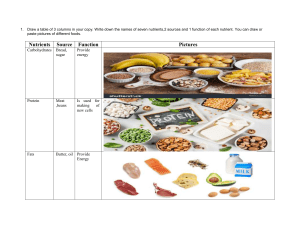
-Salmonella raw/undercooked poultry, poultry products (ex. eggs, meat, fish, dairy products, unpasteurized apple cider/juice Symptoms: cramps, nausea, fever & diaherra -E.coli raw ground beef, undercooked meat, unpasteurized milk, apple cider/juice Symptoms: serve abdominal cramps, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, kidney failure, brain damage + death -Listeria ice cream, deli meats, frozen yogurt, poultry, meat, seafood, milk + cheese products Symptoms: headaches, fevers, chills, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea + backache -Botulism under processed foods, canned low acid foods, untreated garlic oil Symptoms: constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, fatigue, muscle weakness, blurred vision + paralysis death -Hepatitis A water, ice, cold cuts, milk, milk products, fruit juice, vegetable, shellfish Symptoms: fatigue, discomfort, fever, headache, nausea, loss of appetite, jaundice + diarrhea -Giardiasis water, ice, salad Symptoms: cramps, nausea, intestinal gas, fatigue -Nutrition the study of nutrients and how they are used by the body -Nutrients substances found in food and needed by the body to function, grow and repair itself and produce energy. These are the fuel for cell activity -Types of Nutrients Macronutrients 1. nutrients needed by the body in large amounts (more than 1g) ex:Carbohydrates, Protein and Fat Micronutrients 2. nutrients needed by the body in small amounts (less than 1g) ex:minerals and vitamins -Recommended Daily intake of Carbs:55% -Recommended Daily intake of Protein:15% -Recommended Daily intake of Fat: 30% -Grocery Store Safety 1. Buy cold/frozen foods at the end of your shopping 2. Look for tags from a federally or provincially inspected plant 3. Put raw foods in individual plastic bags and pack separately in reusable bags 4. Always keep raw, meat, poultry and seafood cold 5. Refrigerate them as soon as you go home 6. Use pre-packaged deli meat within 4 days, preferably 2-3 days, after opening even if the data is different that the best-before-date 7. Best-before-date only applies to unopened packages 8. Always check all cans for bulging lids, bottoms , leaky seams or lids,dents and rust -Food Safety 1. Make sure your refrigerator is set to 4°C (40°F) or lower and your freezer is at -18°C (0°F) or lower. 2. Always store eggs in original carton 3. Don't pack your fridge with food - cold air must circulate to keep foods safe 4. Check the temperatures in your refrigerator using a thermometer 5. Use the "FIFO" method for proper food rotation 6. Date your foods so you know which is the oldest and needs to be used first 7. Do not mix left over products with new food items Refrigerator: 1. Top Shelf ready to eat foods ex. salads, sandwiches, cooked meat, vegetables, cheese + dairy) 2. Upper Middle Shelf products that need to be washed but no further temperature adjustment ex. unwashed fruits + vegetables) 3. Lower Middle Shelf left over that needs to be re-heated before eating ex. leftover pasta and pizza 4. Bottom Shelf raw/uncooked meats ex. poultry, meat, fish -Danger Zone 4°C bacteria freezes --> doesn't grow but doesn't die -Danger Zone 4°C - 60°C after 2 hours, bacteria doubles every 20 minutes -Danger Zone 60°C heat kills bacteria -Types of Carbs 1. Simple -usually found in foods with fewer nutrients and tend to be less satisfying and more fattening ex:table sugar, corn syrup, candy, white bread, cake and etc 2. Complex -starches - main ingredient for this dietary fibre - important for maintaining good health (ex. apply, spinach, yam, carrot and etc) -Ways Nutrients Work 1. They give you energy 2. they're needed for growth, maintenance and repair of the body 3. They keep the different systems in your body working smoothly -6 Types of Nutrients Carbohydrate, Protein, Fat, Vitamin, Minerals and Water -Functions of fibre 1. absorb water to prevent constipation 2. speeds transit times (food in your body) 3. increase fecal volume 4. binds toxic foods and may help prevent cancer -Benefits of fibre 1. may lower heart/artery diseases 2. may reduce risk of colon cancer 3. help control type 2 diabetes -Protein should take up 15% of daily intake. it is 1/5 of body weight -Functions of Protein 1. Build and maintain tissues --> necessary part of every cell --> makes new tissues 2. makes important compounds - like enzymes for digestion, hormones, antibodies and etc 3. Main acid base balance - balance in blood - can act as a buffer if blood is too acidic 4. Provides energy - body's priority is to produce cells with energy - if carbs/fats are lacking, it will take over to provide body with energy