220-1001 Exam Simulation
QBank Quiz September 14, 2021
Question #1 of 60
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Test ID: 182327079
Question ID: 1171786
You want to use Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology in a laptop. Which components must support this technology to use it? (Choose all that apply.)
A) Software drivers
B) BIOS
C) Operating system
D) Motherboard
Explanation
If you want to use Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology in a laptop, the motherboard, BIOS, and operating system must support SpeedStep. In addition, the chipset and
processor must support the technology.
The software drivers do not need to support SpeedStep. Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology allows the computer to dynamically adjust processor voltage and core
frequency, which decrease average power consumption and average heat production.
You disable SpeedStep in the system's BIOS. SpeedStep would prevent a computer from using 100% of the CPU.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot common mobile device issues while adhering to the appropriate procedures.
References:
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.5 Given a scenario, troubleshoot common
mobile device issues while adhering to the appropriate procedures
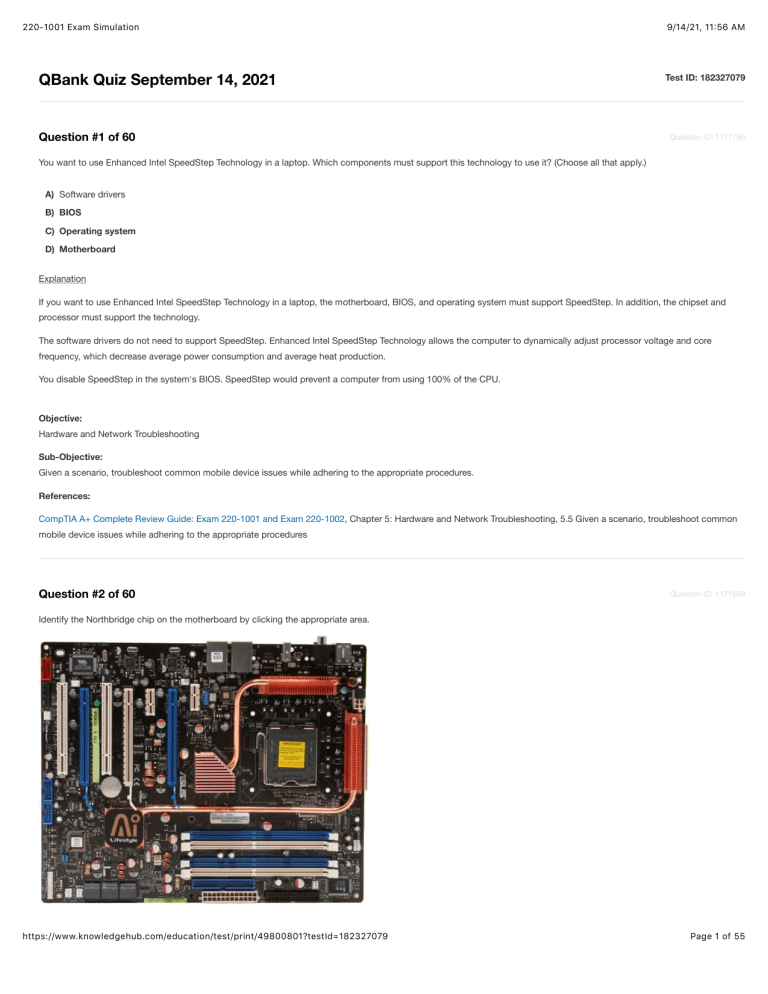
Question #2 of 60
Question ID: 1171699
Identify the Northbridge chip on the motherboard by clicking the appropriate area.
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 1 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
A) 199,80,221,233
B) 10,362,26,411
C) 67,381,158,410
D) 99,262,167,335
E) 2,220,24,295
F) 60,80,82,230
G) 484,93,506,120
H) 26,73,48,220
I) 94,71,116,221
J) 165,81,182,126
K) 235,375,337,394
L) 347,392,441,412
M) 233,73,250,118
N) 219,300,466,375
O) 127,79,149,229
P) 344,132,434,238
Q) 480,313,502,340
R) 236,169,310,251
S) 112,237,16
T) 251,395,341,414
Explanation
In the exhibit given, the Northbridge chip is located between the PCI and PCI-E expansion slots and the CPU socket.
For testing purposes, you should be able to recognize different components on a motherboard. Because there are so many different motherboard configurations available, you
should research many different motherboards and familiarize yourself with them. In the References section, we provide links to several motherboard diagrams that are found
on the Internet. You can also use the motherboard manufacturers' websites to locate the motherboard's user documentation.
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 2 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure motherboards, CPUs, and add-on cards.
References:
Motherboard Diagram, http://gohappycomputer.blogspot.com/2010/03/motherboard-diagram.html
Motherboard Components and Functions, http://www.buildcomputers.net/motherboard-components.html
Question #3 of 60
Question ID: 1175639
A company representative has just landed a significant order at a trade show. He has all the necessary information on his laptop and needs to transmit it to the home office for
processing. However, he calls you on his company-issued Android phone and notifies you that Internet access is down at the trade show. He is on an LTE connection. What
should you recommend?
A) Enable tethering on the Android phone.
B) Connect the laptop to the company network over a VPN.
C) Set the Android phone to Airplane Mode.
D) Pair the phone and laptop via Bluetooth.
Explanation
You should recommend that he enable tethering on the Android phone. Tethering will allow the laptop to use the data connection on the Android phone as a WiFi hot spot to
transmit the order to the home office.
Pairing the phone and laptop via Bluetooth is not correct. That process will allow the two devices to communicate, but will not allow the laptop to transmit the order to the
home office.
Setting the Android phone to Airplane mode will disable the cellular and data connectivity on the phone.
Connecting the laptop to the company network over VPN is not correct. A VPN connection first requires an Internet connection, and then a VPN connection can be
established.
To enable tethering on an Android phone, you should select the Setting option on the Home Screen. Then select More, & Networks, and Tethering & portable hotspot. Select
the Portable Wi-Fi hotspot option. In Portable Wi-Fi hotspot settings, create a WiFi Network name and password. This creates the WiFi hotspot and will allow you to tether
(attach) another device to that network.
On the other device, go to the wireless settings, select the WiFi network you just created, and enter the proper credentials. When connected, you are tethered to the Android
device and using the data connection on the Android device.
To connect your mobile device with a Bluetooth headset or other device, you should first enable Bluetooth on the mobile device on the other device. Both devices must have
Bluetooth pairing enabled. This will allow the second device to find the mobile device for pairing. The second device will then create and display a PIN code that you must
enter into the mobile device. When you enter the appropriate PIN code, the two devices will pair. At this point, you can test connectivity.
Objective:
Mobile Devices
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, configure basic mobile device network connectivity and application support.
References:
All you need to know about tethering with your Android device, http://www.androidauthority.com/what-is-tethering-android-280456/
How to use a Google Android phone as a Wi-Fi hotspot, http://www.pcadvisor.co.uk/how-to/mobile-phone/how-tether-google-android-phone-image-3279408/
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 3 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
Question #4 of 60
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Question ID: 1192026
Users are having trouble accessing a server. You want to view the server's DNS entry on the DNS server. Which command should you use?
A) nslookup
B) ipconfig
C) ping
D) tracert
Explanation
You should use the nslookup command to view the server's DNS entry on the DNS server. The nslookup command has two modes: interactive and non-interactive. If you only
need to obtain one piece of information, you should use non-interactive mode. Otherwise, interactive mode is probably best. This command can be used to resolve a remote
host's name to its IP address.
You should not use the ipconfig command. This command is used to view the TCP/IP settings on the computer, including IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS
servers.
You should not use the tracert command. This command displays the route a packet takes to a remote host.
You should not use the ping command. This command tests connectivity for a computer. To check functionality of the TCP/IP protocol, you can issue the ping 127.0.0.1
command. This pings the loopback address. To check communication between your local computer and a remote computer, you can ping the remote computer. For example,
if the remote computer was named client1.kaplanit.com and had an IP address of 172.16.3.1, you could issue the ping client1.kaplanit.com or ping 172.16.3.1 command.
For the A+ exam, you need to understand the following network tools:
Cable tester – Verifies that the cable is functioning properly. Multimeters can also perform this function. A cable tester, though, is more specialized and can tell you what
exactly is wrong with the cable.
Loopback plug – Plugs into the network port and verifies that the network port is functioning properly
Punch-down tool – Secures cable to patch panel
Toner generator and probe – Locates the correct cable coming into a patch panel. These are two-piece units that are referred to as a Fox and Hound.
Wire strippers – Prepares the end of the cable for a connector
Crimper – Attaches a connector to the cable
Wireless locator – Locates wireless networks in your vicinity. Many of them will also display the signal level and the SSID of the wireless networks. Finally, some will even
display more detailed information like channel used, location of the wireless network, and a map of the wireless network showing connected devices.
For the A+ exam, you need to understand the following command-line tools:
Ping – Uses ICMP to test connectivity between two devices
Ipconfig/ifconfig – Displays the TCP/IP configuration of a device. You should be familiar with its switches, including the /all, /release, /registerdns, /renew, and /flushdns
switches. The ifconfig is the Unix/Linux equivalent of ipconfig.
Tracert – Traces the path a packet traverses through a network. It displays the name and IP address of every single device through which the packet passes.
Netstat – Displays what ports are listening on a TCP/IP device
Nbtstat – Displays NetBIOS information
Net – A powerful Windows command. The net use subcommand allows you to view what is currently shared. Research the various ways you can use the net command.
Netdom – Joins a computer to a Windows domain, manages computer accounts on a Windows domain, and establishes trust relationships between Windows domains. It
is available by default with Windows 8 and later.
Nslookup – Queries the Domain Name System (DNS) to obtain domain name or IP address mapping or for any other specific DNS record.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot common wired and wireless network problems.
References:
How to Use Nslookup to Verify DNS Configuration, https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa997324(v=exchg.65).aspx
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.7 Given a scenario, troubleshoot common
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 4 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
wired and wireless network problems
Question #5 of 60
Question ID: 1191882
You want to buy a longer charging cord for your iPhone 8. When you get to the store, there are many options to choose from. Which cable should you select?
A) Lightning
B) IEEE 1394
C) Micro-USB/Mini-USB/USB-C
D) Tethering
Explanation
You should choose a Lightning cable. Lightning cables are proprietary to Apple devices, beginning with the iPhone 5, iPod Touch and the iPod Nano. The cable was
introduced in 2012 as a replacement for the 30-pin connector.
You should not choose a tethering cable because there is no such cable. Tethering refers to using the Internet connection on a cell phone on another device, like a laptop or a
tablet. This can be accomplished using BlueTooth, USB or wireless. The phone becomes a “hot spot.” In essence, tethering allows a device to reach the Internet without
otherwise having a connection.
You should not choose a Micro-USB, Mini-USB, or USB-C cable. These cables are used in many portable devices, but the Apple iPhone 8 uses a proprietary Lightning
connector.
You should not choose an IEEE 1394 cable, also referred to as FireWire. While it was used in early versions of Apple mobile devices, FireWire is not used in iPhone 8.
Other proprietary vendor-specific ports for communication and power include Thunderbolt for Apple devices. Apple used a cable with a 30-pin connector for mobile devices
from 2007 until the Lightning cable was introduced in 2012.
Objective:
Mobile Devices
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, connect and configure accessories and ports of other mobile devices.
References:
What Is a Lightning Connector? https://www.lifewire.com/lightning-connector-4156298
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 1: Mobile Devices, 1.5 Compare and contrast accessories and ports of other mobile
devices
Question #6 of 60
Question ID: 1171749
A user has been using his desktop computer on a daily basis for over a year now. Today, when he starts his computer, he notices that the computer does not power on. You
have been dispatched to troubleshoot this problem.
What could be the reason for this?
A) The memory is faulty.
B) The CPU is overheated.
C) The power supply is bad.
D) The hard disk has crashed.
Explanation
The most likely reason for this problem is a bad power supply. A power supply unit (PSU) provides power to the computer. If the power supply is faulty, it will not provide the
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 5 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
necessary power voltage, and the computer will not power up. This problem could also be caused by the power cord not being connected to the power source properly or by
the power strip or surge protector being powered down. Technicians should always check for the most obvious problems first. However, in this case, checking the power cable
or surge protector was not an option.
Faulty memory does not stop the computer from powering on. You would receive a string of beeps during the boot process or an error message in case of faulty memory.
An overheated CPU will cause the computer to reboot randomly. An overheated CPU can be caused by a bad heat sink or a faulty fan attached to the CPU. An overheating
CPU does not prevent the computer from being powered on.
A crashed hard disk does not prevent the system from being powered on. The hard disk is a storage device that retains data even when there is no power. You will receive an
error message if the hard disk has crashed, but the computer will still be powered on. If the hard drive starts making a grinding noise or giving off a burnt odor, you should
replace the drive before it crashes completely.
You can also experience power supply issues if the devices installed in the computer require more power than the power supply is capable of providing. If a computer's
internal power needs are greater then what the power supply can provide, you need to upgrade the power supply. If the power supply wattage is too low, the computer will be
unable to boot or internal devices will not function.
Other problems that may be the result of a bad, insufficient, or failing power supply include occasional rebooting, overheating, electric shock felt on computer case, and the
hard drive ceasing to work.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot problems related to motherboards, RAM, CPUs, and power.
References:
Foner Books, ATX Power Supply Failure Diagnostics, http://www.fonerbooks.com/power.htm
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.2 Given a scenario, troubleshoot problems
related to motherboards, RAM, CPUs, and power
Question #7 of 60
Question ID: 1171662
If you were explaining to your company's IT personnel the difference between their old hard drive technology and newer solid state drives, which statement would be FALSE?
A) They do not require an external power source.
B) They are not as fragile as magnetic hard drives.
C) They are silent when in operation.
D) They use a read/write assembly.
Explanation
Solid state drives or SSD do NOT use a read/write assembly. A solid state drive does not have any moving parts. They are not as fragile as magnetic hard drives because they
do not have any moving parts and are resistant to shock. When in operation, solid state drives are silent. Solid state drives are faster, more reliable, and require less power
than magnetic drives.
Solid state drives do NOT require an external power source. They pull electrical current for operation from the USB drive. Serial ATA (SATA) solid state drives do require
electricity by plugging into the power supply.
Flash drives are solid state drives. IDE hard drives, CD-ROM drives, DVD drives, and tape drives are all considered magnetic media. For some time now, tape drives have been
the primary means of offsite storage of data backups. More companies are moving toward optical media and drives for backup storage. There are hybrid and embedded
MultiMediaCard (eMMC) versions of solid state drives (SSDs) that work mainly in portable devices, but are also used to troubleshoot hard drive failures due to their SATA port
compatibility. Hybrid drives are a combination of a hard drive with some moving parts and a true SSD, which is basically flash memory. The data is stored differently, but
serves the same purpose by giving users a performance like an SSD. SSD cards are preferred over eMMC cards.
Objective:
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 6 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, select, install and configure storage devices.
References:
Solid-state Drives versus Hard-Disk Drives in Laptops, http://www.pcworld.com/article/134185/solidstate_drives_versus_harddisk_drives_in_laptops.html
Definition of: SATA, http://www.pcmag.com/encyclopedia/term/50811/sata
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 3: Hardware,
3.4 Given a scenario, select, install and configure storage devices, Solid-State Drives
, Chapter 3: Hardware, 3.4 Given a scenario, select, install and configure storage devices, Magnetic Hard Drives
Question #8 of 60
Question ID: 1191982
A user complains that his computer is taking a long time to boot. During the boot process, you observe that the hard drive activity light is staying on. You discover that the
hard drive is nearing its maximum capacity. The computer contains a single 150 GB hard drive. What should you do?
A) Defragment the hard drive.
B) Add an identical hard drive and configure a RAID-1 volume.
C) Add an identical hard drive and configure a RAID-5 volume.
D) Add an identical hard drive and configure a RAID-0 volume.
Explanation
You should add an identical hard drive and configure a RAID-0 volume. RAID 0 is disk striping. In this configuration, the two drives will appear as a single drive to the user.
Data will be striped across the two drives. Anytime you experience long boot times and the hard drive activity light stays on during the boot, the most likely cause is that the
hard drive is nearing its maximum capacity.
You should not add an identical hard drive and configure a RAID-1 volume. RAID 1 is disk mirroring. If you use RAID 1, all the data on the first drive will be mirrored onto the
new drive. This would not increase the availability of disk space.
You should not add an identical hard drive and configure a RAID-5 volume. RAID 5 requires a minimum of three disks.
You should not defragment the drive. Defragmenting a drive can increase its performance but rarely frees any disk space. In this scenario, you need to either free up some
space on the current drive or add a new hard drive.
For the A+ exam, you need to be familiar with the following hard drive symptoms and how to fix them:
Read/write failure – This is usually caused by damaged sectors on the hard drive or by hard drive failure. Run the chkdsk command to scan the drive for damaged sectors.
If the hard drive has completely failed, you will need to replace the drive and restore the data from backup.
Slow performance – This can be caused by memory or hard drive. If you do not have enough memory, there will be excessive paging. In this case, add more memory. If
you think the hard drive itself is causing the performance issue, check the hard drive to see if it has sufficient free space. If it does not, you need to add more hard drives to
your computer. If it has sufficient free space, the performance issue could be caused by fragmented files. Run the defrag utility to defragment the hard drive and increase
hard drive performance.
Loud clicking noise – This often occurs right before the hard drive dies. Because loud noises can also be caused by other components, you first need to confirm that the
noise is coming from the hard drive. If you have confirmed this, completing a backup of your data should be your first priority. Then replace the hard drive and restore the
data from the backup.
Failure to boot – This problem can be caused by many different issues. If the system cannot locate the boot files, it cannot boot. If you suspect this is the problem, you
should ensure that your BIOS is set to boot from the drive where the boot files reside. Also, it may be necessary to check the BOOT.INI file to ensure that the partition
information is entered correctly. Finally, you may have to repair corrupted boot files. You should use the Recovery Console to repair corrupt system files. Finally, check to
make sure that the connections to your hard drive are still intact. If you receive any Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.) errors, research the
specific error you receive to find out what you need to do.
Drive not recognized – This usually involves either an incorrect master/slave setting or the inability of the BIOS or operating system to recognize the drive. Check to make
sure that the master/slave jumpers are configured appropriately. Check the BIOS to make sure that the disk parameters are configured appropriately. Finally, you made
need to install the appropriate drivers for the operating system. This may require that you obtain the third-party drivers from the hard drive vendor. In legacy systems that
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 7 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
do not support drives higher than 504 MB, you may need to implement logical bus addressing (LBA).
OS not found – This usually is a software issue where the boot sector cannot be located. Reboot the computer into the Recovery Console and repair the operating system.
RAID not found – If hardware RAID is implemented in the computer, the problem is usually with the RAID controller. Check the controller and replace as necessary. If
software RAID is implemented, make sure that the BIOS is set to RAID. You should also check all RAID connections. Finally, test the individual RAID drives. If one of the
drives has failed, replace it and restore the data.
RAID stops working – This is usually caused by the failure of a single hard drive in the RAID array. You need to determine which hard drive has failed and replace it. If the
failed drive is in a RAID-1 or RAID-5 array, the array will continue to operate, but performance will be degraded until the failed hard drive is replaced. Use the RAID setup
program to set the RAID configuration back up.
Proprietary crash screens (BSOD/pin wheel) – If a BSOD occurs after you install a new hard drive or new drivers, you should immediately suspect the hard drive as the
cause. Remove the hard drive or roll back its driver to troubleshoot the BSOD. If the BSOD no longer occurs, you should then research the change you made to discover if
there is a known issue with the hard drive or driver. Make sure that you only remove one hard drive or roll back one driver at a time to help determine the true cause of the
BSOD. Pinwheel errors are Apple computers equivalent to BSOD. Pinwheel errors occur when users see the spinning rainbow pinwheel. Causes include bugs in
applications, event processing issues, and virtual memory issues.
S.M.A.R.T. errors – Self Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.) performs a quick analysis of the hard drive for problems during system boot up. It
reports on such hard drive parameters as read error rate, throughput performance, and seek error rate. The main purpose of using S.M.A.R.T. is to ensure that you receive
warnings prior to a complete drive failure so that the drive can be replaced before complete failure.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot hard drives and RAID arrays.
References:
RAID, http://www.prepressure.com/library/technology/raid
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.3 Given a scenario, troubleshoot hard
drives and RAID arrays
Question #9 of 60
Question ID: 1191963
Match the printer maintenance task on the left with the printer where it should be implemented. Each maintenance task will only match to a single printer type, and each
printer type will only have a single maintenance task.
{UCMS id=5157983975636992 type=Activity}
Explanation
You should match the printer maintenance techniques as follows:
Laser – Replace toner
Inkjet – Clean heads
Thermal – Clean heating element
Impact – Replace ribbon
A laser printer has the following maintenance tasks: replace toner, apply maintenance kit, calibrate, and clean.
An inkjet printer has the following maintenance tasks: clean heads, replace cartridges, calibrate, and clear jams.
A thermal printer has the following maintenance tasks: replace paper, clean heating element, and remove debris.
An impact printer has the following maintenance tasks: replace ribbon, replace print head, and replace paper.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and maintain various print technologies.
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 8 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
References:
CompTIA Exam Guide 220-901 Objective 1.15, http://certification.comptia.org/certifications/a#examdetails
Question #10 of 60
Question ID: 1171708
You have purchased a new 20-pin power supply to replace one that failed. However, the motherboard only has a 24-pin connector. What should you do?
A) Purchase a 24-pin power supply.
B) Plug the 20-pin power supply into the motherboard, leaving pins 11, 12, 23, and 24 on the motherboard unconnected.
C) Plug the 20-pin power supply into the motherboard, leaving pins 1, 2, 13, and 14 on the motherboard unconnected.
D) Purchase a motherboard with a 20-pin power connector.
E) Change the setting on the voltage selector switch.
Explanation
You should plug the 20-pin power supply into the motherboard, leaving pins 11, 12, 23, and 24 unconnected. These four pins are for higher current capabilities of the
processor, which do not need to be used in the current scenario.
It is not necessary to replace either the power supply or motherboard. The current configuration will work if plugged properly.
You should not change the setting on the voltage selector switch, sometimes referred to as dual voltage options. This would allow you to convert the power usage of the
power supply between the U.S. and UK standards to allow the power supply to operate at different voltages. The voltage selector switch allows you to switch between
110/120 Volts AC or 220/240 Volts AC.
A dual rail power supply is designed to split the power in the PSU and provide direct support for the CPU.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Summarize power supply types and features.
References:
Using a 20-pin Power Supply with a 24-pin ATX Motherboard, http://www.smps.us/20-to-24pin-atx.html
Question #11 of 60
Question ID: 1191897
You are setting up a network segment in the Research and Development department. Due to the sensitive and proprietary nature of the work in this department, you want to
ensure that only computers belonging to that department can access that network segment. Which option would you use?
A) DMZ
B) QoS
C) MAC filtering
D) NAT
Explanation
You should use MAC filtering. MAC filtering allows you to specifically configure which computers are allowed on the network, and to specify which computers are denied
access to the network. You would include the MAC addresses of departmental computers on an Allow list (referred to as whitelisting). Likewise, you would include MAC
addresses of computers that should not be given access on the Block list (referred to blacklisting). Some devices may only allow you to configure an allow or deny list, but not
both. Whitelisting/blacklisting is a function of MAC filtering.
A demilitarized zone (DMZ) places a firewall between your private network (LAN) and the public network (the Internet) or between two networks. Devices such as web servers
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 9 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
and mail servers are often put inside a DMZ
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows traffic from a private network to reach the Internet and return. For example, assume a computer on the internal private LAN has an IP
address of 192.168.1.140, and the default gateway has an IP address of 71.38.117.45. When traffic from 192.168.1.140 is sent, the gateway assigns it a port number in the
ephemeral range, say 45798. The gateway router then uses its own IP address and the assigned port (71.38.117.45:45798) to route traffic to the Internet.
Quality of Service (QoS) assigns priorities to different types of network traffic. This allows the network to allocate more bandwidth to traffic with higher priority, and less
bandwidth to traffic that you have designated as having a lesser importance. QoS does not affect which device is allowed to access a network.
Objective:
Networking
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure a basic wired/wireless SOHO network.
References:
How do I configure a MAC filter?, http://usatcorp.com/faqs/configure-mac-filter/
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 2: Networking, 2.3 Given a scenario, install and configure a basic wired/wireless SOHO
network
Question #12 of 60
Question ID: 1171842
You suspect that a hacker has compromised a computer using one of its open ports. Which command would allow you to view the open ports on the computer?
A) tracert
B) net use
C) ssh
D) netstat
Explanation
The netstat command would allow you to view the open ports on the computer. The parameters used with the netstat command are shown in the following exhibit:
You should not use the net use command. The net use command connects or disconnects shared resources. The syntax for the command is shown in the following exhibit:
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 10 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
There are other parameters available with the net command, as shown in the following exhibit:
You should not use the tracert command. This command displays the route a packet takes to a remote host. Its output is similar to the output of the ping command. The
syntax of the command is shown in the following exhibit:
You should not use the ssh command. Secure shell (SSH) is a command that allows you to remotely connect to a host in a secure fashion. It is very similar to Telnet. However,
Telnet does not provide the same security as ssh.
You should also understand the usage of the net command. The syntax of the net command is shown in the following exhibit:
An example of the output of the ping command is as follows:
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 11 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
An example of the output of the ipconfig command is as follows:
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 12 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
An example of the output of the nbtstat command is as follows:
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 13 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
An example of running the netdom command is as follows:
An example of the output of the nslookup command is as follows:
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 14 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot common wired and wireless network problems.
References:
How to detect hackers with netstat, http://computer-networking.wonderhowto.com/how-to/detect-hackers-with-netstat-262222/
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.7 Given a scenario, troubleshoot common
wired and wireless network problems
Question #13 of 60
Question ID: 1171579
Which well-known UDP port does DNS use?
A) 80
B) 161
C) 53
D) 110
Explanation
Ports allow more than one service or application to communicate at the same time between computers. The Domain Name System (DNS) service uses port 53 to
communicate information between name servers. DNS uses both TCP port 53 and UDP port 53. Administrators can assign additional ports for communication on an intranet
and through the Internet. There are a total of 65,536 ports from which to choose. Of these, only 1,024 ports are considered well known and, therefore, reserved for a particular
service.
Port 80 is used by Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) for browsing the World Wide Web.
Port 110 is used by Post Office Protocol Version 3 (POP3) for email.
Port 161 is used by Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) for network diagnostics.
Objective:
Networking
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast TCP and UDP ports, protocols, and their purposes.
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 15 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
References:
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 2: Networking, 2.1 Compare and contrast TCP and UDP ports, protocols, and their
purposes
Question #14 of 60
Question ID: 1171813
A user from the accounting department has contacted you regarding problems with a dot matrix printer. When you examine the output from the printer, several letters have
missing dots from the page. What should you do?
A) Replace the print head.
B) Print a test page.
C) Clean the print head.
D) Replace the ribbon.
Explanation
You should replace the print head. Over time, the pins on the print head can become clogged or bent. It is best to replace the print head in this situation.
You should not replace the ribbon. When a ribbon ages over time, the print output becomes fainter. Ribbon issues do not affect the individual letter quality.
You should not clean the print head unless the printer manufacturer suggests this. Most dot matrix printer manufacturers do NOT suggest cleaning the print head because it
comes into contact with the ribbon. It is usually easier and cheaper just to replace the print head.
You should not print a test page. This will not clear up the print quality issue you are experiencing.
Always keep in mind that you should check the obvious first when troubleshooting a printer. If the printer is not printing, you should make sure it is plugged in and turned on.
You should also make sure that it has paper. Most technicians can tell you stories about how they were called in for troubleshooting an issue that had a very obvious fix. Also,
keep in mind that some internal components should only be replaced by individuals who are experienced in repairing printers. These printer technicians are usually employed
by the vendor from which you purchased the printer.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot printers.
References:
Troubleshoot common dot matrix printer problems with these techniques, http://www.techrepublic.com/article/troubleshoot-common-dot-matrix-printer-problems-with-thesetechniques/5034829/
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.6 Given a Scenario, Troubleshoot Printers
with Appropriate Tools
Question #15 of 60
Question ID: 1171824
A user keeps receiving a printer error message before the print job is sent to the print spooler. Which printer issue would cause this?
A) The printer power is off.
B) The printer is paused.
C) The printer queue is stalled.
D) The printer driver is corrupt.
Explanation
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 16 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
When the printer is turned off, an error message will be displayed before the print job is sent to the print spooler. The print job will then reside in the print queue until the printer
is turned on.
If the printer is paused or the printer queue is stalled, any error messages would be displayed after the print job is sent to the print spooler. If the printer driver is corrupt, the
error message will be displayed after the print job is sent to the print spooler.
Always keep in mind that you should check the obvious first when troubleshooting a printer. If the printer is not printing, you should make sure it is plugged in and turned on.
You should also make sure that it has paper. Most technicians can tell you stories about how they were called in for troubleshooting an issue that had a very obvious fix. Also,
keep in mind that some internal components should only be replaced by individuals who are experienced in repairing printers. These printer technicians are usually employed
by the vendor from which you purchased the printer.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot printers.
References:
Basic Printer Troubleshooting Steps, http://www.computerhope.com/issues/ch000248.htm
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.6 Given a Scenario, Troubleshoot Printers
with Appropriate Tools
Question #16 of 60
Question ID: 1191949
A newly hired user with minimal computer skills calls the help desk. The manual for a new mobile device tells the user to enter the SSID information and a password that are
given. Your organization does not broadcast SSIDs, so you can understand why the new hire is confused about where to enter this information. Where can the user go to
enter this information?
A) Touchscreen configuration
B) Wireless settings
C) Application installation/configuration
D) Account setup/settings
Explanation
The System Set Identifier (SSID) is the name used to identify a wireless network to which you wish to connect. SSID configuration is found in wireless settings. Configuring the
SSID is one of the areas where users require the most assistance with their laptops and common mobile devices.
Wireless settings can be configured in the systems tray area of the Windows task bar, as shown in the following exhibit:
When you click it, you will see the list of available wireless networks. Networks that do not broadcast SSIDs will be listed as Hidden Network. Select the Hidden Network and
enter the SSID and password.
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 17 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure common devices.
References:
How do I connect to a hidden network?, https://kb.netgear.com/30740/How-do-I-connect-to-a-hidden-network
Question #17 of 60
Question ID: 1171609
Which of the following is an example of an IPv6 address?
A) 00-0C-F1-56-98-AD
B) 127.0.0.1
C) fe80::200:f8ff:fe21:67cf
D) 192.1.0.1
Explanation
An example of an IPv6 address is fe80::200:f8ff:fe21:67cf.
An example of an IPv4 address is 127.0.0.1 and 192.1.0.1.
An example of a MAC address, which is hard-coded into the network interface card (NIC) by the manufacturer, is 00-0C-F1-56-98-AD.
Objective:
Networking
Sub-Objective:
Explain common network configuration concepts.
References:
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 2: Networking, 2.6 Explain common network configuration concepts
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 18 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
Question #18 of 60
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Question ID: 1191994
You are instructing a user on how to properly use a new laptop. He asks about the special function keys that are used to perform tasks such as toggling the display or
adjusting the display brightness. Which key should the user strike in combination with the special function keys?
A) The Alt key
B) The Fn key
C) The Shift key
D) The Ctrl key
Explanation
The user should use the Fn key on a laptop in combination with the special function keys. Almost every laptop allows you to bypass the operating system menu to perform
some functions, such as toggling screen displays, increasing or decreasing screen brightness, and putting the computer in the Standby mode, by pressing a combination of
keys. These keys are referred to as special function keys. The laptops that allow you to perform these special functions also contain a key named Fn that is used to activate
and deactivate special function keys.
The Fn key and the special function keys on a laptop are typically marked in blue. To enable the function keys that are marked in blue, you should press the Fn key and a
particular special function key that you want to enable or activate. When the Fn key is not pressed, the special function keys act like normal character keys.
The options stating Ctrl key, Shift key, and Alt key are incorrect because the Fn key is used to activate the special function keys.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot common mobile device issues while adhering to the appropriate procedures.
References:
Fn key, http://www.answers.com/topic/fn-key-1
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.5 Given a scenario, troubleshoot common
mobile device issues while adhering to the appropriate procedures
Question #19 of 60
Question ID: 1171571
Jacob is new to your department and must be taught how to remove and install RAM into laptops. Which steps would you recommend he do BEFORE he performs this task?
A) Turn off the laptop. Remove the cover for the RAM port. Replace the RAM. Replace the port cover.
B) Turn off the laptop. Remove and set aside all screws. Replace the RAM. Replace the screws.
C) Turn off the laptop and remove all power sources, including the battery and power cords. Put on an antistatic wristband. Remove
the cover for the RAM port. Replace the RAM. Replace the port cover.
D) Turn off the laptop and remove all power sources, including the battery and power cord. Put on an antistatic wristband. Diagram the
placement of screws, then remove and set aside all screws. Replace the RAM. Replace the screws. Replace the power sources.
Explanation
You should instruct Jacob to take the following steps:
1. Turn off the laptop and remove all power sources, including the battery and power cord.
2. Put on an antistatic wristband.
3. Diagram the placement of screws, then remove and set aside all screws.
4. Replace the RAM.
5. Replace the screws.
6. Replace the power sources.
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 19 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
When instructing beginners on how to install fragile parts like RAM or CPUs in any electronic device, you must make sure that you educate them about electrostatic discharge
(ESD). ESD is the amount of static electricity in a person's body. There is enough ESD in a person's body to damage a small stick of RAM or a CPU, so users should always
wear proper safety devices when installing.
There is no specialized RAM port with a cover to be removed before replacing the RAM in a laptop. You must remove screws to reach the RAM. When removing screws, be
sure to diagram their placement or number them for correct reassembly.
You must remove all power sources before replacing components within a laptop.
Objective:
Mobile Devices
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure laptop hardware and components.
References:
How to Upgrade the RAM (Memory) on a Laptop, http://www.laptopmag.com/articles/ram-upgrade-tutorial
Question #20 of 60
Question ID: 1192017
You are the network administrator for Nutex Corporation. You have configured a wireless network for a group of users to provide Internet access. However, users complain that
they are facing intermittent loss of wireless connection. You have verified the hardware and software configuration of both your Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL)
modem and wireless router and your DSL line from the Internet Service Provider (ISP). What could be causing your problems?
A) Cordless phones
B) Wireless router
C) DSL filters
D) Television set
Explanation
Cordless phones and other type of physical obstructions can cause intermittent loss in wireless connectivity. Wireless devices use 2.4 GHz range, which is also used by
devices such as cordless phones and microwaves. These devices can interfere with wireless devices. For example, if you are experiencing wireless connectivity problems
every day around noon, a microwave being used to heat lunches could be causing the problem. You can reduce the radio frequency interference (RFI) by relocating the
interfering devices. You could also reduce the range of the wireless network. Different wireless frequencies experience different RFI problems. You should always research the
frequency that you plan to deploy to determine which devices will cause you problems.
DSL filters cannot cause interference in wireless networks.
The wireless router is not the problem. As mentioned in the scenario, you have already verified the hardware and software configuration of the wireless router. You do not need
to test it again.
A television set does not cause any problem in wireless communication. Only the devices that use wireless range that are on your networks can cause interference in wireless
connectivity.
You should also keep in mind that most wireless access points have a maximum range. If you are outside that range, you will not receive a signal. Transmission ranges can be
adjusted.
For the A+ exam, you must understand how to troubleshoot the following wired and wireless network symptoms:
No connectivity – When there is no network connectivity, it is usually either the computer's hardware or the network hardware. Check the network cabling, the network
adapter, and the configuration of the network adapter. For a wireless network, check the wireless card and its configuration.
APIPA/link-local address – An Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) address is used when a computer cannot communicate with a DHCP server. If a computer has
been issued an APIPA address, the computer will be unable to communicate with computers that have been issued addresses by the DHCP server. In this situation, check
to make sure that the DHCP server is functional and that the DHCP server has enough IP addresses for its clients' needs. Make sure that all routers function as DHCP
relay agents. Finally, ensure that the computer's hardware is functional and allows it to connect to the network. A link-local address is IPv6's version of APIPA. As with
APIPA, a link-local address will only allow the client computer to connect to computers and other devices on the same subnet.
Limited connectivity – In this situation, a computer can connect to the network but cannot access a specific resource on the network. The problem could be because the
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 20 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
user does not have permission to access the resource. If you can ping the resource but cannot access the resource by its host name, the DNS server could be down. The
problem could lie with the remote resource. See if other computers can connect to it.
Local connectivity – This problem arises when a computer can connect to local resources but not to resources outside the local subnet. This is usually due to an incorrect
subnet mask, an incorrect default gateway address, or a router problem. Check the TCP/IP settings for the computer's NIC. Check the connectivity to the router.
Intermittent connectivity – This problem can be hardware or software related. Check the network cable and the NIC and its settings. Ensure that the DHCP and DNS
servers are fully functional. If using wireless, check for radio frequency interference (RFI).
IP conflict – An IP address can be used by a single network host. If an IP address is duplicated on the network, one or possibly both the computers will not be able to
communicate on the network. This problem most often occurs in situations where static IP addresses are used. You need to locate one of the computers involved in the
conflict situation and change its IP address. If the computers are both using dynamic addressing, you can use the ipconfig /release command on one of the computers.
Slow transfer speeds – This is usually caused by interference, incorrect cabling, a malfunctioning NIC, router misconfiguration, or switch misconfiguration. If only one client
is experiencing the problem, check that computer's cabling and NIC. You only need to check for interference, router misconfiguration, or switch misconfiguration if more
than one client is experiencing this problem.
Low RF signal – This wireless issue occurs because radio transmissions have a limited maximum distance. This will require either moving the wireless router and wireless
client so that they are closer together or increasing the signal strength. In many cases, objects can cause obstruction or interference. Performing a site survey can help you
determine these issues.
SSID not found – If a computer cannot find a Set Service Identifier (SSID), which is the identifier for a wireless network, then it is usually either due to the wireless access
point being turned off or the SSID being changed. Try rebooting the wireless access point. Also, check the wireless access point to ensure that it is using the same SSID.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot common wired and wireless network problems.
References:
Six Things That Block Your Wi-Fi, and How to Fix Them, http://www.pcworld.com/article/227973/six_things_that_block_your_wifi_and_how_to_fix_them.html
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.7 Given a scenario, troubleshoot common
wired and wireless network problems
Question #21 of 60
Question ID: 1191984
You are the system administrator for your company. You are troubleshooting a network computer that displayed the following error message:
“Boot Error Press F1 to Retry”
What should you do to fix the problem?
A) Boot the computer to the Last Known Good Configuration.
B) Restore the master boot sector.
C) Run Registry Checker.
D) Run System Restore.
Explanation
You should restore the master boot sector. The error message is displayed when the physical hard drive is not detected in the system, or when the boot sector or master boot
record (MBR) is damaged or missing on the hard drive. You can attempt to re-create MBR in the hard drive or replace the hard drive, if necessary. You should not run System
Restore to fix the problem. You can run System Restore only when the system boots to Windows. System Restore is used to restore the system to an earlier state or can also
be used to back up registry in the computer.
You should not run Registry Checker to fix the problem. Registry Checker is run to fix registry related problems and perform backups of the system registry.
You should not boot the computer to Last Known Good Configuration to fix the problem. You can boot the computer to Last Known Good Configuration when the recently
installed program or device drive has caused the system to boot to Windows.
For the A+ exam, you need to be familiar with the following hard drive symptoms and how to fix them:
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 21 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Read/write failure – This is usually caused by damaged sectors on the hard drive or by hard drive failure. Run the chkdsk command to scan the drive for damaged sectors.
If the hard drive has completely failed, you will need to replace the drive and restore the data from backup.
Slow performance – This can be caused by memory or hard drive. If you do not have enough memory, there will be excessive paging. In this case, add more memory. If
you think the hard drive itself is causing the performance issue, check the hard drive to see if it has sufficient free space. If it does not, you need to add more hard drives to
your computer. If it has sufficient free space, the performance issue could be caused by fragmented files. Run the defrag utility to defragment the hard drive and increase
hard drive performance.
Loud clicking noise – This often occurs right before the hard drive dies. Because loud noises can also be caused by other components, you first need to confirm that the
noise is coming from the hard drive. If you have confirmed this, completing a backup of your data should be your first priority. Then replace the hard drive and restore the
data from the backup.
Failure to boot – This problem can be caused by many different issues. If the system cannot locate the boot files, it cannot boot. If you suspect this is the problem, you
should ensure that your BIOS is set to boot from the drive where the boot files reside. Also, it may be necessary to check the BOOT.INI file to ensure that the partition
information is entered correctly. Finally, you may have to repair corrupted boot files. You should use the Recovery Console to repair corrupt system files. Finally, check to
make sure that the connections to your hard drive are still intact. If you receive any Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.) errors, research the
specific error you receive to find out what you need to do.
Drive not recognized – This usually involves either an incorrect master/slave setting or the inability of the BIOS or operating system to recognize the drive. Check to make
sure that the master/slave jumpers are configured appropriately. Check the BIOS to make sure that the disk parameters are configured appropriately. Finally, you made
need to install the appropriate drivers for the operating system. This may require that you obtain the third-party drivers from the hard drive vendor. In legacy systems that
do not support drives higher than 504 MB, you may need to implement logical bus addressing (LBA).
OS not found – This usually is a software issue where the boot sector cannot be located. Reboot the computer into the Recovery Console and repair the operating system.
RAID not found – If hardware RAID is implemented in the computer, the problem is usually with the RAID controller. Check the controller and replace as necessary. If
software RAID is implemented, make sure that the BIOS is set to RAID. You should also check all RAID connections. Finally, test the individual RAID drives. If one of the
drives has failed, replace it and restore the data.
RAID stops working – This is usually caused by the failure of a single hard drive in the RAID array. You need to determine which hard drive has failed and replace it. If the
failed drive is in a RAID-1 or RAID-5 array, the array will continue to operate, but performance will be degraded until the failed hard drive is replaced. Use the RAID setup
program to set the RAID configuration back up.
Proprietary crash screens (BSOD/pin wheel) – If a BSOD occurs after you install a new hard drive or new drivers, you should immediately suspect the hard drive as the
cause. Remove the hard drive or roll back its driver to troubleshoot the BSOD. If the BSOD no longer occurs, you should then research the change you made to discover if
there is a known issue with the hard drive or driver. Make sure that you only remove one hard drive or roll back one driver at a time to help determine the true cause of the
BSOD. Pinwheel errors are Apple computers equivalent to BSOD. Pinwheel errors occur when users see the spinning rainbow pinwheel. Causes include bugs in
applications, event processing issues, and virtual memory issues.
S.M.A.R.T. errors – Self Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.) performs a quick analysis of the hard drive for problems during system boot up. It
reports on such hard drive parameters as read error rate, throughput performance, and seek error rate. The main purpose of using S.M.A.R.T. is to ensure that you receive
warnings prior to a complete drive failure so that the drive can be replaced before complete failure.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot hard drives and RAID arrays.
References:
"Missing Operating System" and "No ROM BASIC" Error Messages, http://support.microsoft.com/kb/80304
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.3 Given a scenario, troubleshoot hard
drives and RAID arrays
Question #22 of 60
Question ID: 1171729
A user has recently reported to you that it appears as if a laser printer used by his department is becoming overheated. When you investigate, you do not find any overheating
issues. You suspect that the problem was with the fuser within the laser printer overheating. Which laser printer component protects a fuser from overheating?
A) A transfer corona
B) A controller
C) A primary corona
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 22 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
D) A thermal fuse
Explanation
Thermal fuses keep fusers from overheating. A thermal fuse is designed to open when it is heated to a particular temperature, much the same way that an ordinary fuse is
designed to open when a particular amount of current is passed through it. Thermal fuses can be one-time-use devices; when the fuse opens, or blows, it must be replaced.
Alternatively, a thermister can be used for temperature protection. When a thermister reaches a certain temperature, it will open the fuser circuit and cut power to the heater.
Fusers, which use heat and pressure to cause toner to melt or fuse to the printed media, are subjected to high temperatures during normal operation. If a fuser's temperature
reaches a threshold value, then the thermal fuse will blow, thus shutting down printer operations to protect the fuser from overheating. A fuser can also be referred to as a
fuser assembly.
The laser printer controller is the internal circuit board that controls laser printer operation.
The primary corona places a uniform negative electric charge on a printer's photosensitive drum. When the image is being written, the negative charge is reduced wherever the
laser beam strikes. Toner is attracted to the drum wherever the charge has been reduced.
The transfer corona creates a positive charge on the surface of the print media, which attracts the toner from the drum to the paper. The fuser then melts the toner onto the
paper.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and maintain various print technologies.
References:
Learn the basics of laser printing, http://www.techrepublic.com/article/learn-the-basics-of-laser-printing/
The inner workings of laser printers and how to troubleshoot them, http://www.techrepublic.com/article/the-inner-workings-of-laser-printers-and-how-to-troubleshoot-thempart-1/
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 3: Hardware, 3.11 Given a scenario, install and maintain various print technologies
Question #23 of 60
Question ID: 1191930
You need to implement a RAID level that duplicates a partition on another physical disk, providing two identical copies of the data. Which RAID level should you use?
A) Level 0
B) Level 4
C) Level 1
D) Level 3
E) Level 5
F) Level 2
Explanation
RAID Level 1, also known as disk mirroring, duplicates the original disk, and this duplicate is placed on a separate disk, creating a "mirror." Disk mirroring requires two disks of
equal size. It is simple to implement and offers fast recovery if a single disk fails. However, because disk mirroring requires the duplication of the initial partition, only 50% of
the total available disk space is used. RAID Level 1 is less efficient when performing disk writes.
Disk duplexing is also implemented at RAID Level 1. Disk duplexing builds on disk mirroring by adding a controller for each disk channel. Disk duplexing eliminates the disk
controller as a single point of failure in the system.
RAID Level 0 is disk striping. A RAID-0 volume consists of two hard drives where data is striped across the entire volume. This RAID level provides no fault tolerance and fast
data-writing speeds.
RAID Level 2 is disk striping with hamming parity. It requires at least three disks. Data is striped across the disks, and hamming parity information is calculated and stored on
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 23 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
the parity disk. This RAID level is not popular.
RAID Level 3 is a striped set with dedicated parity. It requires at least three disks. One disk in the volume is a dedicated parity disk. Data is striped across the remaining disks.
RAID Level 4 is similar to RAID Level 3. However, RAID Level 4 does block-level striping instead of byte-level striping.
RAID Level 5 is disk striping with parity. It requires at least three disks. This level provides fault tolerance. All of the disks in the volume appear as one disk to the end user, and
parity information is spread across all the disks.
There is also a special type of RAID called RAID1+0 or RAID 10. This RAID level is mirrored stipe sets. A minimum of four drives is required for this RAID level.
A serial ATA (SATA) or Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) adapter is required to use RAID volumes. The RAID level implemented refers to how data is distributed between
multiple drives.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, select, install and configure storage devices.
References:
RAID, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RAID
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 3: Hardware, 3.4 Given a scenario, select, install and configure storage devices,
Configurations
Question #24 of 60
Question ID: 1171672
You are teaching a class on computer hardware to new IT technicians. You are discussing the component on an Advanced Technology eXtended (ATX) motherboard that
supports communication between the central processing unit (CPU) and random access memory (RAM). Which component provides this functionality?
A) Southbridge chip
B) Northbridge chip
C) Advanced Technology Attachment (ATA) interface
D) Firmware
Explanation
The Northbridge chip (also referred to as the north bridge) supports communication between the RAM and the CPU. It also supports the Peripheral Component Interconnect
(PCI) bus, the Level2 cache, and the Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) port. It provides communication to higher speed devices than the south bridge chip.
The Southbridge chip (also referred to as the south bridge) supports slower devices, such as expansion slots, Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) drives, Parallel ATA drives, and
USB ports. It handles all input/output (I/O) functions.
The ATA interface is used to connect storage devices to the motherboard, such as CD-ROM drives and hard disks.
Firmware is a software program that stores a set of programming instructions in read-only memory to control the desired device functionality.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure motherboards, CPUs, and add-on cards.
References:
What is Northbridge?, http://searchcio-midmarket.techtarget.com/sDefinition/0,,sid183_gci750600,00.html
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 24 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Question #25 of 60
Question ID: 1171597
What is the maximum data transmission speed for Bluetooth technology?
A) 100 Mbps
B) 54 Mbps
C) 3 Mbps
D) 11 Mbps
Explanation
The maximum data transmission speed for Bluetooth is 3 Mbps. Bluetooth is used for short-range wireless connections. For example, Bluetooth will be used to connect
wireless devices, such as the keyboard and mouse, to the computer.
Bluetooth does not operate on 11 Mbps. The 802.11b wireless standard operates up to a maximum of 11 Mbps. The 802.11b standard's indoor range is 100 feet at 11 Mbps
and 300 feet at 1 Mbps.
Bluetooth does not operate on 54 Mbps. The 802.11g wireless standard operates up to a maximum of 54 Mbps. 802.11g is used for long-distance wireless connections and
provides high data transfer speed. 802.11g is compatible with both 802.11a and 802.11b.
Bluetooth does not operate on 100 Mbps. The 802.3u Ethernet standard operates at 100 Mbps. 802.3u uses Cat 5 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable. 802.3u provides a
physical communication mechanism in a network. All of the 802.11 standards are considered to be radio frequency (RF) standards.
For the A+ exam, you need to understand the following 802.11 specifications:
Specification
Frequency
Speed
802.11a
5 GHz
up to 54 Mbps
802.11b
2.4 GHz
up to 11 Mbps
802.11g
2.4 GHz
up to 11 Mbps
802.11n
either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz
up to 600 Mbps
802.11ac
5 GHz
up to 1,300 Mbps with multiple access points
802.11g devices are backwards compatible with 802.11b devices.
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a low-power communications protocol for short ranges between two devices. One device will typically create radio-wave fields that can
target, detect, and access small amounts of data to be transferred. It is similar to RFID but slower, especially when compared to Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
Objective:
Networking
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast wireless networking protocols.
References:
Bluetooth Basics, http://www.bluetooth.com/Pages/Basics.aspx
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 2: Networking, 2.4 Compare and contrast wireless networking protocols
Question #26 of 60
Question ID: 1171696
During a class, the instructor discusses technology that allows a single processor to handle two independent sets of instructions at the same time. Which technology provides
this functionality?
A) CPU throttle technology
B) Dual independent bus (DIB)
C) Dual-core technology
D) Hyper-Threading (HT) technology
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 25 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Explanation
Hyper-threading (HT) technology allows a single processor to handle two independent sets of instructions at the same time. HT technology converts a single physical
processor into two virtual processors. CPU throttle technology does not allow a single processor to handle two independent sets of instructions at the same time. CPU
throttling is a feature that protects a CPU from heat damage.
When a CPU is not cooled properly and the temperature of the CPU becomes very high, the CPU throttle technology slows down the clock rate on the CPU to prevent further
overheating and damage. When the clock rate of a CPU is reduced, it requires very little power to operate, and thus the heat generation is also reduced. The CPU throttling
technology also causes the system to operate at a lower speed. For example, if the actual speed of the CPU is 1 GHz, after throttling down the clock rate, the CPU might
show only 500 MHz.
Dual-core technology does not allow a single processor to handle two independent sets of instructions at the same time. A dual-core processor contains two processor cores
in a single processor package. The dual-core technology is different from HT technology because HT technology only simulates two processors in a single physical unit,
whereas dual-core processor actually contains two processor cores in a single processor package.
The dual independent bus (DIB) architecture was created to improve processor bus bandwidth and performance. DIBs enable the processor to access data from either of its
buses simultaneously and in parallel, rather than in a singular sequential manner. The DIB architecture does not allow a single processor to handle two independent sets of
instructions at the same time.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure motherboards, CPUs, and add-on cards.
References:
What is Hyper-Threading?, http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/Hyper-threading-technology-explained/
Upgrading And Repairing PCs 21st Edition: Processor Features, http://www.tomshardware.com/reviews/processors-cpu-apu-features-upgrade,3569-10.html
Question #27 of 60
Question ID: 1175642
Your organization has decided to use SSL over port 465 on the SMTP server, smtp.dreamsuites.com. You need to change the settings on your iPhone. What should you do?
A) Edit the Incoming Mail Server settings so that the server uses SSL.
B) Edit the Outgoing Mail Server settings so that the server uses SSL.
C) Edit the Incoming Mail Server settings so that the server uses SSL, and change the port to port 465.
D) Edit the Outgoing Mail Server settings so that the server uses SSL, and change the port to port 465.
Explanation
You should edit the Outgoing Mail Server settings so that the server uses SSL and change the port to 465.
You should not edit ONLY the Outgoing Mail Server settings so that the server uses SSL. By default, the Outgoing Mail Server uses port 587. You need to change the port to
465.
You should not edit the Incoming Mail Server settings because the SMTP server is the outgoing mail server, not the incoming mail server.
Objective:
Mobile Devices
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, configure basic mobile device network connectivity and application support.
References:
Setup iPhone Email, http://www.iphoneemailsettings.com/
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 26 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Setup Android Email, http://www.androidemailsettings.com/
Question #28 of 60
Question ID: 1192019
You are a desktop administrator for Nutex Corporation. A user reports that he is unable to access network resources. You notice a break in the network cable. You need to
create a new network cable to connect the computer to the RJ-45 jack in the wall. What should you use to connect the end of the cable to an RJ-45 connector?
A) Wire crimper
B) Optical tester
C) Time-domain reflectometer
D) Pliers
Explanation
A wire crimper should be used to connect the end of an Ethernet cable to an RJ-45 cable. A time-domain reflectometer is used to find the point of breakage in cables, such as
Ethernet or copper cables. You can also use digital multimeter to test for breakage in copper cables. An optical tester is a tool used to measure the light signal energy emitted
from an optical cable. You cannot use pliers to connect the end of a cable to an RJ-45 connector. Needle-nose pliers can be useful if you need to remove a loose screw from
inside a computer case.
Another helpful tool is a plastic shim or wedge, which will help you open the plastic case of an LCD screen in a laptop.
Plastic screwdrivers are the best choice when working with computer equipment. Plastic screwdrivers will not conduct electricity. In addition, you may also need an extension
magnet to retrieve dropped screws.
For the A+ exam, you need to understand the following network tools:
Cable tester – Verifies that the cable is functioning properly. Multimeters can also perform this function. A cable tester, though, is more specialized and can tell you what
exactly is wrong with the cable.
Loopback plug – Plugs into the network port and verifies that the network port is functioning properly
Punch-down tool – Secures cable to patch panel
Toner generator and probe – Locates the correct cable coming into a patch panel. These are two-piece units that are referred to as a Fox and Hound.
Wire strippers – Prepares the end of the cable for a connector
Crimper – Attaches a connector to the cable
Wireless locator – Locates wireless networks in your vicinity. Many of them will also display the signal level and the SSID of the wireless networks. Finally, some will even
display more detailed information like channel used, location of the wireless network, and a map of the wireless network showing connected devices.
For the A+ exam, you need to understand the following command-line tools:
Ping – Uses ICMP to test connectivity between two devices
Ipconfig/ifconfig – Displays the TCP/IP configuration of a device. You should be familiar with its switches, including the /all, /release, /registerdns, /renew, and /flushdns
switches. The ifconfig is the Unix/Linux equivalent of ipconfig.
Tracert – Traces the path a packet traverses through a network. It displays the name and IP address of every single device through which the packet passes.
Netstat – Displays what ports are listening on a TCP/IP device
Nbtstat – Displays NetBIOS information
Net – A powerful Windows command. The net use subcommand allows you to view what is currently shared. Research the various ways you can use the net command.
Netdom – Joins a computer to a Windows domain, manages computer accounts on a Windows domain, and establishes trust relationships between Windows domains. It
is available by default with Windows 8 and later.
Nslookup – Queries the Domain Name System (DNS) to obtain domain name or IP address mapping or for any other specific DNS record.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot common wired and wireless network problems.
References:
Crimping tool, https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/c/crimp.htm
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 27 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.7 Given a scenario, troubleshoot common
wired and wireless network problems
Question #29 of 60
Question ID: 1171589
Your company has a wireless network for its small office network. The wireless network does not broadcast its service set identifier (SSID). You configure a user's Windows
Vista computer to connect to the wireless network by manually setting the SSID. You need to ensure that the user's computer does not send probe requests to discover if the
wireless network is in range. What should you do?
A) Ensure the Connect automatically when this network is in range option on the Connections tab of the wireless connection is cleared.
B) Ensure the Connect even if the network is not broadcasting option on the Connections tab of the wireless connection is selected.
C) Ensure the Connect even if the network is not broadcasting option on the Connections tab of the wireless connection is cleared.
D) Ensure the Connect automatically when this network is in range option on the Connections tab of the wireless connection is selected.
Explanation
You should ensure the Connect even if the network is not broadcasting option on the Connections tab of the wireless connection is cleared. If this option is enabled, probe
requests are sent to discover if a nonbroadcast network is in range.
You should not change the configuration of the Connect automatically when this network is in range option. This option ensures that the connection is reestablished when the
wireless network is detected.
When you disable automatic configuration of an SSID, the SSID is not automatically transmitted to all computers within the wireless network range. This provides a low level of
security. The only way to connect to the wireless network is to enter the SSID manually.
Objective:
Networking
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure a basic wired/wireless SOHO network.
References:
How to connect to a hidden Wi-Fi network in Windows 10, https://windowsreport.com/connect-hidden-wi-fi-network-windows-10/
Question #30 of 60
Question ID: 1171691
After performing several upgrades on a computer, the user reports that he is having trouble with an overheating problem. You want to make recommendations to help prevent
the computer from overheating during use. What should you recommend?
A) Apply a higher voltage to the cooling fans.
B) Use an installed video card rather than a built-in video chip on the system board.
C) Keep the computer cover closed and secured.
D) Use a blank-screen screen saver.
Explanation
Keeping the computer cover closed and secured helps prevent a computer from overheating because the closed case maintains the desired airflow cooling circulation pattern
through the computer. The computer case, or enclosure, is the box that contains the components of a computer. The case provides a chassis to which components are
attached, an electrical ground through the power supply's power cable, and a cover that isolates the inside components from the outside world.
Heat is produced by all devices and components that use electricity, and nondissipated heat often leads to either temporary or permanent component failure. To dissipate the
heat, computers are equipped with one or more cooling fans. The fans provide a convection current of air through vents in the case. Typically, cool air enters the front of the
case, flows across the system board and expansion cards and through the power supply, and then is discharged out the rear of the case. The power supply fan provides the
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 28 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
motive force for this process, and sometimes an additional intake fan is provided at the inlet vent.
In a well-designed system, the air stream establishes a circulation pattern that provides optimal cooling. A computer should also have slot covers in place for unused
expansion slots. Heat production can be decreased by enabling reduced power modes when the computer is idle for extended periods, and heat dissipation can be increased
by adding additional fans within the case.
The use of a screen saver will affect only the monitor and not the computer itself. The voltage applied to cooling fans is not a user-adjustable variable. Every added device will
increase the amount of heat generated within the case, so installing and using a video card will not help prevent overheating.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure motherboards, CPUs, and add-on cards.
References:
Get IT Done: Strategies for keeping systems cool during summer heat, http://www.techrepublic.com/article/get-it-done-strategies-for-keeping-systems-cool-during-summerheat/
Question #31 of 60
Question ID: 1191968
You have begun the process of replacing the CPU in your computer by physically installing the CPU. You must ensure that the motherboard recognizes the new CPU. What
should you do first?
A) Contact the motherboard vendor to inquire about compatibility.
B) Access the motherboard vendor's website to find out if the CPU is compatible with the motherboard.
C) Update the driver.
D) Update the firmware.
Explanation
You should update the motherboard's firmware to ensure that the motherboard recognizes the new CPU.
You should not update the driver until after you have ensured that the motherboard recognizes the new CPU and the computer has booted in the operating system.
You should not access the motherboard vendor's website to find out if the CPU is compatible with the motherboard. You should perform this step prior to physically installing
the CPU.
You should not contact the motherboard vendor to inquire about compatibility. You should first check the motherboard's documentation or the vendor's website. If you cannot
find the information you need at those places, you could directly contact the motherboard vendor. This should be completed before physically installing the new CPU.
The A+ exam lists the following specific symptoms that an A+ technician must understand:
Unexpected shutdowns – Random shutdowns that are not accompanied with a particular error message are usually the result of overheating. Make sure that all fans are
working effectively. You may also want to deploy additional cooling options. Make sure that all open ports in the computer have a cover. If an unexpected shutdown is
accompanied by a blue screen of death (BSOD), please refer to the BSOD section below.
System lockups – System lockups occur when the system mysteriously stops functioning and no error or BSOD is displayed. Examine the system log files to troubleshoot
the issue. Usually system lockups are due to memory issues, viruses, malware, or video issues.
POST beep codes – When a system boots, the power-on self-test (POST) will check the devices for functionality. If a device fails during the POST, a series of beep codes
will sound to indicate the problem. The codes that are used vary based on the manufacturer of the BIOS. An A+ technician should be familiar with the beep codes of the
major BIOS manufacturers or know how to locate the beep codes. Keep in mind that one short beep means that the system is operational.
Blank screen on bootup – For this issue, always test the obvious. Usually a blank screen is a video device problem. Make sure the monitor is plugged in to the wall socket,
plugged in to the computer, and turned. It may also be necessary to test the wall outlet. You may also need to verify that the computer is plugged in to the wall socket and
turned on. Finally, you may want to replace the video card with a known good video card. If you hear the system fan but the computer is not making the POST beep
sound, you may have a failed motherboard.
BIOS times and settings reset – If you encounter this issue, the problem is with the CMOS battery. Replace the CMOS battery and make sure to reset your BIOS settings.
Attempts to boot to incorrect device – This issue is usually related to the BIOS boot order. It was more common when floppy drives were listed as the first boot device. If a
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 29 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
non-bootable floppy were left in the floppy drive at boot time, the computer would display a non-system disk or disk error at startup. Once the floppy disk was removed
from the drive, the computer would boot. Today, a CD-ROM or DVD drive is often listed as the first boot device. You can change the boot order in the BIOS. This issue can
also result from missing or corrupt boot files. If you suspect that this error is due to boot files being missing or corrupt, you should enable boot logging from the Windows
Advanced Menu and replace the missing or corrupt boot files using the Windows installation DVD.
Continuous reboots – Reboots are usually the result of electrical issues, power supply issues, or overheating. Brownouts or blackouts cause computers to reboot.
Attaching a computer to an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) will ensure that you can safely shut down the computer if these occur. If the power supply in the computer
is the issue, you should replace it with one that supplies adequate power to the computer. Finally, if overheating is causing the reboots, you should check all fans and
ensure that the CPU heat sink is still attached. You may need to replace these or add another cooling device to your computer.
No power – Once again, check the obvious. Make sure that the computer is plugged in and that the wall outlet is supplying power. If a UPS or surge protector is used,
check to see if its breaker was tripped by a power surge. Finally, check the computer's power supply by replacing with known good unit.
Overheating – This is usually the result of cooling fan or cooling system failures. Make sure that all open slots are covered. In addition, ensure that all system fans are
functional.
Loud noise – Loud noise is usually caused by system fans, the power supply, or the hard drives because very few internal devices have moving parts. Check those three
devices to trace the noise. Replace the part that is making the noise because the noise usually means that the device is close to failure.
Intermittent device failure – First, make sure that you have the latest driver for the device. If the problem persists, you should replace the device. If intermittent failures are
occurring with different devices, you could have a motherboard that needs replacing.
Fans spin, no power to other devices – If no beep codes are heard, you probably have motherboard failure. If you hear beep codes, record the code that is heard and
research that code to find the problem device. This problem could also mean that the power supply was not properly plugged into the motherboard.
Indicator lights – Many components in a computer have indicator lights. In most cases, indicator lights will blink when activity is occurring and will be steady green when
idle. However, some devices will have other lights and/or colors. Always consult the vendor documentation. If problems continue, you should replace the device.
Smoke – This is a horrible problem to have but is usually easy to trace. Shut down the computer immediately and locate the device that is producing the smoke. Replace
that device.
Burning smell – This problem usually accompanies smoke. As with smoke, you should shut down the computer immediately and locate the device that is producing the
smoke. Replace that device.
Proprietary crash screens (BSOD/pin wheel) – Windows Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) errors are usually the result of hardware issues. You should always replace hardware
one device at a time, following by a system boot. If the new hardware did not fix the issue, then that component is not the issue. Replace the component with the original
and try replacing another component. Some of the more common BSOD errors are listed below:
Data_Bus_Error – Faulty hardware has been installed or existing hardware has failed. Usually this error is related to RAM, cache, or video RAM.
Unexpected_Kernel_Mode_Trap – Remove or replace any recently installed hardware. Run hardware diagnostics to determine which component has failed. Replace the
failed hardware. This error can also be caused if you set the CPU to run at a higher speed than the CPU supports.
Page_Fault_in-nonpaged_area – This error is caused by RAM, cache, or video RAM. Replace the failed component.
Irq1_not_less_or_equal – This issue is usually caused by a device driver, system service, virus scanner, or backup tool that is not compatible with the version of Windows
you are running. Make sure that all your drivers and software is updated to the version that is compatible with the Windows OS you are using.
Pinwheel errors occur when users see the spinning rainbow pinwheel. Causes include bugs in applications, event processing issues, and virtual memory issues.
Distended capacitors – Capacitors are included in computers on the motherboards, video cards, and power supplies. Capacitors can fail prematurely, causing the
capacitor's case to bulge or rupture. In most cases, the only way to fix this problem is to replace the card that has the swollen capacitor. It is possible to replace them, but
the process requires soldering experience. Replacing the capacitor is an electrical hazard and should only be attempted with proper trainingproper training.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot problems related to motherboards, RAM, CPUs, and power.
References:
5 More PC Upgrade Mistakes (And How To Avoid Them), https://www.pcworld.com/article/236731/more_pc_upgrade_mistakes.html
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.2 Given a scenario, troubleshoot problems
related to motherboards, RAM, CPUs, and power
Question #32 of 60
Question ID: 1175653
Of the terms below, which is the term for the cloud computing concept that allows the provider to share services with multiple subscribers, as opposed to the subscriber
having a dedicated cloud service?
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 30 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
A) community cloud
B) rapid elasticity
C) measured service
D) resource pooling
Explanation
Resource pooling is the term for the cloud computing concept that allows the provider to share services with multiple subscribers, as opposed to the subscriber having a
dedicated cloud service. The following exhibit demonstrates the difference.
Community cloud deals with a cloud-based infrastructure for several customers with common needs.
Rapid elasticity allows the provider to dynamically allocate resources based on demand. Examples include increased bandwidth, storage, or memory requirements.
Measured service is a term that applies to paying for services on a per-use basis, such as CPU time, GB of storage, or network bandwidth use. Your cell phone data plan,
measured in GB of data transferred per month, could be an example of a measured service.
For the A+ exam, you must understand the following basic cloud concepts:
SaaS - Software as a Service. Instead of installing software on their computers, users can access the software over the Internet, typically paying a subscription fee for use.
An example is Microsoft Office 365.
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 31 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
IaaS - Infrastructure as a Service. Instead of buying servers, storage, and other hardware components that make up the company's infrastructure, organizations can
subscribe to a service over the Internet. The service host maintains the infrastructure components and makes them available on a per-use or subscription basis. An
example is Amazon Web Services.
PaaS - Platform as a Service. The provider makes hardware and software available over the Internet on a per-use or subscription basis. PaaS is often used in application
development.
Public vs. Private vs. Hybrid vs. Community - Public clouds are those that are made available to (typically) anyone that can pay. Private clouds are used by a single
organization. Community clouds are for groups of subscribers that have common usage and requirements. Hybrid clouds are comprised of more than one type of cloud.
On-demand - makes the resource available whenever it is desired by the client. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is an example of an on-demand service.
Objective:
Virtualization and Cloud Computing
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast cloud computing concepts.
References:
What is Cloud Computing? A Tutorial, http://leverhawk.com/what-is-cloud-computing-tutorial-2012120519
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) definition, http://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Infrastructure-as-a-Service-IaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS) definition, http://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Platform-as-a-Service-PaaS
Question #33 of 60
Question ID: 1171800
After troubleshooting a laptop computer issue, you discover that that the motherboard is faulty. The computer is under warranty, and the manufacturer ships you a
replacement motherboard that is the same model as the defective one. You need to replace the laptop's motherboard. All of the following are guidelines when replacing the
motherboard EXCEPT
A) remove the laptop's keyboard, and disconnect it from the motherboard
B) remove the RAM and hard drive from under the laptop's keyboard
C) remove the fan and heatsink from the processor, and then remove the processor
D) remove any peripheral cards that are directly plugged into the motherboard
Explanation
You should not remove the RAM and hard drive from under the laptop's keyboard. In most laptop computers, the RAM and hard drive must be removed from the bottom of the
laptop. The guidelines for replacing a laptop motherboard are as follows:
1. Power the laptop off and flip it over.
2. Remove the battery and all screws from the bottom of the laptop.
3. Remove the covers from the bottom of the laptop that cover the RAM and hard drive
4. Remove the RAM from its slots.
5. Slide the hard drive out of the laptop and disconnect any cables.
6. Remove the CD-ROM or DVD drive and disconnect any cables.
7. Turn the laptop right side up and open the lid.
8. Remove the plastic bezel that is above the keyboard.
9. Remove the keyboard and disconnect any cables.
10. Remove the fan and heatsink from the processor and disconnect any cables.
11. Determine if a separate graphics adapter is used in the computer. If so, disconnect it from the motherboard and remove the adapter card.
12. Remove any other peripheral devices that may interfere with the motherboard replacement. (On most current computers, the wireless adapter will need to be removed.)
13. Remove the screws from the motherboard. Label each screw as it is removed and place the screw on a piece of tape to ensure it is not lost.
14. Remove the faulty motherboard and replace it with the new motherboard.
15. Replace, in order, all the other parts that you have removed, ensuring that all cables are reconnected.
When replacing a motherboard, the most common issue is that a cable is not reconnected properly or that an adapter card or RAM module is not firmly seated. If a cable is
not reconnected properly, one of the laptop's ports may be non-operational.
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 32 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot common mobile device issues while adhering to the appropriate procedures.
References:
A Guide to Laptop Motherboard Repair, https://www.thewindowsclub.com/complete-guide-laptop-motherboard-repair
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.5 Given a scenario, troubleshoot common
mobile device issues while adhering to the appropriate procedures
Question #34 of 60
Question ID: 1171808
Your laser printer produces accurate images that smear easily. Which printer component should you examine?
A) The transfer corona
B) The photosensitive drum
C) The feed roller
D) The fuser
Explanation
A laser printer's fuser contains two rollers that use heat and pressure to fuse an image onto paper. If the fuser subsystem fails to heat properly or supply sufficient pressure,
the toner merely rests on the surface of the paper and can be easily smeared. Toner is a powdery ink consisting of pigment, such as carbon black or iron, bound in a polymeric
or waxy matrix. The transfer corona places the toner from the drum onto the paper through an electrostatic attraction process. If the fuser roller does not heat up, then you
should look for a blown fuse. Another common problem with the fuser assembly is a pressure roller contaminated with toner. A contaminated pressure roller will cause black
specks to appear on the back of a printout. Cleaning the fuser rollers with a soft cloth and alcohol can occasionally resolve this problem; the cleaning should be performed
after the rollers are allowed to cool briefly.
Defective feed rollers can cause multiple sheets of paper to be fed simultaneously, sometimes resulting in a feed jam. Defective feed rollers can also cause the image to be
compressed or expanded vertically.
The transfer corona is a wire that transfers an attractive electrostatic charge to paper so that toner will transfer from the drum to the paper. Failure to keep the transfer corona
clean can result in faded printouts.
A laser printer's photosensitive drum has a cylindrical surface that is struck by laser light. The light writes a path on the drum and leaves an electrical charge wherever it strikes
the drum, eventually placing the image of an entire page on the drum. If the drum is scratched or otherwise damaged, then the image that appears on paper will not match the
page that was supposed to be printed. Running stapled paper through a laser printer can damage the drum and cause vertical lines to appear on the printout.
Smeared images can also be caused when you use an incorrect paper type.
Always keep in mind that you should check the obvious first when troubleshooting a printer. If the printer is not printing, you should make sure it is plugged in and turned on.
You should also make sure that it has paper. Most technicians can tell you stories about how they were called in for troubleshooting an issue that had a very obvious fix. Also,
keep in mind that some internal components should only be replaced by individuals who are experienced in repairing printers. These printer technicians are usually employed
by the vendor from which you purchased the printer.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot printers.
References:
The inner workings of laser printers and how to troubleshoot them, http://www.techrepublic.com/article/the-inner-workings-of-laser-printers-and-how-to-troubleshoot-thempart-1/
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 33 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.6 Given a Scenario, Troubleshoot Printers
with Appropriate Tools
Question #35 of 60
Question ID: 1191991
You are replacing an old PCI video card in your computer with a new PCI Express video card. You remove the old video card. You insert the new video card into an available
slot and reattach all the cables. However, no display is shown when the computer boots. What should you do?
A) Reboot the computer in Safe Mode.
B) Reseat the video adapter.
C) Configure the BIOS.
D) Install the video driver.
Explanation
More than likely, you did not seat the video adapter properly when you first installed it. You should first attempt to reseat the video card and reboot the computer. You should
not configure the BIOS. Nothing special needs to be done to the BIOS because the old PCI card worked.
You can only install a video driver if the computer will boot with a video display. Rebooting the computer in Safe Mode is not an option because a display is not given.
If a computer turns off during the initial boot after the replacement of a video card, the power supply may not be providing enough power for the new video card.
For the A+ exam, you need to understand how to troubleshoot the following video and display symptoms:
VGA mode – This symptom is usually caused when a video card is configured for higher resolution than the monitor supports or when an incompatible device driver is
installed. If it is a resolution issue, you will need to lower the resolution settings to one supported by the monitor. If it is a driver issue, you will need to download and install
the latest device driver for the installed video card. VGA mode is referred to as low resolution in Windows Vista and Windows 7.
No image on screen – This problem is usually caused by a dead monitor or no signal being received from the computer. First, you should try the obvious by making sure
that the monitor is plugged in to the wall outlet and turned on. Then you should make sure that the monitor is properly connected to the computer. If the problem still
exists, replace the existing monitor with a known-good monitor. If this does not fix the problem, replace the video card with a known-good video adapter.
Overheat shutdown – If the video card is overheating, the image on the display may appear garbled or flicker. It may even stop operation all together. Once it cools, the
display will work again. Often, cleaning out the inside of the computer case will remove the debris that is causing the overheating. Also, make sure that all internal fans are
operational and fully functional. If problems persists, you should replace the adapter with a known-good card. If the monitor is overheating, you will likely need to replace
the monitor because repairs to monitors should only be done by properly trained technicians.
Dead pixels – Two types of pixel issues exist: stuck pixels or dead pixels. Stuck pixels have a fixed color and never change. Dead pixels are black. While the monitor can
be repaired, only trained technicians should work on monitors. Replace the monitor with a known-good unit. If the monitor is under warranty, you should contact the
manufacturer.
Artifacts – While this visual abnormality can be caused by any hardware component in the computer that causes data corruption, it is most often caused by the video card.
Replace the video card with a known-good card.
Color patterns incorrect – If the display is fine when the computer first boots but has problems after Windows loads, the problem is probably with the display settings
configured in the operating system. If the display has color problems from the start of booting, you have a hardware problem. Test each component, including cabling,
monitor, and video, one at a time until you discover which component is causing the problem.
Dim image – This problem is usually caused by the brightness setting on the monitor. If changing the brightness setting does not fix this issue, there are different steps to
take, depending on which type of monitor you have. If you have a CRT monitor, the monitor is probably dying and should be replaced. If you have an LCD monitor, the
backlight is probably going bad. The backlight can be replaced without replacing the entire monitor.
Flickering image – For this problem, make sure that all your cables are seated properly. If that does not fix the issue, replace the cables. Finally, this problem can be
caused if the refresh rate is not compatible with the high resolution. Increase the refresh rate.
Distorted image – This is usually caused by power issues. Replace the power cable. If that does not help, plug the monitor into another outlet. If the problem persists, you
may need to contact building maintenance or electrical professionals because it could be an electrical issue in the office or building.
Distorted geometry – If the picture displayed on a monitor has a curvature to the left and right edges, you need to adjust the geometry settings built into the monitor.
Pincushion or barrel distortion is not caused by the video card.
Burn-in – This occurs when the same desktop display is left on a monitor long enough to affect the function of the individual pixels within the monitor's screen. If burn-in
occurs, you will have to either replace the monitor or have it repaired. To prevent burn-in, you should configure all computers to use a screen saver that changes, moves,
or goes completely dim.
Oversized images and icons – This is usually the result of configuring the operating system to use large images and icons. Depending on the operating system used, you
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 34 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
would need to access the display settings and change it to using normal images and icons. This can also be affected by the resolution used.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot video, projector, and display issues.
References:
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.4 Given a scenario, troubleshoot video,
projector, and display issues
Question #36 of 60
Question ID: 1191909
Which improvements does IPv6 provide over the current IP addressing scheme? (Choose two.)
A) Header fields have been made mandatory to reduce processing requirements.
B) The IP header options allow more efficient forwarding and less rigid length limits.
C) The IP address size is increased from 64 bits to 128 bits with simpler auto-configuration of addresses.
D) A new type of address is used to deliver a packet to a specific address node.
E) Some header fields have been dropped or made optional.
F) The IP address size increased from 128 bits to 156 bits with simpler auto-configuration of addresses.
Explanation
IPv6 (version 6) or IPng (next generation) offers the following improvements over IPv4:
IP address size will increase from 32 bits to 128 bits.
Some of the header fields have been dropped.
Version 6 has less rigid length limits and the ability to introduce new options.
Packets will indicate particular traffic type.
Support will be provided for data integrity and confidentiality.
The IPv6 header is 40 fixed bytes and has eight fields of information.
Objective:
Networking
Sub-Objective:
Explain common network configuration concepts.
References:
Understanding Networks and TCP/IP, http://www.samspublishing.com/articles/article.asp?p=131034&seqNum=4&rl=1
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 2: Networking, 2.6 Explain common network configuration concepts
Question #37 of 60
Question ID: 1175643
You need to configure an iPhone with iOS 12 to connect to your company's 802.11g network. You navigate to the Settings. What should you do NEXT?
A) Enable Personal Hotspot.
B) Enable Bluetooth.
C) Enable Wi-Fi.
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 35 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
D) Enable Airplane Mode.
Explanation
You should enable WiFi. WiFi networks include 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n.
Airplane Mode should not be enabled. This actually turns all signals, including cell tower signals, WiFi signals, and Bluetooth signals.
Personal Hotspot actually makes your iPhone a WiFi hotspot. Enabling it allows other devices to use your iPhone as a wireless hotspot.
Bluetooth should not be enabled. Bluetooth should be enabled if you want to connect other devices to your iPhone.
Objective:
Mobile Devices
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, configure basic mobile device network connectivity and application support.
References:
How to Enable WiFi on Your iPhone and iPad, https://www.imore.com/how-enable-wi-fi-your-iphone-and-ipad
Question #38 of 60
Question ID: 1171644
You are adding a new computer to an existing 1000BaseT network. Which cable connector is used in this network?
A) MTRJ
B) RJ-45
C) ST
D) SC
Explanation
The RJ-45 cable connector is used in a gigabit Ethernet or 1000BaseT network. The RJ-45 connector is used with unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) copper wire cabling and can
be used to carry data at up to 1,000 Mbps, which is 1 gigabit per second (Gbps).
The SC, ST, and MTRJ connectors are used with fiber optic cabling. For instance, these cable connectors can be used in a 100BaseFX network.
An RJ-11 connector is used to connect telephone cable to a computer modem. While an RJ-11 connector looks similar to an RJ-45 connector, the RJ-11 connector is
narrower than an RJ-45 connector because it uses fewer wires.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Identify common connector types.
References:
Ethernet 1000Base-T Gigabit Connector, ttps://www.allpinouts.org/index.php/Ethernet_1000Base-T_Gigabit
What is 1000Base-T?, http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/1000BASE-T
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 3: Hardware, 3.2 Identify common connector types
Question #39 of 60
Question ID: 1171666
Beverly has contacted you and stating that her computer will not boot and keeps beeping. Which components must pass a computer's power-on self-test (POST) before an
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 36 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
operating system will load? (Choose three.)
A) The video card
B) The memory
C) The central processing unit (CPU)
D) The hard disk drive
E) The network interface card (NIC)
F) The keyboard
Explanation
A computer will not load an operating system if it encounters fatal errors during the POST. A central processing unit (CPU), memory, or video card failure during the POST
routine will generate a fatal error and halt the startup process. A hard disk drive and a keyboard are both optional devices for a computer. Many server computers do not have
a keyboard for security reasons, and most basic input/output system (BIOS) routines allow the POST to bypass a keyboard error.
Although a hard disk failure will prevent the loading of an operating system from that disk, not all computers load the operating system from a hard disk. For example, many
computers can load the operating system from a floppy disk, a CD-ROM drive, or a network drive.
Failure of a network interface card (NIC) will prevent the loading of an operating system from a network location, but an operating system can still be loaded from a local
device.
The POST of a computer is designed to test the essential components of the system during power on. During the built-in diagnostics performed by the BIOS, the CPU,
memory, and video card must function properly. After the POST executes, the boot loader phase occurs. The BIOS contains a setting for the memory (RAM), hard drive, optical
drive, and CPU.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure motherboards, CPUs, and add-on cards.
References:
Computer POST/beep codes, http://www.computerhope.com/beep.htm
Question #40 of 60
Question ID: 1191976
You are a desktop engineer for DreamSuites Corporation. Irene Jones has joined DreamSuites as an HR executive in the London office. You configure a new computer for
Irene. The computer will not power up, and you have been asked to troubleshoot the problem. Which action is NOT required to troubleshoot the problem?
A) Set the power output of the wall outlet to 230 volts.
B) Check the power cords.
C) Ensure that the 115/230 voltage selector switch is set to the correct voltage.
D) Ensure that power is available.
Explanation
In this scenario, troubleshooting the problem will NOT require you to set the power output to 230 volts. The voltage selector switch on the back of the computer may be set to
115. Applying 230 volts to a system set at 115 volts will ruin the power supply. You should first ensure that the 115/230 voltage selector switch is set to 230 volts before
changing the power output to 230 volts.
While troubleshooting the problem, you must ensure that the 115/230 voltage selector switch is set to the correct voltage. The 115/230 voltage selector switch is on the back
of the computer. You must be aware of the correct voltage for your region. You must unplug the computer from the power source before changing the 115/230 voltage selector
switch position.
While troubleshooting the problem, you must ensure that the power is available. You can directly connect the monitor to the wall socket to test the power. The monitor power
led will light up if power is available. Make sure that the computer is plugged in and that the wall outlet is supplying power. If a UPS or surge protector is used, check to see if
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 37 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
its breaker was tripped by a power surge. Finally, check the computer's power supply by replacing with a known good unit.
While troubleshooting the problem, you must check the power cords. To do this, you can try unplugging and reattaching the power cord, and then power on the computer. You
can also try to change or swap the power cables if available.
The A+ exam lists the following specific symptoms that an A+ technician must understand:
Unexpected shutdowns – Random shutdowns that are not accompanied with a particular error message are usually the result of overheating. Make sure that all fans are
working effectively. You may also want to deploy additional cooling options. Make sure that all open ports in the computer have a cover. If an unexpected shutdown is
accompanied by a blue screen of death (BSOD), please refer to the BSOD section below.
System lockups – System lockups occur when the system mysteriously stops functioning and no error or BSOD is displayed. Examine the system log files to troubleshoot
the issue. Usually system lockups are due to memory issues, viruses, malware, or video issues.
POST beep codes – When a system boots, the power-on self-test (POST) will check the devices for functionality. If a device fails during the POST, a series of beep codes
will sound to indicate the problem. The codes that are used vary based on the manufacturer of the BIOS. An A+ technician should be familiar with the beep codes of the
major BIOS manufacturers or know how to locate the beep codes. Keep in mind that one short beep means that the system is operational.
Blank screen on bootup – For this issue, always test the obvious. Usually a blank screen is a video device problem. Make sure the monitor is plugged in to the wall socket,
plugged in to the computer, and turned. It may also be necessary to test the wall outlet. You may also need to verify that the computer is plugged in to the wall socket and
turned on. Finally, you may want to replace the video card with a known good video card. If you hear the system fan but the computer is not making the POST beep
sound, you may have a failed motherboard.
BIOS times and settings reset – If you encounter this issue, the problem is with the CMOS battery. Replace the CMOS battery and make sure to reset your BIOS settings.
Attempts to boot to incorrect device – This issue is usually related to the BIOS boot order. It was more common when floppy drives were listed as the first boot device. If a
non-bootable floppy were left in the floppy drive at boot time, the computer would display a non-system disk or disk error at startup. Once the floppy disk was removed
from the drive, the computer would boot. Today, a CD-ROM or DVD drive is often listed as the first boot device. You can change the boot order in the BIOS. This issue can
also result from missing or corrupt boot files. If you suspect that this error is due to boot files being missing or corrupt, you should enable boot logging from the Windows
Advanced Menu and replace the missing or corrupt boot files using the Windows installation DVD.
Continuous reboots – Reboots are usually the result of electrical issues, power supply issues, or overheating. Brownouts or blackouts cause computers to reboot.
Attaching a computer to an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) will ensure that you can safely shut down the computer if these occur. If the power supply in the computer
is the issue, you should replace it with one that supplies adequate power to the computer. Finally, if overheating is causing the reboots, you should check all fans and
ensure that the CPU heat sink is still attached. You may need to replace these or add another cooling device to your computer.
No power – Once again, check the obvious. Make sure that the computer is plugged in and that the wall outlet is supplying power. If a UPS or surge protector is used,
check to see if its breaker was tripped by a power surge. Finally, check the computer's power supply by replacing with known good unit.
Overheating – This is usually the result of cooling fan or cooling system failures. Make sure that all open slots are covered. In addition, ensure that all system fans are
functional.
Loud noise – Loud noise is usually caused by system fans, the power supply, or the hard drives because very few internal devices have moving parts. Check those three
devices to trace the noise. Replace the part that is making the noise because the noise usually means that the device is close to failure.
Intermittent device failure – First, make sure that you have the latest driver for the device. If the problem persists, you should replace the device. If intermittent failures are
occurring with different devices, you could have a motherboard that needs replacing.
Fans spin, no power to other devices – If no beep codes are heard, you probably have motherboard failure. If you hear beep codes, record the code that is heard and
research that code to find the problem device. This problem could also mean that the power supply was not properly plugged into the motherboard.
Indicator lights – Many components in a computer have indicator lights. In most cases, indicator lights will blink when activity is occurring and will be steady green when
idle. However, some devices will have other lights and/or colors. Always consult the vendor documentation. If problems continue, you should replace the device.
Smoke – This is a horrible problem to have but is usually easy to trace. Shut down the computer immediately and locate the device that is producing the smoke. Replace
that device.
Burning smell – This problem usually accompanies smoke. As with smoke, you should shut down the computer immediately and locate the device that is producing the
smoke. Replace that device.
Proprietary crash screens (BSOD/pin wheel) – Windows Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) errors are usually the result of hardware issues. You should always replace hardware
one device at a time, following by a system boot. If the new hardware did not fix the issue, then that component is not the issue. Replace the component with the original
and try replacing another component. Some of the more common BSOD errors are listed below:
Data_Bus_Error – Faulty hardware has been installed or existing hardware has failed. Usually this error is related to RAM, cache, or video RAM.
Unexpected_Kernel_Mode_Trap – Remove or replace any recently installed hardware. Run hardware diagnostics to determine which component has failed. Replace the
failed hardware. This error can also be caused if you set the CPU to run at a higher speed than the CPU supports.
Page_Fault_in-nonpaged_area – This error is caused by RAM, cache, or video RAM. Replace the failed component.
Irq1_not_less_or_equal – This issue is usually caused by a device driver, system service, virus scanner, or backup tool that is not compatible with the version of Windows
you are running. Make sure that all your drivers and software is updated to the version that is compatible with the Windows OS you are using.
Pinwheel errors occur when users see the spinning rainbow pinwheel. Causes include bugs in applications, event processing issues, and virtual memory issues.
Distended capacitors – Capacitors are included in computers on the motherboards, video cards, and power supplies. Capacitors can fail prematurely, causing the
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 38 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
capacitor's case to bulge or rupture. In most cases, the only way to fix this problem is to replace the card that has the swollen capacitor. It is possible to replace them, but
the process requires soldering experience. Replacing the capacitor is an electrical hazard and should only be attempted with proper training.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot problems related to motherboards, RAM, CPUs, and power.
References:
How to troubleshoot a PC power supply, https://www.neweggbusiness.com/smartbuyer/components/how-to-troubleshoot-a-pc-power-supply/
Question #41 of 60
Question ID: 1171668
Every time a Windows 8 computer boots, you receive an error message stating that the cover was previously removed. You want to prevent this alert from being displayed. In
which location should you disable this alert?
A) In the BIOS
B) In Event Viewer
C) In Device Manager
D) In the System Configuration utility
Explanation
To prevent an alert regarding the cover being removed from displaying, you should disable the chassis intrusion detection, no matter which operating system you are running.
Chassis intrusion detection is always configured in the system BIOS. Chassis intrusion detection is a method of physical intrusion detection. It provides an alert the next time
the computer is booted that tells the user that the chassis has been opened. Often, hackers will physically open a computer to insert hardware that is used to capture
confidential or sensitive information.
Chassis intrusion detection is not configured in the System Configuration utility, in Event Viewer, or in Device Manager.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure motherboards, CPUs, and add-on cards.
References:
PC Chassis Intrusion Detection, http://bucarotechelp.com/computers/netsafe/88100101.asp
Question #42 of 60
Question ID: 1171610
Which IP address is used by a Class A private network?
A) 192.168.0.0
B) 127.0.0.1
C) 10.0.0.0
D) 172.16.0.0
Explanation
The 10.0.0.0 address is a Class A IP address for private networks. Private network IP addresses cannot be used on the Internet. The 172.16.0.0 address is a Class B IP
address for private networks. The 192.168.0.0 address is a Class C IP address for private networks.
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 39 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
The 127.0.0.1 address is not reserved for private networks. This IP address is the software loopback address.
Objective:
Networking
Sub-Objective:
Explain common network configuration concepts.
References:
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 2: Networking, 2.6 Explain common network configuration concepts
Question #43 of 60
Question ID: 1191961
You are in the process of replacing the toner cartridge for a laser printer. However, you notice that toner particles have been spilt inside the printer. What should you use to
effectively remove these particles?
A) Damp cloth
B) ESD-safe vacuum cleaner
C) Compressed air
D) Household vacuum cleaner
Explanation
An ESD-safe vacuum cleaner is recommended for effectively cleaning a laser printer if toner particles spill into the printer. An ESD-safe vacuum cleaner is a special type of
vacuum cleaner that has an electrically conductive hose and a high-efficiency filter. It is recommended for cleaning toner spills because it prevents toner particles from
developing static-electric charges when these particles are rubbed against the vacuum hose, and the high-efficiency filter in an ESD-safe vacuum cleaner prevents toner
particles from passing through the exhaust. To prevent toner spills and to provide optimum performance, it is recommended to use only genuine cartridges from the same
manufacturer. Using compressed air can blow toner particles deep inside the printer where it cannot be cleaned easily.
Using a household vacuum cleaner is incorrect because toner particles are very fine and can easily pass through the household vacuum cleaner bag. Toner particles that are
spread in the air can be dangerous to humans.
A damp cloth is incorrect because it does not clean the toner spills as effectively as an ESD-safe vacuum cleaner.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and maintain various print technologies.
References:
Step By Step 16 - Preventative Maintenance, http://www.dansdata.com/sbs16.htm
Question #44 of 60
Question ID: 1175647
You need to synchronize your mobile device data with your desktop computer. For security reasons, your organization prohibits syncing devices over wireless connections or
the Internet. Which connection(s) could you use to perform the synchronization?
A) Ethernet
B) USB
C) Bluetooth
D) 802.11
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 40 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Explanation
You could use a USB connection to perform the synchronization. This will attach the mobile device directly to the desktop computer.
You should not use 802.11, Bluetooth, or Ethernet connections to perform the synchronization. 802.11 and Bluetooth are wireless connections, which are prohibited for
security reasons. Ethernet connections are not available on a mobile device because there are no connectors for an Ethernet cable on mobile devices.
Objective:
Mobile Devices
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, use methods to perform mobile device synchronization.
References:
USB vs. Bluetooth vs. Wi-Fi: The best way to tether to your iPhone or iPad!, http://www.imore.com/usb-vs-bluetooth-vs-wi-fi-whats-best-way-tether-your-mac-your-iphoneor-ipad
Description of Windows Mobile Device Center, https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/931937
Setup Guide - Sync Android via USB, http://www.companionlink.com/support/kb/Setup_Guide_-_Sync_Android_via_USB
Question #45 of 60
Question ID: 1171706
Your company purchases a new USB mouse for a server. Which statement characterizes this mouse?
A) You cannot connect it if another USB device is already connected to the computer.
B) You can plug it into a computer while the computer is on.
C) You must restart the computer immediately after connecting it.
D) You must connect it to the computer through a parallel port.
Explanation
You can attach USB devices to a computer that is functioning and then use the USB devices immediately without having to restart the computer; doing so is often referred to
as hot swapping or hot plugging. The operating system should recognize any newly attached USB devices and prompt users for drivers, if necessary. If the device driver has
previously been installed, then you should be able to use the device immediately. A mouse is an input device.
USB is an external expansion bus standard that allows many compatible devices to be connected simultaneously through a single USB port. By utilizing USB hubs in
conjunction with the USB ports available on the local machine, up to 127 of these devices can be connected to the computer. The devices are connected to the computer by a
4-pin connector. USB is also designed to be faster than ordinary RS-232 ports to support telephony applications such as low-resolution video conferencing.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Explain the purposes and uses of various peripheral types.
References:
Hot Swapping, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hot_swapping
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 3: Hardware, 3.6 Explain the purposes and uses of various peripheral types
Question #46 of 60
Question ID: 1175655
Which cloud computing term refers to a feature that allows a provider to dynamically adjust resource allocation, based on demand?
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 41 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
A) rapid elasticity
B) resource pooling
C) measured service
D) on demand
Explanation
Rapid elasticity is a cloud computing term that refers to a feature that allows a provider to dynamically adjust resource allocation, based on demand. Examples of such
resources include CPU allocation, memory, storage, and bandwidth.
Resource pooling allows the provider to service multiple customers using the same resources. This means that the consumers share the physical devices on which they
reside. Organizations should research the security implications of such a deployment scenario.
Measured service is a term that applies to paying for services on a per-use basis, such as CPU time, GB of storage, or network bandwidth use. Your cell phone data plan,
measured in GB of data transferred per month, could be an example of a measured service.
On demand is a term that refers to a cloud provider's ability to make resources available to clients when needed. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is an example of an on-demand
service.
For the A+ exam, you must also understand the following basic cloud concepts:
SaaS - Software as a Service. Instead of installing software on their computers, users can access the software over the Internet, typically paying a subscription fee for use.
An example is Microsoft Office 365.
IaaS - Infrastructure as a Service. Instead of buying servers, storage, and other hardware components that make up the company's infrastructure, organizations can
subscribe to a service over the Internet. The service host maintains the infrastructure components and makes them available on a per-use or subscription basis. An
example is Amazon Web Services.
PaaS - Platform as a Service. The provider makes hardware and software available over the Internet on a per-use or subscription basis. PaaS is often used in application
development.
Public vs. Private vs. Hybrid vs. Community - Public clouds are those that are made available to (typically) anyone that can pay. Private clouds are used by a single
organization. Community clouds are for groups of subscribers that have common usage and requirements. Hybrid clouds are comprised of more than one type of cloud.
Objective:
Virtualization and Cloud Computing
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast cloud computing concepts.
References:
What is Cloud Computing? A Tutorial, http://leverhawk.com/what-is-cloud-computing-tutorial-2012120519
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) definition, http://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Infrastructure-as-a-Service-IaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS) definition, http://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Platform-as-a-Service-PaaS
Question #47 of 60
Question ID: 1191913
You need to provide users with an external hard drive. The company issued laptops have two Type A USB ports that are black, and an additional Type A port that is teal. To
provide the best data transfer, which USB connector should the external drives have?
A) USB 2.0
B) USB
C) USB-C
D) USB 3.0
Explanation
Universal Serial Bus (USB) 3.0 has a data transfer capacity of 5 gigabits per second (Gbps) and was introduced in late 2008. The connector and ports are typically blue. USB
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 42 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
3.1 was introduced as an improvement to USB 3.0 and has a capacity of 10 Gbps. USB 3.1 connectors and ports are typically a teal color.
USB, also known as USB 1.1, has a data transfer capacity of 12 megabits per second (Mbps). USB cables were introduced in the late 1990s as replacements for parallel and
serial connections. USB has gone through several evolutions, the most recent version being USB-C. Each new version has provided improvements in data transfer speeds.
USB-C uses a smaller connector instead of the “universal” flat and wide Type A connector. USB-C is an implementation of USB 3.1, which is capable of data transfer rates of
up to 10 Gbps.
USB 2.0 has a data transfer capacity of 480 Mbps in high-speed mode. USB 2.0 was introduced in early 2000, and is backwards-compatible with USB 1.1.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Explain basic cable types, features, and their purposes.
References:
USB Type-C and Thunderbolt 3: One port to connect them all, https://www.cnet.com/how-to/usb-type-c-thunderbolt-3-one-cable-to-connect-them-all/
Question #48 of 60
Question ID: 1171816
You notice that the pages coming out of your laser printer have toner that you can brush off. Which printer component is MOST likely causing the problem?
A) Pickup roller
B) Fuser assembly
C) Toner cartridge
D) Photoreceptor
Explanation
If the pages coming out of your laser printer have extra toner that you can brush off, the fuser assembly printer component is most likely creating the problem. The fuser
assembly printer component holds two rollers that get heated to a high temperature to bind the dry toner ink to the paper fabric. When the printed pages carry extra toner that
you can rub off, it usually indicates that the fuser roller is not getting heated enough to melt the dry toner particles properly and fuse the toner ink with the paper fibers.
The toner cartridge cannot be the problem because a toner cartridge, if not working properly, can cause problems such as uneven or variable density printing. A toner
cartridge is a printer component that contains toner ink that is fused to the paper during the printing process.
The pickup roller cannot be the problem because the pickup roller is a printer component that draws the paper from the paper tray into the printer. A malfunctioning pickup
roller can cause false paper jams wherein the printer is not able to pick up the paper from the tray because the pickup roller fails to turn.
A photoreceptor cannot be the cause of the problem. A photoreceptor is a photosensitive printer component that is used to transfer a latent electro-photographic image
created by the laser beam on to the paper during the printing process.
Always keep in mind that you should check the obvious first when troubleshooting a printer. If the printer is not printing, you should make sure it is plugged in and turned on.
You should also make sure that it has paper. Most technicians can tell you stories about how they were called in for troubleshooting an issue that had a very obvious fix. Also,
keep in mind that some internal components should only be replaced by individuals who are experienced in repairing printers. These printer technicians are usually employed
by the vendor from which you purchased the printer.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot printers.
References:
Learn the basics of laser printing, http://www.techrepublic.com/article/learn-the-basics-of-laser-printing/
The inner workings of laser printers and how to troubleshoot them, http://www.techrepublic.com/article/the-inner-workings-of-laser-printers-and-how-to-troubleshoot-themhttps://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 43 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
part-1/
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.6 Given a Scenario, Troubleshoot Printers
with Appropriate Tools
Question #49 of 60
Question ID: 1171688
You have decided to enable overclocking to increase the performance of a computer. On which computer components can you specifically enable overclocking? (Choose all
that apply.)
A) Motherboard
B) Processor
C) RAM
D) System bus
E) Hard drive
Explanation
You can specifically overclock the processor, RAM, and system bus. No other computer components can be overclocked. However, overclocking the system bus may also
cause other components to be overclocked. Overclocking allows you to run the processor or system bus at a higher speed than the manufacturer's rating to gain increased
performance.
Overclocking cannot be specifically enabled on the motherboard or hard drive.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure motherboards, CPUs, and add-on cards.
References:
Overclocking Types, http://www.pcguide.com/opt/oc/introTypes-c.html
Question #50 of 60
Question ID: 1171647
You have been tasked with performing several upgrades in a computer. Which hardware component will require the least amount of time to replace?
A) Memory module
B) Motherboard
C) Network interface card
D) Power supply unit
Explanation
A memory module is inserted into the memory slot without investing substantial effort. The memory module will require the least time to replace. Memory modules are usually
just inserted into the slot and snapped into place. No screws are required. You should install additional memory of the same type and speed as existing memory to ensure
RAM compatibility.
The network interface card (NIC), processor, motherboard, and power supply unit are field replaceable units (FRUs) of a computer. A motherboard will require disassembly of
the entire system unit before being replaced. Therefore, a motherboard is not the hardware component that requires the least amount of time to replace. A power supply unit
will also require a substantial amount of effort to replace compared to a memory module. With a power supply, all of the power connectors would need to be disconnected
from the motherboard and all peripheral devices. Typically, a NIC is installed as an add-on card that can be taken out of the system unit by opening a single screw. A NIC will
require more time to be replaced than a memory module.
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 44 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install RAM types.
References:
Adding memory to your PC, http://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=130915&seqNum=5
Question #51 of 60
Question ID: 1191999
A user notifies you that the monitor on her notebook computer is not displaying anything. What should you do FIRST?
A) Plug in an external monitor to test the external output.
B) Use the Fn key to toggle to the internal video display.
C) Replace the video output port.
D) Reboot the computer.
Explanation
You should use the Fn key to toggle to the internal video display. The Fn key used with the F4 key switches the video display between the laptop monitor only, the external
monitor only, or both on at once. Users often accidentally hit this key function, and thereby prevent the internal monitor from displaying any image.
You should not replace the video output port. This port is not used by the notebook computer's monitor. Therefore, it is not the cause of the problem. This port is used by
external monitors. However, it will not function unless the Fn + F4 keys are pressed.
You should not plug in an external monitor to test the external output. The monitor on a notebook computer does not use the external output. Testing the external output
should be done if the toggling of the display using the Fn key does not work. The external output is strictly for any external display devices to which you may connect a
notebook computer.
You should not reboot the computer. It is not necessary to reboot the computer. In addition, rebooting the computer may not fix the problem. Most notebooks revert back to
the last used configuration when rebooted. Therefore, if the video display is toggled to use an external monitor only, rebooting the computer will not reset this to a previous
configuration.
For the A+ exam, you need to be familiar with the following common symptoms for laptops and other mobile devices:
No display -–This is most often caused when the display is dimmed via the controls or when the display has been sent to the external device. Try changing the screen
dimness, or use the appropriate function key to cycle through the different display options. If neither of these solutions fixes the problem, you could have a failed backlight
or inverter, which are both internal components that will need to be replaced to troubleshoot the problem. For an iPhone or iPad that has dimmed or turned black, you
should press and hold down the Sleep/Wake button and the Home button simultaneously for at least 10 seconds. This should soon display the Apple logo on the black
background. For Android tablets and smartphones, you must take off the back cover, reseat your battery, and then charge your phone for a few hours. However, just like
the blue screen of death on PC-based devices, Android can have the same issue. If this is the case, you will have to remove the SIM card and battery and leave them out
for 5–10 seconds. At this point, you need to charge the battery, as well. Finally, sometimes you may have to perform a hardware factory reset. This process will
permanently remove the customer's data from the device. Make sure to back up all personal data to a computer or to the cloud. To perform a hardware factory reset, you
would press and hold the Volume Up, Power, and Home keys simultaneously and select Factory reset/wipe data using the volume keys. Then you would press the Power
key to start the hardware factory reset.
Dim display – This is most often caused when the display is dimmed. Change the screen dimness to see if this fixes the problem. Also, you may need to check the switch
on the laptop that tells the system that the lid is closed. If neither of these solutions resolves the problem, either the backlight or inverter could be the cause. Replace each
of these components to troubleshoot the issue. Smartphones and tablets have dim screen controls in the Settings menu. On an iPhone, you can swipe up the Control
Center and change the display. Android devices have apps you can download for free, such as Screen Dimmer. The dimmer feature is a great way to change the
brightness of your screen and save your battery.
Flickering display – This is usually caused by an incorrect video driver or low screen refresh rate. Update the driver first. If this does not resolve the problem, consult the
display device manufacturer's documentation for the appropriate refresh rate. Finally, flickering can be caused by loose or bad connections. Check the internal
connections for the display if none of the other solutions works.
Sticking keys – Dust accumulation can cause keys to stick. In addition, most keys have a spring that can wear out. First, you should try to blow out the keyboard using
compressed air. It may also be necessary to clean the individual keys. In some laptops, keys can be detached for individual cleaning. Be careful when detaching individual
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 45 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
keys because this can damage keyboard components. If this does not fix the problem, replace the integrated keyboard or purchase an external keyboard. Spilled liquids
are most often the cause of sticking keys.
Intermittent wireless – This is usually caused by radio frequency interference (RFI). Research the wireless network environment. Try to minimize the obstructions between
the laptop and the wireless access point. For example, microwaves and cordless phones can interrupt the flow or signal and cause disturbances to your flow and
connection, so do not place routers near those types of electronics. Also, research the particular frequency in use on your wireless network to discover if you have
deployed any devices that could be causing the problem. You may need to increase the signal strength on the wireless access point. Finally, the problem could be with the
internal wireless card. Check the internal cable connections for the wireless card if none of the other troubleshooting techniques has solved the problem.
Battery not charging – If the battery will no longer charge properly, you should totally drain the battery's power to eliminate the memory effect. If this does not solve the
problem, replace the battery with a new one. However, the A+ number one rule is to always check the connection, so make sure that your plug snuggly fits on the charging
device. Loose or disconnected cables can be frustrating, so do not eliminate that step when troubleshooting.
Ghost cursor/pointer drift – This usually occurs when the track pad is too sensitive. You can change the sensitivity settings to see if this fixes the problem. If the problem
still exists, you should try installing the latest driver for the touch pad. Finally, you could disable the touch pad and connect an external mouse. You can also search Google
for the Phantom Cursor to troubleshoot various devices.
No power – This is usually caused when you are no longer connected to an external power source and the battery has been depleted. Make sure that the laptop is plugged
in to a functional external power source. Plug the laptop into a power source and allow the battery to recharge. You may also want to reconfigure the power settings to
ensure that certain devices are not enabled when you are working using battery.
Num Lock indicator lights – To enable or disable the number lock function, you may need to press a single Num Lock key or use a function key combination. Read the
laptop vendor's documentation to learn the appropriate way to enable and disable the number lock function. If the number lock function is disabled, you will notice that
the cursor moves around when you use the number keys instead of numbers being entered on the screen. If your keyboard has calculator type keys built in, you will need
to enable Num Lock to use the calculator as desired.
No wireless connectivity – This is usually caused when the wireless device has been disabled. Read the laptop vendor's documentation to learn the appropriate function
key combination that can be used to enable/disable wireless. The device can also be disabled in Device Manager. If neither of these solutions fixes the problem, you
should check the wireless card to make sure that it is seated properly and attached to the antenna. Replacing the wireless card or antenna may be necessary. For most
mobile devices, you simply need to make sure that Wi-Fi is enabled or turned on. You also may need to make sure that Airplane Mode is turned off. Airplane Mode
disables several features, including WiFi.
No Bluetooth connectivity – This is usually caused when Bluetooth has been disabled. Read the laptop vendor's documentation to learn the appropriate function key
combination that can be used to enable/disable Bluetooth. If this does not fix the problem, you should check the wireless card to make sure that it is seated properly and
attached to the antenna. Replacing the wireless card or antenna may be necessary. For mobile devices, you probably only need to make sure that Bluetooth is enabled. As
with Wi-Fi, Airplane Mode disables Bluetooth on most devices.
Cannot display to external monitor – This is most often caused when the display has been sent to the internal. Use the appropriate function key to cycle through the
different display options. If this does not fix the problem, you should check the cabling to the external monitor. For some displays, you will also need to make sure that that
display device itself is set to the appropriate source.
Touchscreen nonresponsive – This is most often caused by a dirty screen. First, remove any screen protectors and try to clean the touchscreen. If that does not work,
reboot the device. If the problem persists, the screen may need to be repaired or replaced. Keeping your screens clean, dust-free, and protected will extend the life of your
tablet or laptop screen. Remember that they are very fragile, so you should handle them with care.
Apps not loading – First, you should make sure that your app and the device operating system is updated. Next, ensure that your firewall isn't configured to block the app.
You could then synchronize the license for the app. As a last resort, try removing and reinstalling the app.
Slow performance – This is usually caused by too many apps running in the background. Stop any unneeded apps from running. If this does not resolve your issue, reboot
the device. Finally, it could be that the drive in your device is reaching its storage capacity. If that is the case, you will need to remove some data and/or apps and possibly
back up unused files to an external backup device, like a server or an external hard drive.
Unable to decrypt email – This is usually caused by a missing or expired key or certificate. Make sure the appropriate key or certificate is installed. It may be necessary to
restore them from backup. It also could be that the device is configured to not allow encrypted email. If this is the case, then you need to enable encrypted email.
Extremely short battery life – Always try completely draining and recharging the battery first. If the battery continues to only have a short life, you need to replace the
battery. For mobile devices, you may try changing battery settings through the Control Panel or Settings.
Overheating – If your mobile device overheats, try removing the protective case that you have it in. Other solutions are to remove the device from direct sunlight, shut
down apps you are not using, or buy a glare screen and turn down the brightness. Finally, turn your mobile device off or put it in Airplane Mode when not in use.
Frozen system – First, try plugging the mobile device into a power supply. Then you should try to power down or restart the device the normal way. If that is not possible,
then remove the battery for a few seconds. Next, you should delete the app that is causing the device to freeze. As a last resort, reset the device to the factory defaults.
For an Apple mobile device, another possible solution is to restore the device using iTunes. You can also consult the manufacturer's website or device documentation on
how to reset the device.
No sound from speakers – This is most often caused by the sound being muted or the device being in silent or vibrate mode. If that does not fix the problem, try adjusting
the volume. As a last resort, reboot the device. If you are using Bluetooth speakers, remove the device through Settings, re-add the speakers, and resync.
GPS not functioning – First, you should ensure that the GPS function is enabled. If that is not the problem, reboot the device. Then try turning location services off and
then back on. Finally, you could perform a GPS reset.
Swollen battery – Swollen batteries are an explosion or leaking hazard and should be replaced immediately. Swollen batteries are usually found in devices like laptops and
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 46 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
mobile devices that use lithium batteries. Batteries can become swollen due to manufacturing defects or by not using the right charger. Lithium-ion batteries do not like to
be overcharged because there is no place for the gasses in the overheated cells to go. The overheated batteries expand, swell, and appear warped. Always replace
swollen batteries.
When troubleshooting a laptop computer, it may be necessary to draw a diagram of your laptop as you disassemble it for when you replace internal parts. It is very important
that all technicians follow the proper procedure to ensure that the laptop can be reassembled properly. Always document and label the cable and screw locations for the
computer. Organize and label all the internal parts to ensure that they are replaced properly. When issues arise, always refer to the manufacturer's documentation or resources.
Use the appropriate hand tools during the disassembly/reassembly process.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot common mobile device issues while adhering to the appropriate procedures.
References:
My laptop computer screen is black, http://www.computerhope.com/issues/ch001319.htm
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.5 Given a scenario, troubleshoot common
mobile device issues while adhering to the appropriate procedures
Question #52 of 60
Question ID: 1191912
You are connecting a video display wall that will use two 4K monitors. Which would be the best type of cable to transfer the video signal from the Windows 10 desktop source
to the monitors?
A) USB
B) Lightning
C) Thunderbolt
D) Serial
Explanation
Thunderbolt-3 cables can provide the bandwidth to support 4K monitors, up to 40 Gbps. Thunderbolt-3 includes a USB-C connection. Including this connection allows the
cable to be used with other USB-C compatible devices. Thunderbolt also allows “daisy-chaining” devices, making it an ideal choice for video display walls that use multiple
monitors.
The Lightning cable replaced Apple’s 30-pin charging cable in 2012. It is used to recharge iPhones beginning with the iPhone 5, as well as numerous other Apple devices. The
cable has the charging connector on one end, and a standard USB-A connector on the opposite end. The USB connector provides the associated device the flexibility to
connect with anything that has a USB port. Lighting cables transfer at USB 3.0 speeds of 5 Gbps.
Universal Serial Bus (USB) cables were introduced in the late 1990s as replacements for parallel and serial connections. USB has gone through several evolutions, the most
recent version being USB 3.1/USB-C. Each new version has provided improvements in data transfer speeds.
The USB types and their associated transfer rates are as follows:
USB 1.0 - 1.5 megabits per second (Mbps)
USB 1.1 – 12 Mbps
USB 2.0 – 480 Mbps
USB 3.0 – 5 gigabits per second (Gbps)
USB 3.1 – 10 Gbps
Serial cables typically have DB9 connections and are considered legacy ports. They are primarily used to configure routers and switches in lieu of an Ethernet
connection. Serial cables have a maximum transfer rate of 115.2 kilobits per second, making them unsuitable for high-speed video transfer.
Objective:
Hardware
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 47 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Sub-Objective:
Explain basic cable types, features, and their purposes.
References:
How to Connect Multiple External Monitors to Your Laptop, https://www.howtogeek.com/306237/how-to-use-mulitple-external-monitors-with-your-laptop/
Question #53 of 60
Question ID: 1191945
Which of the following is NOT considered an input device?
A) Barcode reader
B) Printer
C) Scanner
D) Digitizer
Explanation
A printer is not considered to be an input device. It is an output device. Output devices include printers, monitors, speakers, and other display devices. Printers are used to
produce a physical printed copy of something on the screen. Monitors are display devices. Speakers are audio devices. Other output devices include a headset and virtual
reality (VR) headset. A headset usually provides audio headphones and a microphone, while a VR headset often provides audio, a microphone, and some sort of display over
your eyes to allow you to be immersed into the video.
Input devices include keyboards, mice, touchpads, touchscreens, scanners, barcode/QR scanners, KVM switches, microphones, biometric devices, game pads, joysticks,
motion sensors, and smart card readers. Keyboards allow you to type text and navigate the screen. A mouse allows you to navigate the screen by moving the mouse. A
touchpad allows you to navigate the screen using your fingers. A touchscreen allows you to navigate or interact with the screen by touching the screen. An automatic
document feeder (adf)/flatbed scanner allows you to scan physical copies of documents or pictures into a computer. An adf scanner automatically feeds the documents, while
a flatbed scanner requires that you manually place the document you want to scan on the flatbed screen. A barcode/QR scanner is used to scan a barcode or QR code. A
keyboard, video, monitor (KVM) switch allows you to connect multiple computers to a single keyboard, video, and monitor. A microphone allows you to transmit or record
audio messages. A biometric device scans a user’s iris, retina, finger, or other biometric input to authenticate the user. A game pad or game controller is used to input game
functionality. A joystick provides a similar functionality to a game pad. Motion sensors detect when motion occurs and notifies the appropriate personnel and/or records a
particular area. Smart card readers read the input from smart cards to provide authentication.
Multimedia input devices include digital cameras/webcams, microphones, webcams, camcorders, and MIDI-enabled devices. Digital cameras/webcams allow the
transmission and recording of videos.
Input and output devices include touchscreen, KVM switches, smart TVs, and set-top boxes.
For the A+ exam, you also need to understand signature pad, magnetic reader/chip reader, and NFC/tap pay device. A signature pad allows a signature to be input and stored
in a computer. A magnetic reader reads the magnetic strip on a card, while the chip reader read the chip’s data from a card. An NFC or tap pay device allows the payment
information to be transmitted to a computer.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Explain the purposes and uses of various peripheral types.
References:
What is the difference between an input and output device?, http://www.computerhope.com/issues/ch001355.htm
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 3: Hardware, 3.6 Explain the purposes and uses of various peripheral types
Question #54 of 60
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Question ID: 1191927
Page 48 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Your company’s mobile sales force is complaining about how slow their laptops are. You are considering replacing the mechanical hard drives in their laptops with solid state
drives (SSD). This will provide an increase in performance, but you are concerned about the SSD’s limited storage capacity. What type of SSD should you consider?
A) SATA 2.5 drives
B) NVME drives
C) Hybrid drives
D) M2 drives
Explanation
You should consider hybrid drives, which have both SSD and mechanical hard drives. Hybrid drives store the operating system, applications and system files on the SSD
side, and use the mechanical hard drive for long-term storage. This type of drive will provide the users with a performance boost while still maintaining the storage capacity of
mechanical drives.
M2 drives provide both the speed and storage increase desired, but they require a special slot on the motherboard. If the motherboard does not have the required slot, the M2
drive will not fit.
Non Volatile Memory Express (NVME) is a technology that replaced SCSI and ATA interfaces for Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)-based SSDs. NVME
reduces latency increases the number of input/output operations per second and can reduce power consumption. While it offers performance increases over SSDs, it will not
meet the capacity requirement.
SATA 2.5 is the most common type of SSD and would most likely fit in the existing laptop slot. You would get the performance increase you need, but you would lose storage
capacity.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, select, install and configure storage devices.
References:
Hybrid Hard Drives Explained: Why You Might Want One Instead of an SSD, https://www.howtogeek.com/195262/hybrid-hard-drives-explained-why-you-might-want-oneinstead-of-an-ssd/
Question #55 of 60
Question ID: 1191980
Your computer only boots with a bootable DVD. It is not able to boot without a bootable DVD. What could be the possible reasons for this problem? (Choose two.)
A) Corrupt operating system
B) Bad CPU
C) Bad hard disk
D) Bad RAM
Explanation
If your computer boots with a bootable DVD but is not able to boot without it, then the problem may be the hard disk or a corrupt operating system. A computer cannot boot
without a bootable disk when the disk drive cannot read the boot information successfully. This could be caused by a bad IDE interface or a bad disk. The computer will not be
able to detect the hard disk if there is a bad IDE interface and will require a bootable disk to boot the computer. If there is a bad disk, the computer will again require a
bootable disk to boot the computer. To solve this problem, you should replace the disk, then reinstall the operating system and reload the data. Corrupt operating systems will
also not allow the computer to boot without bootable disks. Operating systems provide a platform on which other application programs run. Booting a computer involves
loading the operating system and other basic software after a power-on self-test (POST) is complete. You may be required to reinstall the operating system if you are unable to
boot the computer without bootable disks.
If you are able to boot the computer with bootable disks, then the computer does not have a problem with the RAM. When you turn on a computer, it performs a POST that
includes checking the CPU, RAM, presence of a video card, and other hardware components. The boot process stops and produces beep codes when the POST encounters
a problem. These are a series of beeps from the computer's speaker. The number, duration, and pattern of the beeps indicate which computer component is causing the
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 49 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
problem. For example, continuous long beeps indicate a problem with the RAM.
If your computer boots with a bootable disk but cannot boot without it, then you can rule out any problem with the CPU. If there is a problem with the CPU, the computer will
not be able to boot, with or without the bootable disk.
For the A+ exam, you need to be familiar with the following hard drive symptoms and how to fix them:
Read/write failure – This is usually caused by damaged sectors on the hard drive or by hard drive failure. Run the chkdsk command to scan the drive for damaged sectors.
If the hard drive has completely failed, you will need to replace the drive and restore the data from backup.
Slow performance – This can be caused by memory or hard drive. If you do not have enough memory, there will be excessive paging. In this case, add more memory. If
you think the hard drive itself is causing the performance issue, check the hard drive to see if it has sufficient free space. If it does not, you need to add more hard drives to
your computer. If it has sufficient free space, the performance issue could be caused by fragmented files. Run the defrag utility to defragment the hard drive and increase
hard drive performance.
Loud clicking noise – This often occurs right before the hard drive dies. Because loud noises can also be caused by other components, you first need to confirm that the
noise is coming from the hard drive. If you have confirmed this, completing a backup of your data should be your first priority. Then replace the hard drive and restore the
data from the backup.
Failure to boot – This problem can be caused by many different issues. If the system cannot locate the boot files, it cannot boot. If you suspect this is the problem, you
should ensure that your BIOS is set to boot from the drive where the boot files reside. Also, it may be necessary to check the BOOT.INI file to ensure that the partition
information is entered correctly. Finally, you may have to repair corrupted boot files. You should use the Recovery Console to repair corrupt system files. Finally, check to
make sure that the connections to your hard drive are still intact. If you receive any Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.) errors, research the
specific error you receive to find out what you need to do.
Drive not recognized – This usually involves either an incorrect master/slave setting or the inability of the BIOS or operating system to recognize the drive. Check to make
sure that the master/slave jumpers are configured appropriately. Check the BIOS to make sure that the disk parameters are configured appropriately. Finally, you made
need to install the appropriate drivers for the operating system. This may require that you obtain the third-party drivers from the hard drive vendor. In legacy systems that
do not support drives higher than 504 MB, you may need to implement logical bus addressing (LBA).
OS not found – This usually is a software issue where the boot sector cannot be located. Reboot the computer into the Recovery Console and repair the operating system.
RAID not found – If hardware RAID is implemented in the computer, the problem is usually with the RAID controller. Check the controller and replace as necessary. If
software RAID is implemented, make sure that the BIOS is set to RAID. You should also check all RAID connections. Finally, test the individual RAID drives. If one of the
drives has failed, replace it and restore the data.
RAID stops working – This is usually caused by the failure of a single hard drive in the RAID array. You need to determine which hard drive has failed and replace it. If the
failed drive is in a RAID-1 or RAID-5 array, the array will continue to operate, but performance will be degraded until the failed hard drive is replaced. Use the RAID setup
program to set the RAID configuration back up.
Proprietary crash screens (BSOD/pin wheel) – If a BSOD occurs after you install a new hard drive or new drivers, you should immediately suspect the hard drive as the
cause. Remove the hard drive or roll back its driver to troubleshoot the BSOD. If the BSOD no longer occurs, you should then research the change you made to discover if
there is a known issue with the hard drive or driver. Make sure that you only remove one hard drive or roll back one driver at a time to help determine the true cause of the
BSOD. Pinwheel errors are Apple computers equivalent to BSOD. Pinwheel errors occur when users see the spinning rainbow pinwheel. Causes include bugs in
applications, event processing issues, and virtual memory issues.
S.M.A.R.T. errors – Self Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.) performs a quick analysis of the hard drive for problems during system boot up. It
reports on such hard drive parameters as read error rate, throughput performance, and seek error rate. The main purpose of using S.M.A.R.T. is to ensure that you receive
warnings prior to a complete drive failure so that the drive can be replaced before complete failure.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot hard drives and RAID arrays.
References:
Chapter 2, Effectively Working with Personal Computer Components, bootable disks [PDF file], http://media.wiley.com/assets/1041/59/4831xc02.pdf
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.3 Given a scenario, troubleshoot hard
drives and RAID arrays
Question #56 of 60
Question ID: 1191898
Your company has decided to implement a wireless network. The wireless network users must be able to connect to resources on your internal network, including file, print,
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 50 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
and DHCP services. Which options should you implement? (Choose all that apply.)
A) APIPA
B) Static IP addresses
C) Infrastructure mode
D) Ad hoc mode
E) A wireless access point
Explanation
Infrastructure mode allows wireless computers to connect to a LAN, a WAN, or the Internet. This means that infrastructure mode wireless computers can access all computers
on the LAN, WAN, and Internet. Infrastructure mode is much more expensive to implement than ad hoc mode because you must configure wireless access points. While
infrastructure mode is harder to set up and configure, its management is much easier than with ad hoc mode. To view the strength of the wireless network, open the properties
dialog box for the wireless network interface card (NIC).
Ad hoc mode allows wireless computers to be configured much faster than infrastructure mode. Ad hoc mode wireless computers all participate in the same network. This
means that the ad hoc wireless computers can access each other but cannot access network resources on a LAN, WAN, or the Internet. Ad hoc mode is much cheaper than
infrastructure mode to implement. In addition, it is easy to set up and configure, and it can provide better performance than infrastructure mode. However, it is difficult to
manage an ad hoc mode wireless network.
Static IP addresses should not be implemented because the corporate network contains a DHCP server. Static addressing refers to the manual configuration of each
computer.
APIPA should not be used for the same reason. In addition, APIPA is used only if a DHCP server is not found. When implementing a wireless network that includes a wireless
access point, you can often enable or disable DHCP. If you enable DHCP, devices on the network will be assigned an IP address. If you disable DHCP, the devices will need to
have statically configured IP addresses.
When you implement an access point, you can configure several settings. MAC filtering will allow or deny connections based on the MAC address of the connecting device.
Disabling the SSID broadcast will ensure that the SSID is not broadcasting, thereby making it a bit more difficult to connect to the wireless network. The encryption method will
ensure that the password for the wireless network is protected. WPA2 is more secure than WPA, which is more secure than WEP.
Objective:
Networking
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure a basic wired/wireless SOHO network.
References:
What’s the Difference Between Ad-Hoc and Infrastructure Mode Wi-Fi?, https://www.howtogeek.com/180649/htg-explains-whats-the-difference-between-ad-hoc-andinfrastructure-mode/
Question #57 of 60
Question ID: 1171693
Your company has decided to make several computers that will be used for specialized functions. You have been tasked with assembling these computers. Management
wants you to ensure that the computers will not experience any overheating issues. Which components are used to help with this? (Choose all that apply.)
A) A ZIF socket
B) A heat sink
C) A fan
D) Thermal compound
Explanation
When installing processors, thermal compound, a heat sink, and a fan are used to help with overheating issues. If the processor is overheating, the computer will shut down
after being on for a while. It can be powered back up after the processor has cooled. If shutdowns continue, you may need to consider replacing the heat sink or fan. Thermal
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 51 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
compound used with a heat sink is a passive cooling system. Fans are active cooling systems because they require electricity to cool. Fans must operate at a certain RPM
level or be replaced. Processor fans should never be removed permanently. While heat sinks are more common for CPUs, you can also purchase heat sinks for memory
modules. You should avoid touching the copper piping on heat sinks because oil from the skin can decrease copper's ability to conduct heat.
Thermal compound should be applied between the heat sink and the processor. If you remove a heat sink, make sure to reapply fresh thermal compound. If you have trouble
removing a heat sink from a processor, heating the thermal compound should help.
The processor is plugged into the processor socket, often a zero insertion force (ZIF) socket. Make sure to insert the processor properly to prevent pin breakage. If a processor
pin is broken, the processor will not function. Once the processor is properly seated, thermal compound should be applied to the top of the processor. The heat sink should
then be mounted on top of the processor. The processor fan should be mounted on top of the heat sink.
Motherboards that support multiple processors have multiple processor sockets. The first processor should be installed in the processor socket referred to as Proc 0. The
second processor should be installed in the processor socket referred to as Proc 1, and so on. When installing multiple processors, it is important that all installed processors
installed operate at the same speed. This ensures optimum performance of the processors.
Fans are also installed in the case, primarily as part of the power supply. Case fans force cool air across the motherboard and help to ensure that air circulates properly within
the case. Some systems include a mechanism that alerts you if the fan is removed. If a fan seems to be operating at a high level or seems to be powering up more often, you
may need to clean the fan to remove dust and debris.
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, install and configure motherboards, CPUs, and add-on cards.
References:
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 3: Hardware, 3.5 Given a scenario, install and configure motherboards, CPUs, and addon cards, Cooling Mechanism
Question #58 of 60
Question ID: 1191890
Match the protocol from the left with the default port it uses on the right. Move the correct items from the left column to the column on the right to match the protocol with the
correct default port.
{UCMS id=5769159096926208 type=Activity}
Explanation
The protocols given use these default ports:
Port 20 – FTP
Port 23 – Telnet
Port 25 – SMTP
Port 53 – DNS
Port 80 – HTTP
FTP also uses port 21, but it was not listed in this scenario.
Objective:
Networking
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast TCP and UDP ports, protocols, and their purposes.
References:
List of TCP and UDP Port Numbers, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_TCP_and_UDP_port_numbers
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 52 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
Question #59 of 60
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
Question ID: 1191915
You have been hired as an IT technician. You have been given a laptop computer that has the following video ports:
You need to identify the ports shown. Match each video port on the left with the appropriate exhibit name on the right.
{UCMS id=5761984152731648 type=Activity}
Explanation
The exhibits should be matched up as follows:
Exhibit A – VGA port
Exhibit B – HDMI port
Exhibit C – S-Video port
Exhibit D – DVI port
A DVI-D connector is shown in the following graphic:
A DVI-I connector is shown in the following graphic:
A DVI-A connector is shown in the following graphic:
An HDMI connector is shown in the following graphic:
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 53 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
A VGA connector is also known as a DB15 or HD15 connector. A DB15 female port is shown in the following graphic:
An S-video connector is shown in the following graphic:
Objective:
Hardware
Sub-Objective:
Explain basic cable types, features, and their purposes.
References:
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 3: Hardware, 3.1 Explain basic cable types, features, and their purposes
Question #60 of 60
Question ID: 1192024
On a network that you administer, you cannot use a Windows computer named Wkst1 to connect to an Internet host with the fully qualified domain name (FQDN)
www.transoft.com. You want to determine whether a WAN link between Wkst1 and www.transoft.com is down. You know that data normally passes through 10 hops in transit
from Wkst1 to www.transoft.com. Which command should you use to test connectivity?
A) tracert www.transoft.com
B) ipconfig www.transoft.com
C) nbtstat www.transoft.com
D) arp www.transoft.com
Explanation
Of the listed commands, you should use the tracert www.transoft.com command to determine whether a WAN link between Wkst1 and www.transoft.com is broken. The
tracert computername command or tracert IP-Address command starts the tracert utility. The tracert utility displays the path that data travels through a network. The path
begins at the host, which is the computer on which the utility is started, and ends at the host specified in the computername or IP-Address variables.
In this scenario, the tracert www.transoft.com command will display the route that data travels between Wkst1 and www.transoft.com. Each host that data traverses on its
route to the destination host is referred to as a hop. The tracert utility numbers each hop and displays the following information for each hop: time required for the data to
travel through the host, the FQDN of the host, and the IP address of the host. You can use the tracert command to determine which WAN link is causing a connectivity
problem. In this scenario, for example, you know that data usually passes through 10 hops from Wkst1 to www.transoft.com. If the tracert utility reports an error transmitting
data from hop 7 to hop 8, then a problem likely exists with the WAN link between hop 7 and hop 8.
You can use the arp command with various switches to determine the status of Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) on a computer and to view the ARP cache. ARP is the
protocol in the TCP/IP protocol suite that resolves media access control (MAC) addresses to IP addresses. Each NIC in a computer is configured with a MAC address, which is
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 54 of 55
220-1001 Exam Simulation
9/14/21, 11:56 AM
used for physical addressing on a network. If you issue the arp www.transoft.com command at a command prompt on a Windows computer, then a new command prompt will
be displayed. You will not be able to view the route that data travels between the Wkst1 computer and the www.transoft.com computer.
You can use the nbtstat command to view information about the status of NetBIOS over TCP/IP on a Microsoft network and to troubleshoot problems with Windows Internet
Name Service (WINS). WINS resolves NetBIOS names to IP address on Microsoft networks. If you issue the nbtstat www.transoft.com command at a command prompt, then
a screen of instructions for the use of the nbtstat command will be displayed.
You can issue the ipconfig command at a command prompt on a Windows computer to view the IP configuration, including the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
address. If you issue the ipconfig www.transoft.com command at a command prompt, an error will occur.
For the A+ exam, you need to understand the following command-line tools:
Ping – Uses ICMP to test connectivity between two devices
Ipconfig/ifconfig – Displays the TCP/IP configuration of a device. You should be familiar with its switches, including the /all, /release, /registerdns, /renew, and /flushdns
switches. The ifconfig is the Unix/Linux equivalent of ipconfig.
Tracert – Traces the path a packet traverses through a network. It displays the name and IP address of every single device through which the packet passes.
Netstat – Displays what ports are listening on a TCP/IP device
Nbtstat – Displays NetBIOS information
Net – A powerful Windows command. The net use subcommand allows you to view what is currently shared. Research the various ways you can use the net command.
Netdom – Joins a computer to a Windows domain, manages computer accounts on a Windows domain, and establishes trust relationships between Windows domains. It
is available by default with Windows 8 and later.
Nslookup – Queries the Domain Name System (DNS) to obtain domain name or IP address mapping or for any other specific DNS record.
Objective:
Hardware and Network Troubleshooting
Sub-Objective:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot common wired and wireless network problems.
References:
CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam 220-1001 and Exam 220-1002, Chapter 5: Hardware and Network Troubleshooting, 5.7 Given a scenario, troubleshoot common
wired and wireless network problems
https://www.knowledgehub.com/education/test/print/49800801?testId=182327079
Page 55 of 55