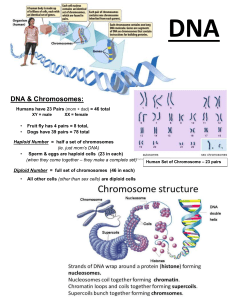
SBI3U Biology Notes: Chromosomes Word NAME: Karyotype Definition Having two copies of each chromosome. One is the maternal copy and one is the paternal copy. Identified as ‘2n’ (n = number of chromosomes). Body cells are diploid cells. Having only one copy of each chromosome (or half of a full, diploid set). Identified as ‘n’ Sex cells are haploid cells Pairs of chromosomes that are the same size, shape, banding pattern and have the same genes in the same order but may have different alleles. Chromosomes that determine non-sexual traits. In humans these are the first 22 homologous chromosome pairs. Chromosomes that determine sex. In humans these are the 23rd pair of chromosomes. XX is a female and XY is a male. This pair is not homologous. When there is one extra chromosome in a person/embryo (three copies of a chromosome) When there is one too few chromosomes in a person/embryo (one copy of a chromosome) A picture of an embryo or fetus’s chromosomes. They are used to determine gender and if there are any chromosomal abnormalities Property of a cell that refers to the number and types of chromosomes it contains Plasmid Small, circular loops of DNA found in prokaryotes that carry extra genetic material Autoradiography A method for visualizing DNA and measuring its length by labeling the DNA with a radioactive isotope of Hydrogen. Diploid Haploid Homologous chromosomes Autosomes Sex chromosomes Trisomy Monosomy Karyogram Prokaryotes have one chromosome consisting of a circular DNA molecule. How many copies of each gene do prokaryotes have? Why is prokaryotic DNA considered ‘naked?’ Some prokaryotes also have plasmids but eukaryotes do not. Cairn’s technique for measuring the length of DNA molecules by autoradiography. Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. In a eukaryotic species there are different chromosomes that carry different genes. Homologous chromosomes carry the same sequence of genes but not necessarily the same alleles of those genes. Comparison of genome size in T2 phage, Escherichia coli, Drosophila melanogaster, Homo sapiens, and Paris japonica. Organism Genome size (million base pairs) T2 Phage Escherichia coli Drosophila melanogaster Homo sapiens Paris japonica Use of online databases to identify locus of a human gene and its protein product. Gene Name CFTR HBB F8 TDF Description Description Haploid nuclei have one chromosome of each pair. How many chromosomes in a haploid human cell? What types of cells have diploid nuclei? Diploid nuclei have pairs of homologous chromosomes. How many chromosomes in a diploid human cell? The number of chromosomes is a characteristic feature of members of a species. Comparison of diploid chromosome numbers of Homo sapiens, Pan troglodytes, Canis familiaris, Oryza sativa, and Parascaris equorum. Scientific Name Parascaris equorum Oryza sativa Homo sapiens Pan troglodytes Canis familiaris Common Name Diploid Chromosome Number Sex is determined by sex chromosomes and autosomes are chromosomes that do not determine sex. A karyogram (karyotype) shows the chromosomes of an organism in homologous pairs of decreasing length. Use of karyotypes to deduce sex and diagnose Down syndrome in humans. What types of cells have haploid nuclei? What features are used to distinguish chromosomes when assembling a karyotype? State the sex of each karyotype and whether or not there is a chromosomal abnormality. Circle the karyotype that shows a Down Syndrome fetus: