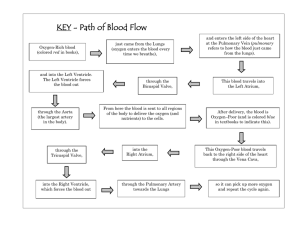
In which of the following reproductive structures does the fertilization of an ovum occur? It occurs in the FALLOPIAN TUBE. - An ovum is a mature female reproductive cell and an unfertilized egg. When it unites with a sperm cell (male reproductive cell), it becomes a zygote. Which type of connection do ligaments create? Ligaments create BONE to BONE connections. - Tendons create MUSCLE to BONE connections. The elbow is what type of joint? The elbow is a HINGE. A patient complaining of pain in their sternum reveals that they were recently in a mild car accident. Which of the following structures may have been injured in the accident? They might have injured their XIPHOID PROCESS. - The xiphoid process is the most bottom part of the sternum. The malleus, incus, and stapes are bones found in the _________. They are found in the EAR. - The malleus, incus, and stapes are tiny bones called ossicles found in the ear. Major passages and structures of the upper respiratory system are : nose, nasal cavity, oral cavity, pharynx (throat), and larynx (voice box). Which of the following is a molecule carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction for all organisms? DNA (Deoxyribonucleic nucleic acid) is a molecule that carries genetic instructions for development, functioning, growth, and reproduction for all organisms. - Ribonucleic acid (RNA) codes for amino acids and acts as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes to make proteins. Which plane divides the body into left and right sides? The SAGITTAL plane divides the body into left and right sides. - Frontal Plane – A vertical plane that divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions. - Median plane – This is a sagittal plane but one that specifically goes through the midline of the body, dividing it into equal left and right halves. - Transverse Plane – A horizontal plane that divides the body into upper and lower parts. Which of the four chambers of the heart has the thickest muscular wall? The LEFT VENTRICLE has the thickest muscular wall. - The right atrium receives oxygen-depleted blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle. - The right ventricle pumps the oxygen-depleted blood to the lungs to be re-oxygenated. - The left atrium receives the re-oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle. - The left ventricle pumps the re-oxygenated blood to the body. Which type of tissue is most widely distributed throughout the body? CONNECTIVE TISSUE is most widely distributed throughout the body. ● Epithelial: these cells cover, line, and protect the body and its internal organs. ● Connective: these cell groups are the framework for the body, providing structure and support for the organs. ● Muscle: tissues that have the ability to contract (shorten). ● Nervous: the tissues of the nervous system, composed of neurons and connective tissue called neuroglia. How does serotonin affect the body? It helps regulate mood, anxiety, sleep, memory, and appetite. - Serotonin is a neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers within the brain that allow communication between nerve cells. Serotonin is involved in regulating mood, stress and anxiety, sleep, overall happiness, and appetite. Low serotonin levels have been linked to depression. Which of the following options correctly lists the layers of the epidermis from the most superficial to the deepest layer? Stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum germinativum The skin (called the integumentary system) is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of two layers: the epidermis (the outermost protective layer made of dead, keratinized epithelial cells) and the dermis (the underlying layer of connective tissue with blood vessels, nerve endings, and the associated skin structures). The layers of the epidermis, from the most superficial layer (outer) to the deepest layer (inner), are: 1. stratum corneum 2. stratum lucidum 3. stratum granulosum 4. stratum germinativum (made up of two sub-sections – the stratum basale and the stratum spinosum). Which of the following best describes the function of the mitral valve? Lets blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle. - Tricuspid valve: This valve is located between the right atrium and the right ventricle. It allows blood to flow from the right atrium into the right ventricle. - Pulmonary valve: The pulmonary valve is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. It allows blood to flow from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery to be taken to the lungs to be re-oxygenated. - Mitral valve: This valve is located between the left atrium and the left ventricle. It allows blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. This valve is also called the bicuspid valve. - Aortic valve: The aortic valve is located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It allows blood to flow from the left ventricle into the aorta. NurseHub Hint: When talking about blood flow, the atrium always comes before the ventricle. Think “A before V.” Which organ is responsible for most of the nutrient absorption in the body? The SMALL INTESTINE is responsible for most of the nutrient absorption in the body. - The small intestine is the part of the digestive system where 90% of the digestion and absorption of food occurs. The main function of the small intestine is absorption of nutrients and minerals from food. A patient complains of decreased sensation in the distal part of their arm and an inability to adduct and abduct their fingers. Based on these symptoms, which nerve is most likely compromised? The ULNAR is most likely compromised. - This is because the distal end of your arm refers to the part of your arm that is away from the point of attachment. This means your lower arm/wrist. The ulnar nerve is one of three main nerves and when compromised, it could result in decreased sensation in the arm. - You have the inability to adduct (pull towards the middle) and abduct (spread out) the fingers. Which of the following is located in the thoracic cavity? The MEDIASTINUM is located in the thoracic cavity. - It is the area in the chest between the lungs that contains the heart, part of the trachea (windpipe), esophagus, ascending aorta, and right/left pulmonary arteries. Which part of the brain is involved in processing auditory information? The TEMPORAL LOBE is involved in processing auditory information because it contains primary auditory context, which receives direct sound input from the ears, so it plays a major role in auditory functioning (hearing). Where is the tibialis anterior located? It is located in the FRONT of the LOWER EXTREMITIES. - Anterior means “towards the front” so tibialis anterior must be located towards the front of the body. Which of the following muscles pulls a body part away from the midline of the body? Abductors pull a body part from the midline of the body. - Adduct (“add” to the body), Abduct (“abduct” - take away), Flexors reduce angle at joint, Extensors increase angle at joint The pulse point located on the neck is palpated over which artery? The pulse point on the neck is palpated over the CAROTID artery and “palpate” means “to examine a part of the body by touch.” - The carotid arteries are in the neck. T-lymphocytes are developed by which of the following glands? T-lymphocytes which are also called T-cells are developed in THYMUS which is located directly posteriorly (behind) to the mediastinum (part of the sternum). Which blood vessel returns blood from the lungs back to the heart? The PULMONARY VEINS return blood from the lungs back to the heart because they are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart. What is secreted by the adrenal glands? The adrenal glands secrete CORTISOL and ALDOSTERONE. - Cortisol is a hormone that regulates a wide range of processes throughout the body and is best known as the body’s “stress hormone.” - Aldosterone affects the body’s ability to regulate blood pressure. Cerumen is secreted by apocrine glands located in which of the following structures? It is the EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL. - Cerumen is ear wax! It is secreted by the ceruminous glands near the outer opening of the auditory (ear) canal, which is located in the external auditory canal. What, in addition to adenosine triphosphate, must be present for a muscle to contract? CALCIUM must be present for a muscle cell to contract along with adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Eccrine glands secrete a watery substance onto the surface of the skin to maintain temperature homeostasis through which process? It maintains temperature homeostasis through EVAPORATION. - Eccrine glands are the most widely distributed sweat glands in the body. When it secretes a watery substance called sweat onto the skin, it cools the body by evaporating. This is called evaporative cooling. - Heat from the body causes the sweat to evaporate which cools the body down because the evaporating sweat takes heat with it. In what area of the body would you expect to find an especially thick stratum corneum? You would find it most likely on the HEEL OF THE FOOT. - This is because stratum corneum is the very top layer of the epidermis and it exists to protect the inner layers. It would make sense to be on the heels of the foot because we are walking all the time and want that part to be thicker. Which part of the eye allows us to see color? The RETINA allows us to see color. - This is because the purpose of the retina is to receive light that the lens has focused, convert it to neural signals, and send those signals to the brain for visual recognition. Which organelle is responsible for storing DNA? The genetic material DNA is found within the membrane-bound NUCLEUS. Mitosis occurs in which layer of the skin? It is STRATUM GERMINATIVUM (innermost layer) because it is the only layer that contains cells that can divide via the process of mitosis so it is the only place that mitosis can occur. A patient reveals to you that they were recently involved in a car accident that they believe resulted in a deviated septum. Which of the following bones may have been injured in the accident, resulting in the deviated septum? The VOMER might have been injured. - The vomer is a thin, vertical bone in the nose. It forms the inferior (back) part of the nasal septum. (part of the nose that separates left and right nostrils). Which of the following describes the distal region of the humerus? The epiphysis that articulates with the radius and ulna because it is the distal epiphysis is the one that is furthest away from your body, therefore it is the end that articulates the bones of your forearm. - Humerus is a long bone. It has 3 sections: diaphysis - middle section (shaft), epiphysis - end of each side of the bone, metaphysis - part where the diaphysis meets each epiphysis - Proximal epiphysis is the end of the bone closest to the point of attachment. - Distal epiphysis is the end farthest away from the point of attachment. Which of the following causes bone matrix resorption in response to a decrease of calcium levels in the blood? OSTEOCLASTS - This is because the parathyroid hormone increases the number and activity of osteoclasts (osteo- means “bone” and clast means “broken”), which are cells that break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood (this process is called bone resorption). Which of the following organelles is responsible for digesting damaged cellular structures, as well as macromolecules and bacteria ingested by the cell? It is LYSOSOMES because they are responsible for intracellular digestion of damaged structures, macromolecules, and bacteria. Which of the following could result from a damaged olfactory nerve? The olfactory nerve is located in the nasal cavity so it is associated with the SENSE OF SMELL. A damaged olfactory could result in a reduced sense of smell maybe entirely. Which of the following describes cellular respiration? It is an OXIDATIVE CATABOLIC ACTIVITY. - Because elements lose electrons to oxygen and it is a reaction in which energy is created, cellular respiration is both an oxidative and catabolic activity. Which of the following types of tissues functions in the covering, lining, and protection of surfaces and body cavities? The EPITHELIAL TISSUE functions as the lining and covering of body surfaces and cavities. The respiratory system is composed of organs that facilitate gas exchange between the blood and the external environment. Which of the following describes the group of organs that function during gas exchange? The group of organs that work together to perform several related functions is an ORGAN SYSTEM. Which of the following cell organelles is correctly paired with its function? Ribosomes are responsible for the synthesis of proteins. White blood cells contain many _________ because they need to dispose of harmful intruders such as bacteria and viruses. Which of the following options correctly completes the statement above? These white blood cells contain a large number of lysosomes because they need to dispose of those harmful intruders such as bacteria and viruses. - Lysosomes are responsible for digesting and removing waste from a cell. This means they can digest the bacteria and viruses that are engulfed by white blood cells in order to protect the body. Which of the types of tissue is responsible for providing the matrix that supports and connects other tissues of the body? Connective tissue is responsible for providing the matrix that supports and connects other tissues of the body. Which of the following is the name of the imaginary vertical plane that equally divides the body into left and right? The sagittal plane is also a vertical plane but it equally divides the body into left and right. Which of the following terms describes the process of forming new red blood cells? ERYTHROPOIESIS - If you remember that red blood cells are also called erythrocytes, it makes sense that - erythropoiesis is the term for forming new red blood cells. “Poiesis” means “to make.” - In the early development of a fetus, erythropoiesis takes place in the yolk sac, spleen, and liver. After birth, all erythropoiesis occurs in the bone marrow. What is one of the functions of the hypothalamus? IT REGULATES BODY TEMPERATURE - The hypothalamus is a small region of the brain that regulates your body temperature, releases hormones, and helps to maintain homeostasis. Which structure lies between the thoracic and abdominal cavities? THE DIAPHRAGM - The diaphragm is a thin muscle that separates the abdominal cavity from the thoracic cavity and is a vital structure when it comes to breathing. When you inhale, the diaphragm contracts, which enlarges the chest cavity and draws air into the lungs. When you exhale, the diaphragm relaxes and the air is pushed out of the lungs. A tissue sample studied under a microscope exhibits the following characteristics: an extracellular matrix providing rigidity to the tissue, and the presence of lacunae. Which type of tissue is this? BONE TISSUE - Bone (particularly spongy bone) is a type of connective tissue that consists of a rigid extracellular matrix. Lacunae are small spaces in the bone tissue. Each lacuna contains an osteocyte, which is a mature bone cell. Which structure in the epidermis is responsible for cooling the body to maintain temperature homeostasis? ECCRINE GLANDS - The epidermal derivative that helps regulate your body temperature are the eccrine glands (also called merocrine glands), which are the glands of the skin that produce a thin, watery secretion (sweat) that cools the body when it evaporates (turns from liquid into a gas). - A derivative of the epidermis (or epidermal derivative) refers to anything that comes out of the epidermis, which is the top and most protective layer of the skin. Epidermal derivatives include sweat glands, sebaceous glands, mammary glands, hair, and nails. In which part of the body would you find aqueous humor? Aqueous humor is the clear liquid found between the cornea and the lens of eye. The aqueous humor helps maintain intraocular pressure and nourishes the lens and cornea. Which of the following about the hyoid bone is correct? The hyoid bone is a U-shaped bone located at the root of the tongue in the anterior (front) of the neck and between the mandible (lower jaw) and the largest cartilage of the larynx (voice box). The primary function of the hyoid bone is to serve as an anchoring structure for the tongue. It is the only bone with no articulation with other bones. This means it is not connected to any other bone. The hormone __________ assists estrogen in stimulating the formation of the endometrium. Progesterone is a hormone produced by the ovaries and is responsible for maintaining the uterine lining, or endometrium. Which of the following structures functions in directing sound waves into the ear? The Auricle (also known as the Pinna) is the part of the external ear that functions in directing sound waves into the ear. Important Note: There are also auricles within the heart. The heart has two auricles, and each one is attached to the anterior surface of the outer walls of both the left and right atria. These pouch-like structures help to increase the capacity of each atrium, which in turn increases the volume of blood each is able to hold. In order to determine which auricle is being discussed in a particular question, look closely for clues that suggest the question is either focused on the ear or the heart. Which of the following is the correct sequence of transport of filtrate from the nephrons to the renal pelvis? Proximal Convoluted Tubule – Loop of Henle – Distal Convoluted Tubule – Collecting Duct – Minor Calyx – Major Calyx – Renal Pelvis - From nephrons, glomerular filtrate is transported from the Proximal Convoluted Tubule to the Loop of Henle, then to the Distal Convoluted Tubule, and finally on to Collecting Ducts. The Collecting ducts come together to form the minor calyces which form the major calyces, and eventually the renal pelvis. The pharynx is a conduit for air and food. It is divided into three segments which contain lymphoid structures that play significant roles in protection and defense. Which segment of the pharynx contains the pharyngeal tonsils? NASOPHARYNX - The Nasopharynx contains the pharyngeal tonsils while oropharynx contains the palatine tonsils. The nasopharynx is exclusive for air passage. The oropharynx is the middle portion that serves as passageway for both food and air. The Laryngopharynx or Hypopharynx is the most inferior portion of the pharynx that also serves as passageway for both food and air. Which of the following salivary glands primarily contributes to the production and secretion of saliva? SUBMANDIBULAR GLANDS - The submandibular glands produce ⅔ of the saliva. If the femoral artery was cut, which of the following blood vessels would not receive blood as a result? POPLITEAL ARTERY - The popliteal artery runs along the back of the knee and is a continuation of the femoral artery. If the femoral artery, which is a large artery, was cut, many arteries that branch off the femoral artery would not receive blood. This includes the popliteal artery. Which blood vessel delivers blood directly into the right atrium? The largest vein, the vena cava, dumps blood directly back into the heart at the right atrium. Which of the following features of veins results in the venous system operating at lower pressures than the arterial side? On the venous side, blood is entering from tissues at much lower pressure because the “pump” activity is not as strong as it is coming from the heart. Additionally, the vessel walls of veins are thinner and more compliant, meaning they stretch more easily, allowing more blood to flow through the venous side but under lower pressure. - This is because the heart develops significant force and pushes blood through the vessel and also because the arteries have thicker, more muscular walls. The components found in blood that carry out blood clotting are: Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are necessary for blood clotting to prevent excessive bleeding. When there is an injury to the blood vessel or tissue, platelets join together to form a clot, thus slowing the bleeding. Which of the following makes up the largest component of whole blood? Blood is composed of two main parts: plasma and hematocrit (i.e. red blood cells). Plasma, the watery portion of blood, makes up roughly 55% of total blood volume with the remaining 45% coming mostly from red blood cells, or erythrocytes. White blood cells and platelets make up a very small portion of total blood. Which system coordinates and regulates processes within the body through the use of hormones? The endocrine system coordinates and regulates processes within the body through the use of hormones. The anterior lobe of pituitary glands is called which of the following? ADENOHYPOPHYSIS - The pituitary gland has two major portions, the anterior lobe and the posterior lobe. The anterior lobe is known as the adenohypophysis, and the posterior lobe is known as the neurohypophysis. Which of the following gets absorbed directly into the blood? Amino acids and simple sugars get absorbed directly into the blood. ● Amino acids are the building blocks for polypeptides. Polypeptides are then used to build proteins. ● Simple sugars are chains made up of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms. Simple sugars are the building blocks of carbohydrates. The diaphragm is _________ to the lungs. Inferior is the correct term, as the diaphragm is located below the lungs. Which glands release an oily secretion through the hair follicles that lubricates the skin and prevents drying? Sebaceous glands release an oily secretion through the hair follicles called sebum that lubricates the skin and prevents drying. What is the outermost layer of the epidermis? STRATUM CORNEUM - The skin consists of two layers: epidermis (the outermost protective layer made of dead, keratinized epithelial cells) and the dermis (the underlying layer of connective tissue with blood vessels, nerve endings, and the associated skin structures). - The layers of the epidermis, from the outer layer to the inner layer, are the stratum corneum, the stratum lucidum, the stratum granulosum, and the innermost stratum germinativum (which includes the stratum basale and the stratum spinosum). Listening to music stimulates which of the following organs? The cochlea is the part of the ear that functions in hearing. - The utricle, saccule, and semicircular canals, on the other hand, play roles in balance and equilibrium. What form of tissue provides support and structure for the organs? Connective tissue serves as the framework of the body, providing support and structure for the organs. - Connective tissue is the most abundant, widely distributed, and varied type of tissue. It includes ligaments, tendons, fat, cartilage, bone, bone marrow, and blood. Like the name implies, connective tissues often bind organs together, hold organs in place, cushion them, and fill space. Which exocrine gland produces sweat on the epidermal surface? The epidermis is the top layer of your skin. Eccrine glands (also called merocrine glands) produce a thin, watery secretion (sweat) directly onto the surface of the epidermis that cools the body when it evaporates. What type of cell division occurs in the gonads? Gametes are produced through the process of meiosis. - In meiosis, one cell divides twice to produce four daughter cells, each containing half the original amount of chromosomes (the chromosomes are reduced from 46 to 23). This is important because when a sperm and ovum unite, the zygote (fertilized egg) will contain the full number of chromosomes – 23 from each parent. Which of the following hormones is primarily produced and secreted by the male reproductive system? Testosterone is the primary male reproductive hormone and is responsible for producing sperm, as well as regulating the development of secondary sex characteristics such as facial and body hair, muscle, and bone mass. Which of the following is the primary organ of the female reproductive system responsible for releasing mature eggs? The ovaries are located in the female pelvic region and have the primary role of releasing eggs every month during menstruation. - In addition, they produce and release estrogen, which is the primary female reproductive hormone. Ovaries exist in pairs, with one on each side of the uterus. Which of the following is a primary function of the male and/or female reproductive systems? The reproductive systems of both males and females have two primary roles which are: producing gametes (i.e. sex cells) and producing the hormones testosterone and estrogen. Gametes (egg cells in females and sperm in males) are cells produced by the reproductive system that contain one set of chromosomes Reabsorption of water and electrolytes occur in various parts of the renal tubules. In which segment is sodium mostly reabsorbed? 60% of Na+ is reabsorbed in Proximal Convoluted Tubules while 30% is reabsorbed in the thick ascending Loop of Henle. The remaining 10% is reabsorbed in Distal Convoluted Tubules and Collecting Ducts. Which muscle is located towards the front of the lower leg? The tibialis anterior is located towards the front of the tibia (the shin bone). The tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi is called ____________. The trachea is the tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi. The _______________ artery is located in the upper arm, and is a continuation of the ________________ artery. The brachial artery is located in the upper arm and supplies blood to the upper arm region. Since the path of blood flow moves from proximal to distal, or away from the heart, the brachial artery is a continuation of the more proximal axillary artery which originates in the axilla, or underarm area. The _________________ carry oxygen rich blood away from the heart, while the ________________ carry oxygen-depleted blood back towards the heart. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the body. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood low in oxygen from the body back to the heart to be reoxygenated. Arteries and veins are two of the body’s main types of blood vessels. The right atrium receives blood from the __________. The vena cava is the large vein that delivers blood into the heart at the right atrium. - The heart is composed of four primary chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The right side of the heart, which includes the right atrium and the right ventricle, receives blood from the body through the vena cava and sends it to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The oxygenated blood returns to the heart at the left side, specifically the left atrium, and then the left ventricle. The left ventricle then ejects blood to the body. The atria act as collection chambers, while the ventricles are the primary pumps of the heart. - The aorta is the larger artery that blood passes through when it leaves the left ventricle. The heart consists of four chambers, which include _________________. right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle - The right side of the heart, which includes the right atrium and the right ventricle, receives blood from the body and sends it to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The oxygenated blood returns to the heart at the left side, specifically the left atrium, and then the left ventricle. The left ventricle then ejects blood to the body. The functions of the circulatory system include all of the following except: to deliver carbon dioxide to body tissues Which of the following is not a function of cortisol? Release growth hormones Which gland releases melatonin? Pineal glands Which of the following acts as a store for fats and aids in bone function? Yellow bone marrow acts as a store for fats and aids in bone function. Skeletal muscles work in pairs. The muscle that executes the given movement is called which of the following? Skeletal muscles must work in pairs: the muscle that executes a given movement is the prime mover. Wrist bones are called which of the following? Carpals -anything beyond the wrist is carpals An irregular epiphysis at each end is present in which of the following? A typical long bone has an irregular epiphysis (the end of the bone) at each end, composed mainly of spongy (cancellous) bone, and a shaft or diaphysis, composed mainly of compact bone. Which of the following muscles draw the limb away from the midline? Abductors draw a limb away from the midline. Which vertebrae fuse to form the sacrum? There are five sacral vertebrae in the vertebral column which fuse to form the sacrum. What connects skin to superficial muscles? The dermis rests on the subcutaneous tissue that connects the skin to the superficial muscles. Stratum basale and stratum spinosum are included in which layer of the epidermis? The stratum germinativum layer, where mitosis occurs, comprises the stratum basale and the stratum spinosum. What type of animal tissue is composed of neurons and neuroglia? Nervous tissue is made up of uniquely specialized cells, neurons and neuroglia. - Neurons that transmit signals (messages) between the different parts of the body and neuroglia are connective tissue cells that support the neurons. This tissue allows the body to be able to use the five senses to inform the brain about stimuli it experiences and subsequently react accordingly. If you were to cut the body through the median plane, what type of sectioning would occur? A sagittal section would occur if you cut the body through the median plane, which is a sagittal plane that divides the body into exactly its left and right halves.