experience trauma-related symptoms, therapy and/or medications are always required 6) Individuals with mood swings with episodes of depression and hypomania (but not full blown manic episodes) 7) All of the above 8) Cognitive Behaviour Therapy 9) Blunted affect, Alogia, Avolition 10) None of the above 11) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors 12) Patients with diagnosis of schizophrenia are “supersensitive” to dopamine as they have more dopamine receptors in the post-synaptic cell. 13) Both A. and C. 14) Sigmund Freud