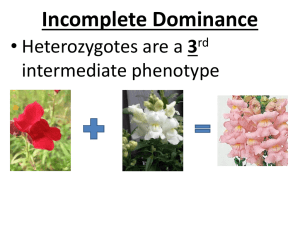
GOOD MORNING TEACHER KEREEN KATE RODA I X e d a r G Pi MEETING REMINDERS Please mute your microphone unless you are asked a question. Don't interlap when someone is speaking or answering. State your name if you want to answer or ask a question. Be respectful and attentive during the discussion. LET'S RECALL Test your vision Test your vision ? ? ? Compare NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS OBJECTIVES distinguish Mendelian from non-Mendelian describe some cases of nonmodes of Mendelian genetic inheritance traits explain sexrelated inheritance distinguish sexlinked traits from other sex-related trait NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS Non-Mendelian inheritance is any pattern of inheritance in which traits do not segregate in accordance with Mendel's laws. MENDELIAN VS. NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS GENETICS the way in which genes and their corresponding traits are passed from parents to their offspring by means of dominant and recessive alleles involve only two alleles two alleles are either dominant or recessive phenotypic proportions can be pre determined theoretically phenotypic traits of pea plants the patterns of inheritance which do not follow the Mendelian inheritance involve multiple alleles or polygenes two alleles are neither dominant or recessive phenotypic proportions differ from theoretic proportions examples include many human traits NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS THE SECOND CONCEPT THE FIRST CONCEPT Incomplete Dominance and Codominance Multiple Alleles THE THIRD CONCEPT Sex Linkage INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE A case in which one allele is not completely dominant over another Homozygous red flowers (RR) when crossed with homozygous white flowers (rr), will produce a heterozygote (Rr)pink flowered plants. White rr Red RR Pink Rr Snapdragon plants CODOMINANCE When both alleles contribute to the phenotype Colors are not blended; they appear separately. Heterozygote simultaneously expresses the phenotypes of both homozygotes A B AB O MULTIPLE ALLELES When there are more than two types of alleles for a given locus or trait, this will result in more than two kinds of phenotypes that may be expressed for that trait. AGOUTI: AGOUTI: dominance hierarchy: C> cch>ch> c AGOUTI: i. CC – Agouti ii. Ccch – Agouti iii. Cch – Agouti iv. Cc – Agouti v. cchcch – Chinchilla vi. cchch – Chinchilla vii. cchc – Chinchilla viii.chch – Himalayan ix. chc – Himalayan x. cc – Albino Inheritance of the ABO blood types in humans involves multiple alleles. Inheritance of the ABO blood types in humans involves multiple alleles. SEX LINKAGE is the phenotypic expression of an allele that is dependent on the gender of the individual and is directly tied to the sex chromosomes. SEX CHROMOSOMES are responsible for the sex or gender of the carrier while autosomes carry all other genes of an organism. In humans, you have learned that females contain two X chromosomes (XX) while males have one X and one Y chromosomes (XY). The sex of humans is determined by the presence or absence of a Y chromosome The inheritance of genes located in the sex chromosomes is referred to as SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE Anne Boleyn Henry VIII SEX-LINKED TRAITS is the phenotype produced by a recessive gene that is located on the sex chromosome X-LINKED TRAIT Y-LINKED TRAIT A sex-linked trait is where the gene or allele for the trait is found on the X chromosome A sex-linked trait where the gene or allele for the trait is found on the Y chromosome. X-LINKED TRAIT Color blindness An X-linked recessive trait where an affected individual could not distinguish red from green color (red green color blindness). The color blindness gene is located on the X chromosome, so men are more likely to be color blind than women. TRIVIA Ishihara test is a common color perception test to determine color blindness in a person. The test consists of pseudo-isochromatic plates that contain dots that appear in random sizes and colors. It was first developed by Dr. Shinobu Ishihara in 1917 at the University of Tokyo. Persons with normal vision will often see a number at the middle of PIP whereas those with color blindness will not recognize any number or will see a different number. X-LINKED TRAIT Hemophilia An X-linked recessive trait where an affected individual suffers from delayed blood clotting during injuries because of the absence of certain blood clotting factors Y-LINKED TRAIT Hypertrichosis pinnae auris a phenotypic trait observed mainly on the human ears. It has been described as the presence of hairs on the lower part of the distal half of the helix of the ears. SEX INFLUENCED TRAIT Any trait in a diploid organism whose expression is affected by an individual’s biological sex; a trait that occurs at a higher frequency in one sex over the other. Sex-influenced traits follow the Mendelian pattern of dominance and recessiveness. However the effect in one sex is dominant whereas it is recessive in another sex. male-pattern hair loss female-pattern hair loss SEX LIMITED TRAIT Any trait in a diploid organism whose expression is limited to just one biological sex Functional mammary glands as an example of a sexlimited trait. Only females can express functional mammary glands that produce milk immediately after giving birth. SEX-LINKED TRAITS caused by genes in X or Y chromosomes SEX-INFLUENCED TRAITS Autosomal trait expressed more frequently in one sex than another. -trait modified by the sex of the individual -male pattern baldness is more frequent in males due to sex hormones differences. SEX-LIMITED TRAIT Autosomal trait expressed ONLY in one sex. -due to anatomical but not genetical differences -uterine defects or sperm motility problems A local hospital has sent word to a family of a possible mix up of some of the children with other families when they were born. To rule out any possible mix up, the hospital obtained the blood types of every individual in the family, including the surviving maternal grandfather and paternal grandmother. The results were as follows: Father: Type O Mother: Type A 1st child: Type O 2nd child: Type A 3rd child: Type B Maternal grandfather: Type AB Paternal grandmother: Type B The police have rounded up the usual suspects in the latest rash of bookstore robberies. The thief got a nasty paper cut at the scene of the crime. The suspects are of blood type A, B, AB, and O. The blood at the crime scene contained i alleles. Which suspect therefore cannot have been involved? Explain. The last Emperor of Russia, Nicolas II, was married to Empress Alexandra, and they had five children, Olga, Tatiana, Maria, Anastasia, and Alexis. Alexis was the only one who was afflicted with hemophilia or the royal bleeding disease; all other members were normal. • If only Prince Alexis was afflicted with the disease, determine his genotype. • What could be the genotypes of the Emperor and Empress? • Is it possible that each daughter could have been a carrier? Explain THANK YOU DO YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS?