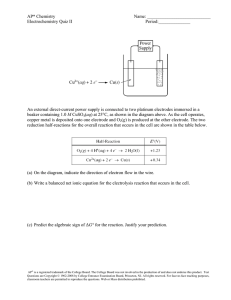
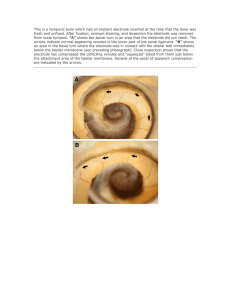
pdfcoffee.com gastat-700-model-service-manual-version-13-4-pdf-free
advertisement

Blood Gas System GASTAT-700 Model SERVICE MANUAL Version# 1.3 TECHNO MEDICA Co., Ltd. MT Promedt Consulting GmbH 5-5-1, Nakamachidai, Tsuzuki-ku, Yokohama, Altenhofstrasse 80, D-66386 Kanagawa 224-0041 JAPAN St. lngbert, Germany 1 Record of change Version Date Author Change Description 1.1 December, 2017 Yasushi Hoshijima 1.2 June, 2018 Yasushi Hoshijima Spare parts list has been modified. 1.3 December, 2018 Hiroyuki Yaginuma A/D Value Reading (page.51) 2 INTRODUCTION Before Use Thank you very much for purchasing our GASTAT-700 Model. Although GASTAT-700 Model is designed to provide you with the utmost safety during use, incorrect usage or disregard of the instructions can cause personal injury or property damage. For your safety, read this manual carefully and thoroughly before using GASTAT-700 Model. Do not discard this manual but keep it near the product for easy reference. In this manual, safety instructions are indicated with the symbols shown below. Be sure to follow the instructions indicated with these symbols to ensure correct and safe operation. Techno Medica shall not be responsible for any accident or malfunction that occurs as a result of negligence to the directions or cautions in this manual. Disclaimer TMC does not bear responsibility for any damage caused by fire, earthquake, acts by third parties, other accidents, customer's intentions or negligence, misuse, or usage under abnormal conditions. TMC does not bear responsibility for any incidental damage (loss of business interest, interruption of business, change / loss of memory contents etc.) resulting from the use or out of use of this product. TMC does not bear responsibility for any damage caused by other usage than described in the operation manual. 3 About Service Manual This service manual is described for the technical people who completed GASTAT-700Model technical training. On the occasion of maintenance, repair of the GASTAT-700Model, the contents of this manual come to offer the beiggest security to you, but may cause the disregard bruch of wrong measures or instructions or the material damage. For your security, please carefully and completely understand this manual before maintenance, repair of the GASTAT-700Model. Preface & Warning / Caution Symbols in this manual In this manual, safety instructions are indicated with the symbols shown below. Warning indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury. Caution indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate injury or product damage. NOTE: NOTE indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in slight injury or product damage. This symbol indicates prohibited actions that must not be performed during maintenance or operation of the instrument. This symbol indicates mandatory actions that must be performed during maintenance or operation of the instrument. 4 Terms and Condition of this manual Any or all of this manual should not be reused or reprinted without written permission of Techno Medica. Contents of manual might be changed without notice. TechnoMedica assumes no liability for damages incurred directly or indirectly from errors, omissions or discrepancies between the instrument and the manual. ©Copyright 2016 Techno Medica Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Necessary testing machine and tooling reparations This section describes GASTAT-700Model repair. the testing machine and tools required for The tester and tools required for the repair of instrument are as follows:Items that is described as "N/A" to "Part #" in table is domestic procurement products. Part # Type " Use purpose N/A Driver Electrical multi-meter Various check N/A With USB key board Display operation USB Mouse N/A USB FLASH Memory, Retrieving data and update of software ≧128Mb Pseudo electrode Check of pH and electrolyte electrode Pseudo electrode PO 2, check of GlcLac electrode (with 100 MΩ, 0.5%) Cable of resistance come Temperature circuit adjust with a (6.1kΩ, 0.05%, TK15) GASTROL-QC Navi after instrument repair AQC forcep N/A Screw The attachment of the tube Driver, Torx Desorb of screw T6,T10,T20 N/A 1.5 mm hex wrench Desorb of screw N/A 2.0 mm hex wrench Desorb of screw N/A 2.5 mm hexagonal wrench Desorb of screw N/A Screw Driver, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 Desorb of screw mm Pozidrive Parallel port Loop-back Check of PC unit Connector RS232 Loop-back connector Check of PC unit 5 GASTAT-700 Model ES7 Windows Embedded Standard 7(ES7) software update Windows ES7 Hotfix Windows ES7 software update GASTAT-700 Model Analyzer Install the GASTAT-700-application software Software, V4.141 Identification number GASTAT-700Model consists of multiple modules, and each module is assigned a unique identification number. This identification number consists of module number and individual Serial No, and it is used for a variety of purposes such as securing of the aircraft. Example: 081701001 of identification number Instrument module configuration The apparatus is configured than module that in the table below. Module Module ID Base Module* XXXX01YYY EL Module* XXXX02YYY Manifold Module* XXXX03YYY Sample Port Module* XXXX04YYY Pump Module* XXXX05YYY Preheater1 Module* XXXX06YYY Preheater2 Module* XXXX07YYY Display Module* XXXX08YYYY Power Module* XXXX09YYY Hb Module* XXXX10YYY OXY Module XXXX11YYY Printer Module* XXXX12YYY BC Scanner Module* XXXX13YYY Hemolysis Module K36718 *:Basic module 6 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION ................................................................................. 3 Before Use .............................................................................................................................. 3 About Service Manual ............................................................................................................ 4 Necessary testing machine and tooling reparations ................................................................ 5 Identification number .............................................................................................................. 6 Instrument module configuration ........................................................................................ 6 GENERAL INFORMATION ............................................................................................... 14 System Description ............................................................................................................... 14 Electrode ............................................................................................................................... 15 Reagents ................................................................................................................................ 17 MODULE OVERVIEW ..................................................................... 20 Flow System ......................................................................................................................... 20 PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and module configuration ................................................... 22 Measurement module............................................................................................................ 23 Machine part ...................................................................................................................... 23 Analog Part PCB ............................................................................................................... 24 LED PCB part ................................................................................................................... 24 Main heater and preheater ................................................................................................. 24 Manifold module .................................................................................................................. 24 Valve .................................................................................................................................. 24 Manifold ............................................................................................................................ 25 Cartridge Holder ................................................................................................................ 25 Manifold PCB ................................................................................................................... 25 Sampling module .................................................................................................................. 26 Sample Port ........................................................................................................................... 27 Pump module ........................................................................................................................ 30 OXY module ......................................................................................................................... 31 OXY module ..................................................................................................................... 32 Hb module ............................................................................................................................ 33 Hb module degradation chart ............................................................................................ 33 Printer module ...................................................................................................................... 34 Barcode scanner module ....................................................................................................... 35 Barcode scanner ................................................................................................................ 35 Human motion sensor........................................................................................................ 35 Display module ..................................................................................................................... 36 7 LCD display ...................................................................................................................... 36 Touch panel ....................................................................................................................... 36 Control box module .............................................................................................................. 37 CPU PCB........................................................................................................................... 37 SBC ................................................................................................................................... 37 Power source ..................................................................................................................... 38 Drive .................................................................................................................................. 38 Software configuration ...................................................................................................... 39 Security Code........................................................................................................................ 41 TEST mode........................................................................................................................ 48 A/D Value Reading ............................................................................................................ 51 Draw out Liquid from Flow System ..................................................................................... 52 System Rebooting ................................................................................................................. 54 Calibration ............................................................................................................................ 56 Calibration Report ............................................................................................................. 56 Calibration Error Threshold .............................................................................................. 58 Expected value for Calibration Report .............................................................................. 59 Calibration Error Flag ....................................................................................................... 60 Count Report ......................................................................................................................... 62 Total Count ........................................................................................................................... 62 Sample Count........................................................................................................................ 63 Sample Count Divided .......................................................................................................... 63 Error flag for Count Report .................................................................................................. 64 Bubble detected Group1,Group3,Group4,Group5 ............................................................ 64 Bubble detected Group2 .................................................................................................... 64 Sample lack in Group1,Group3,Group4,Group5 .............................................................. 65 Error flag for Count Report .................................................................................................. 66 Procedure to Get Log File..................................................................................................... 67 Calibration history ............................................................................................................. 67 AutoQC LOG .................................................................................................................... 68 Data exchange ................................................................................................................... 69 Log output ......................................................................................................................... 71 MAINTENANCE ................................................................................ 72 Preventive Maintenance ........................................................................................................ 72 External Cleaning .............................................................................................................. 72 Hb Cleaning....................................................................................................................... 76 Valve Cleaning ...................................................................................................................... 82 8 INSTRUMENT CHECK .................................................................... 86 Consumable Amount Check ................................................................................................. 86 Printing Consumable Amount Status .................................................................................... 87 Consumable replacement alert .............................................................................................. 88 Printing paper check ............................................................................................................. 89 Self Diagnostic...................................................................................................................... 90 Electrode check ................................................................................................................. 90 Flow check ........................................................................................................................ 93 FS (flow sensor) calibration check .................................................................................. 100 Valve check ..................................................................................................................... 104 Temperature check .......................................................................................................... 106 GND check ......................................................................................................................... 109 Flow cell check (Hb unit) ................................................................................................... 112 Flow cell check (OXY unit) ................................................................................................ 113 Sensor of CAL Cartridge and Bottle check ........................................................................ 114 Printer check ....................................................................................................................... 115 Software version check ....................................................................................................... 116 FLOW SEQUENCE ........................................................................................................... 117 Tube Diagram ..................................................................................................................... 119 Sequence Diagram .............................................................................................................. 120 Regular Flush Sequence .................................................................................................. 121 Calibration sequence ....................................................................................................... 125 FLUSH cleaning sequence after Calibration ................................................................... 135 Syringe Measurement sequencee .................................................................................... 137 Capillary measurement sequence .................................................................................... 143 CRS measurement sequence ........................................................................................... 149 QC measurement sequence ............................................................................................. 154 AQC Measurement sequence .......................................................................................... 164 Dialysate measurement sequence .................................................................................... 176 Micro mode measurement sequence ............................................................................... 184 Self diagnostic (Electrode) sequence .............................................................................. 189 Self diagnostic(flow) sequence ....................................................................................... 196 Self diagnostic (flow sensor calibration) sequence ......................................................... 205 Self diagnostic (Valve) sequence..................................................................................... 208 Internal cleaning introduction sequence .......................................................................... 214 Internal cleaning sequence .............................................................................................. 215 External cleaning introduction sequence ......................................................................... 221 External cleaning sequence ............................................................................................. 222 9 Replacement .................................................................................. 225 Periodic replacement part ................................................................................................... 225 Other tubes ...................................................................................................................... 225 Battery ............................................................................................................................. 226 Unscheduled replacement part ............................................................................................ 227 Sampling port door .......................................................................................................... 227 Fuse ................................................................................................................................. 228 Sampling nozzle .............................................................................................................. 229 Flow sensor ..................................................................................................................... 230 Touch panel display module ............................................................................................ 231 Printer unit ....................................................................................................................... 232 Hb unit & lighting source ................................................................................................ 233 OXY unit, hemolysis unit and light source ..................................................................... 235 Electrode module unit ..................................................................................................... 238 Sampling module............................................................................................................. 239 Manifold unit & Valve ..................................................................................................... 240 Barcode scanner unit ....................................................................................................... 243 Preheater unit................................................................................................................... 244 CPU/PC-BOX (remain SBC) .......................................................................................... 245 SBC ................................................................................................................................. 247 fan .................................................................................................................................... 249 Pump unit ........................................................................................................................ 251 SSD.................................................................................................................................. 252 Troubleshooting chart ................................................................. 254 Flow path flowchart ........................................................................................................ 255 I/F system flow chart ....................................................................................................... 258 Standby Screen Checking ................................................................................................... 260 "○ Ready " status ............................................................................................................. 261 "× Measurement " Unable status ..................................................................................... 261 Errors Displays in Instrument Status Field ......................................................................... 262 Errors Displays in Electrode Status Field ........................................................................... 263 Check method of Electrode condition ............................................................................. 263 Coping at calibration error .............................................................................................. 267 Calibration failure of pH/Na/K/Cl/Ca ............................................................................. 269 Calibration failure of Ref ................................................................................................ 270 Calibration failure of pCO2 and pO2 .............................................................................. 271 Hb/OXY troubleshooting ................................................................................................ 274 10 troubleshooting of flow path ........................................................................................... 275 troubleshooting of errors and navigation systems .............................................................. 276 Temperature Error (Error code 03600) ............................................................................ 278 Flow sensor error ............................................................................................................. 280 Measurement module cover is open ................................................................................ 282 Flow cell installation error (Error code 03744) ............................................................... 282 Waste bottle error (Error code 03703) ............................................................................. 283 Flush bottle empty error (Error code 03731) .................................................................. 283 CAL Cartridge empty error ............................................................................................. 284 Battery error (03803) ....................................................................................................... 285 No calibration conduct error (Error code 03802) ............................................................ 286 Calibration error .............................................................................................................. 288 Barcode Error...................................................................................................................... 289 Printer Error ........................................................................................................................ 289 Display Problem ................................................................................................................. 290 Touch-panel calibration ...................................................................................................... 291 Troubleshooting QC Analysis ............................................................................................. 292 If you get bad GASTROL-QC results ............................................................................. 292 Auto QC Measured value error ....................................................................................... 293 Q&A ................................................................................................... 294 System trouble .................................................................................................................... 294 Function and utility ............................................................................................................. 297 Communication error with HIS/LIS ................................................................................... 298 Status of the power ............................................................................................................. 300 Software invocation ranking and troubleshooting .............................................................. 302 Adjustment Nozzle position ............................................................................................... 303 Error code ....................................................................................... 306 Service error code ............................................................................................................... 306 Error category .................................................................................................................. 306 Error code form ............................................................................................................... 306 Sequence code ................................................................................................................. 307 Error code ........................................................................................................................ 308 Hardware error .................................................................................................................... 328 PCB error......................................................................................................................... 328 Spare parts ..................................................................................... 330 Main module and cover ...................................................................................................... 330 11 EL Module .......................................................................................................................... 332 Manifold Module ................................................................................................................ 334 Sampling Module................................................................................................................ 337 Pump Module...................................................................................................................... 339 Display Module .................................................................................................................. 340 Power Supply Module ........................................................................................................ 341 HB Module ......................................................................................................................... 343 OXY Module ...................................................................................................................... 345 Printer Module .................................................................................................................... 347 Barcode Reader Modules .................................................................................................... 348 PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and connection point ............................................................ 349 CPU (Central Processing Unit) PCB (Printed Circuit Board)......................................... 349 PSR (Photo Solder Resist) PCB (Printed Circuit Board) ................................................ 350 Full Analog PCB (Printed Circuit Board) ....................................................................... 351 LED PCB (Printed Circuit Board) .................................................................................. 352 Hb Meter PCB (Printed Circuit Board) ........................................................................... 352 Hb PCB (Printed Circuit Board) ..................................................................................... 353 Hb LED PCB (Printed Circuit Board)............................................................................. 353 OXY Meter PCB (Printed Circuit Board) ....................................................................... 354 Neon Driver PCB (Printed Circuit Board) ...................................................................... 354 OXY LED PCB (Printed Circuit Board) ............................................................................ 355 Neon Light PCB (Printed Circuit Board) ........................................................................... 355 Power PCB (Printed Circuit Board) ................................................................................ 356 Valve Div PCB (Printed Circuit Board) .......................................................................... 357 Printer PCB (Printed Circuit Board) ............................................................................... 358 SBC PCB (Printed Circuit Board) ................................................................................... 359 TROUBLE SHOOTING ................................................................. 361 Calibration failure ............................................................................................................... 361 Trouble Shooting Flow .................................................................................................... 362 Error on ISE parameter ................................................................................................... 363 Error on GAS parameter ................................................................................................. 365 Error on enzyme parameter ............................................................................................. 367 Error on Hb parameter..................................................................................................... 369 Error on all parameter ..................................................................................................... 369 Bad QC result .................................................................................................................. 370 Software upgrade (procedures to upgrade SH (Micro computer)) ..................................... 375 Interface setting ............................................................................ 380 12 Set up Instrument ................................................................................................................ 380 Network settings .............................................................................................................. 381 Communication Specification ................................................... 383 Barcode Configuration........................................................................................................ 384 Data Flow............................................................................................................................ 386 String Format ...................................................................................................................... 388 13 GENERAL INFORMATION System Description Below chart describes a model name of GASTAT-700 Model and their consumables. Reagent Model CAL Cartridge 710 CAL Cartridge pH, pCO2, pO2, Flow pH, pCO2, pO2, cHb cell, TH, Ref 710aqc AQC CAL Cartridge pH, pCO2, pO2, Flow pH, pCO2, pO2, cHb cell, TH, Ref 720 720aqc 730 735 730aqc 735aqc Flush Solution Cl, Ca, Flow cell, TH, cK+, cCl-, cCa²+, cHb Ref Cartridge pH, pCO2, pO2, Na, K, pH, pCO2, pO2, cNa+, AQC CAL Cartridge CAL Measurable Parameter pH, pCO2, pO2, Na, K, pH, pCO2, pO2, cNa+, CAL CAL Cartridge Electrode Cl, Ca, Flow cell, TH, cK+, cCl-, cCa²+, cHb, TH Ref Same for all models pH, pCO2, pO2, Na, K, pH, pCO2, pO2, cNa+, Cl, Ca, Glc, Lac, Flow cK+, cCl-, cCa²+, cGlc, cell, TH, Ref cLac, cHb, pH, pCO2, pO2, Na, K, pH, pCO2, pO2, cNa+, Cl, Ca, Glc, Lac, Flow cK+, cCl-, cCa²+, cGlc, Cartridge cell, TH, Ref cLac, cHb, sO2, FO2Hb, FCOHb, FMetHb, FHHb AQC CAL Cartridge pH, pCO2, pO2, Na, K, pH, pCO2, pO2, cNa+, Cl, Ca, Glc, Lac, Flow cK+, cCl-, cCa²+ cGlc, cell, TH, Ref cLac, cHb, AQC CAL Cartridge pH, pCO2, pO2, Na, K, pH, pCO2, pO2, cNa+, Cl, Ca, Glc, Lac, Flow cK+, cCl-, cCa²+, cGlc, cell, TH, Ref cLac, ctHb, sO2, FO2Hb, FCOHb, FMetHb, FHHb, ctBil 14 Electrode Electrodes used in the GASTAT-700 Model are maintenance free for membrane. Store electrodes under proper conditions described in below. Electrode pCO2,pO2 Storage conditions and expiry Store it in the refrigerator to keep it in the range from 2-10 centigrade. It is secured to be valid for 18 months from the date of manufacture. Then it shall be disposed immediately when the valid period is expired. The electrode may be exposed to room temperature during the transportation period. However you have to keep it in the refrigerator once receiving it. In terms of room temperature storage, the validity period may be shorter than 18 months from the date of manufacture. Na, pH Store it in the refrigerator to keep it in the range from 2-10 centigrade. It is secured to be valid for 20 months from the date of manufacture. Then it shall be disposed immediately when the valid period is expired. The electrode may be exposed to room temperature during the transportation period. However you have to keep it in the refrigerator once receiving it. In terms of room temperature storage, the validity period may be shorter than 20 months from the date of manufacture. K,Cl,Ca Store it in the refrigerator to keep it in the range from 2-10 centigrade. It is secured to be valid for 12 months from the date of manufacture. Then it shall be disposed immediately when the valid period is expired. The electrode may be exposed to room temperature during the transportation period. However, you have to keep it in the refrigerator once receiving it. In terms of room temperature storage, the validity period may be shorter than 12 months from the date of manufacture. Ref electrode Store it in the room temp which is range of 2-10 centigrade. inner core It is secured to be valid for 18 months from the date of manufacture. Then it shall be disposed immediately when the valid period is expired. The electrode may be exposed to room temperature during the transportation period. However, you have to keep it in the refrigerator once receiving it. In terms of room temperature storage, the validity period may be shorter than 12 months from the date of manufacture. Ref electrode Store it in the room temp which is range of 2-30 centigrade. Body It is secured to be valid for 18 months from the date of manufacture. Then it 15 shall be disposed immediately when the valid period is expired. Glc, Lac TH, cell Store it in the refrigerator to keep it in the range from 2-10 centigrade. It is secured to be valid for 6 months from the date of manufacture. Then it shall be disposed immediately when the valid period is expired. The electrode is very sensitive to the temperature and must be kept inside the refrigerator after receipt. This electrode will be transported with cool. However, do not be frozen unless otherwise membrane will be damaged and cannot be used. Flow Store it in the room temp which is range of 2-30 centigrade. It is secured to be valid for 18 months from the date of manufacture. Then it shall be disposed immediately when the valid period is expired. NOTE: Date of expiry is represented in the barcode which is attached on the electrode body. Information contained in the barcode is, a) first five digits are Product code, b) next three digits are the date of expiry, c) next four digits are lot number, and d) last two digits are check sum calculated by barcode number. If the barcode is not reading well, enter these barcode manually. i.e.) In case barcode number is 83812212000250, 83812 212 0002 50 Product code: 83812 Valid term: till December 2012 Lot number: 0002 Barcode check sum: 50 16 Reagents GASTAT-700 Model uses two kinds of CAL Cartridges depending on the model. Each CAL Cartridges contains different kind of reagent pack inside. Product code Item 0171931 CAL Cartridge 0171932 AQC CAL Cartridge 0128935 Flush Reagent Description and storage condition CAL Cartridge Cartridge contains Calibration 1 reagent (CAL1), Calibration 2 reagent (CAL2), Cleaner and Quality control Level 1, Quality control Level 2, and Quality control Level 3 maximum. CAL1, CAL2 and CAL3 calibrate the system upon predefined schedule. Cleaner cleans the system once per day automatically. If the instrument is with AQC model, three quality packs are measured in predefined schedule. Shake the cartridge gently before use. Store it in the range of 4-30 centigrade. Dispose it after 9 months from the date of manufacture. CAUTION ・ CAL Cartridge is single use. ・ If the Cartridge is exposed under temperature higher than 30 degrees, Cartridge is no longer valid for 9 months. NOTE ・ Quality control level 1, level 2, and level 3 are contained for with AQC model only. Material contains in reagent are shown below. CAL1 (300ml) reagent: Buffers, Surfactant, Detergent, Preservative, Deionized water. CAL 2 (200ml) reagent: Buffers, Surfactant, Detergent, Preservative, Deionized water. Cleaner (80ml): Surfactant, Detergent. Quality control Level 1 (200ml): Buffers, Surfactant, Detergent, Preservative, Deionized water. 17 Quality control Level 2 (200ml): Buffers, Surfactant, Detergent, Preservative, Deionized water. Quality control Level 3 (200ml): Buffers, Surfactant, Detergent, Preservative, Deionized water Flush Flush cleans the flow line of the instrument after each calibration, sample analysis and cleaning. It is also used for periodical conditioning of flow system.Store it in room temp in the range of 4-30 centigrade. Dispose it after 9 months from date of manufacture. Material contains in reagent are shown below. Flush (550mL): Buffers, Surfactant, Preservative, Deionized water. CAUTION ・ Flush is single use. Do not re-use it even if solution remains a little in the bottle. ・ If Flush is exposed under temperature higher than 30 degrees, cartridge is no longer valid for 9 month. NOTE: ・ AQC CAL Cartridge has the 2 kinds of barcode, which are CAL Cartridge barcode and AQC barcode. Below chart is meaning of each figure for CAL Cartridge and AQC barcode number. Number of CAL Cartridge is 71931 0812 0050 382350125500838800250. No Start position Length Mean Example Value 1 1 5 Catalog number 71931 2 6 4 Expiry date 0812 3 10 4 Serial number 0001 4 14 3 CAL1-pH 382 7.382 5 17 3 CAL1-pCO2 350 35.0 6 20 3 CAL1-Ca 125 1.25 7 24 3 CAL1-pO2 500 150.0 8 27 3 CAL2-pH 838 6.838 9 30 3 CAL-Ca 250 2.50 10 33 1 Check digit 0 Dec, 2008 18 Number of AQC is 2893911090510001210635042041040009506101851350. No Start position Length Mean Example Value 1 1 5 Catalog number 71933 2 6 4 Expiry date 2009 3 10 4 Serial number 0001 4 14 3 Level1-pH 210 7.21 5 17 3 Level1-pCO2 635 63.5 6 20 4 Level1-pO2 420 42 7 24 3 Level2-pH 410 7.41 8 27 3 Level2-pCO2 400 40 9 30 4 Level2-pO2 950 95 10 34 3 Level3-pH 610 7.61 11 37 3 Level3-pCO2 185 18.5 12 40 4 Level3-pO2 1350 135 Value Sep. 2020 ・ Below chart is meaning of Flush barcode number. Number of Flush is 71935 2008 0005 0 No Start position Length Mean Example 1 1 5 Catalog number 71935 2 6 4 Expiry date 2008 3 10 4 Serial number 0005 4 14 1 Check digit 0 Aug. 2020 19 MODULE OVERVIEW Flow System Flow system consists by 5 modules and 2 preheaters. 20 Module Sampling module Function ・ Sample container detectction ・ Sample aspiration ・ Sample, Calibration, Flush solution and waste transportation ・ Fluid valve maintenance in flow path at the port rubber and nozzle Preheater 1 Measurement module ・ Pre warm of sample and cleaning solution ・ Sample, Calibration, Flush solution and waste transportation ・ pH/blood gas, electrolyte and metabolite parameters measurement ・ Control Temperature to be 37 ℃ Oxy module ・ Sample, Calibration, Flush solution and waste transportation ・ Hemolysis of sample ・ Oxy parameters measurement ・ Control Temperature to be 37 ℃ Preheater 2 ・ Pre warm of cleaning solutions Pump module ・ Sample, Calibration, Flush solution and waste transportation Manifolded module ・ Sample, Calibration, Flush solution and waste transportation and swiching path ・ Flush bottle and CAL Cartridge connection and hold 21 PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and module configuration This chapter describes configuration between PCB and modules and their function. Double line shows power supply line and single line shows signal line. 22 Measurement module O-ring Pipe Bush Preheater1 Bush Ring Flow SensorP O-ring Preheater2 Flow Block Machine part Electrode case have each electrode (pH, pCO2, pO2, TH, Na, K, Cl, Ca, Ref, Glc, Lac), each sensor (FS-P, FS-M, FS-R), preheater , LED control and analog measurement system. Measurement flow path keep temperature (37±0.5 ℃). As for module case, electromagnetic shielding wire processing is applied, and be protecting analog measurement system from external noise. FS-P Reagent is detected to arrive, air bubble presence. And monitoring dispersion (uniformity) state of blood sample FS-M Reagent is detected when arrival. FS-R 23 Reagent is detected when arrival, and use to start signal of Glc/Lac measurement. Analog Part PCB Electrode output signal with each pH, pCO2, pO2, TH, Na, K, Cl, iCa, Ref, Glc, Lac is altered A/D. Measurements of pH, pCO2, Na, K, Cl, iCa are altered by voltage amplification circuit . Measurements of pO2, Glc, Lac are altered by amplification circuit electric current-voltage. Measurement of TH is altered by resistance measurment circuit. LED PCB part Control temperature of Electrode block and LED of flow path from CPU PCB is relaid. Main heater and preheater Preheater1 is instlled and connected between Electrode module and sampling module to warm reagent in CAL cartridge. Preheater2 is instlled and connected between Electrode module and pump1 to warm cleaning solution. Manifold module Cartridge Adjust Pin O-ring Needle Needle Holder Flow Sensor Valve Relay PCB Valve O-ring Cartridge Holder Sensor Bottle Sens. Pin O-ring Bottle Joint Plug Plug Holder Cover Base Door Stopper Cover Spring Door Stopper Valve G-700 Model is installed 12 valves (2 species of Two electromagnetic valve and 1 species of Three electromagnetic valve). And valve drives at DC12V. 24 Valve No.1 ~ 5: Two electromagnetic valve (small type) Valve No.6, 7, 11, 12: Two electromagnetic valve (medium type) Valve No.8 ~ 10: Three electromagnetic valve (medium type) Manifold Mnifold swiched flow path between path circuits. It is connected CAL cartridge by needle, and it is connected Flush and waste bottle by pulg. CAL cartridge and bottoles is monitered by each independent sensors. Cartridge Holder Cartridge Holder has Guide and Holder to insert CAL cartridge into manihold. And Door restricts access to needle to avoid injuly. Manifold PCB Control of valves and output of Cal cartridge and bottles presence sensor signal is relaid from CPU PCB 25 Sampling module Sensor Position Adjuster Sample Port Nozzle Holder Sample Nozzle Sample Door Stepping Motor Guide Shaft Slipping Screw Position Sensor 26 Sample Port Cross section view of sample port below. Port Rubber Housing Narrow Path Point Syringe Fitting Part Capillary Fitting Part Port Rubber Waste Outlet Reagent Inlet Sampl port rubber and sampling nozzle have role as valve in sample port. 27 No. Position Function Origin position Standard position for moving nozzle. 1 Nozzle Hole Fulsh position (1) Position for cleaning tip of nozzle . 2 Home/CAL position Position for feeding calibration, cleaning solution, AQC solution. 3 Capillary measurement Position for suction sample from capillary fitting part in capillary measurement. 4 28 Flush position (2) Position for cleaning syringe fitting part and capillary fitting part. 5 29 Pump module Pump module is configured by 1 cover of pump module and 3 peristaltic pump and piping tubings on the rear side, and CPU PCB control it. 30 OXY module Hemolysis Unit Controller 31 OXY module Optical Fiber [11-003] Neon Lamp Driver OXI Module PCB Hemolysis Unit Oxy-LED PCB Base O-ring O-ring Spacer Cap Handle Spectrometer Neon Lamp Flow Sensor-L 32 Hb module Hb module degradation chart FC Holder Flow Cell O-ring Hb Module PCB Flow Sensor Hb-LED FC Sensor Spectrometer PCB 33 Printer module Printer Head Unit Head Opening Lever Printer PCB 34 Barcode scanner module Barcode scanner module is installed on the bottom, and detect human motion to turn ON/OFF backlight of display. And control Irradiation from scanner. Barcode scanner Reading beam is irradiated forward by fixed formula CCD scanner. And SBC sontrol CCD scanner. Human motion sensor Sensor of infrared reflective type can detect human movement within 2m. BC Scanner Motion Sensor 35 Display module Display module is used display and input as GUI device of SBC. LCD display LCD display is 12.1 inch, and adopted white LED backlight with longer-life. Touch panel With analog resistive film methods, in over touch endurance 10 million times resistant to, dust and water-droplet, and touch enabled even with her of gloves on. LCD with Touch Pannel 36 Control box module This module controls instrumen parts whole. And it Consists of by CPU PCB, SBC, Power Supply PCB, AC Inlet, Serge Absorber, Battery, and SW Power Supply primarily. Power Supply Relay CPU PCB SSD Battery Serge Absorber AC Inlet (noise filter) Power PCB SBC SW Power Supply CPU PCB Renesas-made SH microcomputer equips, and is featuring Μ-ITRON, real-time multi-tasking OS. SBC Domestic-made single-board computer equips, and SSD is employed for storage device, and vibration and resistant to power failure is leading to high system design. Windows 7 embedded is employed for user interface, and is developing high usability. 37 Power source Power source that is fed to part of instrument shown in the table below. Input Output CPU DC3.3V,5V,12V N/A SBC DC12V N/A Battery DC24V DC13.5V Power PCB DC12V,24V DC3.3V,5V,12V SW Power Supply AC85~240 DC24V, 10A AC Inlet AC85~240 AC85~240 Drive Instruments incorporate SSD(Solid State Disk) as device storage of SBC for, and in addition to Windows OS and GASTAT-700 execution program database is install here. 38 Software configuration This chapter describes software configuration. Arrow in figure below shows subordinate part. 9. 10. 39 Module OS Function description SBC : Windows Embedded standard 7 CPU: μ-ITRON GASTAT-700 Flow Control program The program for the GASTAT-700 fluid control system is designated, and the operation of the pump, the solenoid motor and the nozzle drive motor is controlled to perform A/D measurement of flow sensor and the electrode. GASTAT-700 program Designating program of GASTAT-700 entire control system, and GUI maintenance, database maintenance, and, external I/F maintenance is included. Driver program Display, print and other input/output devices. MS-SQL Pointing to database of loading the equipment, and measurement data, operate log data, operational log data are controlled batch. OXI module A measurement program OXI modules shall acquire the spectroscopic data of photometry section. Hemolyzer Program of hemolysis modules. Hb module A measurement program Hb modules shall acquire the spectroscopic data of photometry section. 40 Security Code If you access to the Security code screen, it is possible to verify the system status or calibration states, changes the configuration of the system. Please check status of instrument and perform 2 point calibration manually after the change of security code. 1. Select Function. 2. Select Others. 3. Select Security code. 41 4. Enter Password “1982” and press OK. 5. Enter security code described in the following chart and press OK. i.e.) If you want to print calibration history, enter security code 9003 and press OK. CAUTION Do not inform the security ID to the end-user unless he is trained well for the GASTAT-700 Model. Unless otherwise, he may enter wrong security code and eventually the system cause mechanical or program failure. Entering wrong security code may incur the critical damage on the instrument. 42 Security code list Code Function 45 Cleaning time for internal cleaning 46 Initial temperature value 47 Interval of internal cleaning (CAL) per sample i.e) If 50, system cleans flow path every 50 sample measurement 48 Time for rebooting instrument. 63 Interval for conditioning flow system 56 Calibration retry times 65 TEST mode ON/OFF 79 Select solution display sample Button Press transitioned 80 Operator administrative Authorization set(operator) 81 Operator administrative Authorization set(blanked) 93 Use ID Authentication Rules (number of barcode leader) 94 Use ID authentication rule set(number of barcode digits) 95 Use ID Authentication Rules (barcode type) 328 329 330 331 361 362 366 372 9108 Measurement switch by barcode (Upper) Measurement parameter switching by barcode (Lower) Measurement switch by barcode (Top) Measurement parameter switching by barcode (Lower) Slope of correction factor for TH sensor Offset of correction factor for TH sensor The system elwctric voltage (Zero voltage) of O2 parameter Initial value of barometric pressure Printing measured barometric pressure Factory settings 180 sec Range 37 ℃ 50 1 to 200 0 20 4 OFF 0 to 23 o'clock 0 to 200 Times ON/OFF 000 12 4 0:Code 39 1:Industrial 2of5 2:ITF 2of5 3:MSI 4:Codabar 5:EAN/UPC 6:Code 93 7:Code 128 Measurement that is set by barcode 83880 reading Measurement parameters set by barcode 8388 reading 1 0 0.5 760 43 Code 553 554 555 596 618 803 Function Number of print data in AQC record Factory settings 3 The number of calibration history Calibration time adjustment (0 – 39 minutes) Correction for pixel of spectrophotometer “d” (aX3 + bX2 + cX + d) Simplified spectroscopic spectroscope pixels correction factors intercept Ultrasonic vibrator is enabled 10 0 0 0 OFF: Use ON without use OFF: effective spectroscope communication s, invalid ON: spectroscopic vessel communication s 804 OXY/simplified spectroscope communication is overridden. 831 923 1000 Inner tube for syringe position of the nozzle OFF is enabled. Calculation factor for Hct from t tHb 2.94 sample barcode-code digit restrictions 0 1012 Language setting 1 1072 Change calibratinon history output to USB 0 1078 1085 R that is used to PO2(A) 0.86 Round-down ON/OFF at the on-on-line measurement limit The operation does not range extension/ 1104 1115 1186 Range tHb remeasurement caution Means(well 4g/dL below this warning message appears, display) Display the measured value with asterisks for 1 outside measurement range 0:Limited-digit disabled Over 1: limitation on digit limitation by set value *Digit real ID digit except for barcode type 1: Japanese 2: English 3: Czech 4: Russian 5: Turkish 0:Printer 1:USB 0:Round 1:round off 0:Making sure that they are not 1: 2:G600 specification 0:Display, print a number 44 1:Display with asterisks, print 1196 1225 1226 1227 1339 1340 Record extracting day Name of 1 dialysate 10 0 Name of 2 dialysate Name of dialysate 3 Valid prediction algorithm/invalid Predictive algorithm: number of extractions 0 0 ON 6 1465 1475 1476 1477 Print a Thermal printer test pattern Consumable order function ON/OFF Lease/sales set During lease shipping expected date of monthly Alert record initial initialize Machine Serial No and MAC address print License key certificate Model information (1-12) A/D result Rrinting reagent amount (formerly 76) Printinc calibration history. A number of records are defined at security code 554 (formerly 77) Initialize all security code value. The system returns to factory setting. (formerly 510) Delete all test results (formerly 520) Delete all QC results (formerly 530) Delete all maintenance history (formerly 540) Delete all log history (formerly 543) Delete all calibration history (formerly 550) Offset value(number of step from home 0 sensor) that adds to nozzle each position Nozzle initial operation Nozzle moves to the flushposition Nozzle moves to the calibration position Nozzle moves to the capillary position Nozzle moves to the waste position Nozzle moves to the syringe position Nozzle moves to the limit position Nozzle moves to the edge position Nozzle moves to the micro syringe position Moves the song position to the nozzle initialization operation after the inner cylinder for syringe position Initialize valve Valve 1 open Valve 1 close 1519 1538 1539 7777 9000 9002 9003 9018 9021 9024 9027 9030 9031 829 9041 9042 9043 9044 9045 9046 9047 9048 9049 9150 9050 9051 9052 45 9053 9054 9055 9056 9057 9058 9059 9060 9061 9062 9063 9064 9065 9066 9067 9068 9069 9070 9071 9072 9073 9074 9077 9078 9079 9080 9081 9082 9083 9086 9087 9088 9089 9090 9091 9092 9095 9096 9097 9098 9099 Valve 2 open Valve 2 close Valve 3 open Valve 3 close Valve 4 open Valve 4 close Valve 5 open Valve 5 close Valve 6 open Valve 6 close Valve 7 open Valve 7 close Value 8 open Value 8 close Value 9 open Value 9 close Valve 10 open Valve 10 close Valve 11 open Valve 11 close Valve 12 open Valve 12 close All pumps motor stop Pump 1 move clockwise in slowest speed Pump 1 moves clockwise in middle speed Pump 1 moves clockwise in fastest speed Pump 1 moves counterclockwise in slowest speed Pump 1 moves counterclockwise in middle speed Pump 1 moves counterclockwise in fastest speed pump 1 stop Pump 2 moves clockwise in slowest speed. Pump 2 moves clockwise in middle speed Pump 2 moves clockwise in fastest speed Pump 2 moves counterclockwise in slowest speed Pump 2 moves counterclockwise in middle speed Pump 2 moves counterclockwise in fastest speed Pump 2 stop Pump 3 moves clockwise in slowest speed. Pump 3 moves clockwise in middle speed Pump 3 moves clockwise in fastest speed Pump 3 moves counterclockwise in slowest speed 46 9100 9101 9104 9105 9112 9120 9121 9122 9123 9124 9125 9126 9127 9128 9140 9141 9016 9017 9142 9143 9145 9146 9997 Pump 3 moves counterclockwise in middle speed Pump 3 moves counterclockwise in fastest speed Pump 3 stop Sensor check (cartridge, bottle, flow cell) print electrode replacement record All liquid feed and discharge Feed Flush to the measurement module Feed CAL 1 to the measurement module Feed CAL 2 to the measurement module Feed Internal cleaner to the measurement module Feed AQC Lev1 to the measurement module Feed AQC Lev2 to the measurement module Feed AQC Lev3 to the measurement module Conditioning sequence OFF of Hb LED ON of Hb LED Turning OFF the LED light for COOX measurement Turning ON the LED light for COOX measurement OFF of lighting oxy hand neon source ON of lighting oxy hand neon source OXY vibrator OFF OXY vibrator ON Printting and display software version 47 TEST mode When system is configured as TEST mode, GASTAT-700 Model always printes calibration result and total count stats whenever calicration and measurement are performed. Enter security code 65 and press OK. Then press Switch to change current setting to ON. When current setting is OK, the system runs under TEST mode. Model name turns to green during the TEST mode. Model name turns to white or black during normal mode. 48 Calibration Report in Test Mode 1 Symbol Item 1 CAL1 2 CAL2 3 CAL1 output 4 CAL2 output 5 Slope 6 Pixel number and light intensity when LED lit. 7 Pixel number and light intensity when LED lit. 2 3 4 5 6 7 49 Sample measurement in test mode 1 Symbol Item 1 Sample count 2 Output voltage 2 50 A/D Value Reading Analogue to digital value for each sensor including or excluding electrode can be observed by Security code 9000. 1. Remove all electrodes from the measurement module. 2. Put rubber plate in electrode holding part and close the measurement module cover. 3. Check A/D result by Security code 9000. 4. Open the measurement module cover and remove the rubber plate. 5. Load all electrodes into the measurement module. 6. Access Security code 9122 to fill CAL1. 7. Check A/D result by Security code 9000. 8. If A/D result is out the range described in the table below, the measurement module or Hb/OXY unit has problem. Perform corrective action. Item A/D result without electrodes A/D result with electrodes filled CAL1 in sample path [S.C.9000] [S.C.9122 ->S.C.9000] Ref 0 or 1 0 or 1 pH ― 2.600±0.900V pCO2 ― ― pO2 0.500 ±0.100V 1.100 ±0.400V Na ― 3.400 ±1.000V K ― 3.200 ±0.700V Cl ― 2.900 ±0.400V iCa ― 2.900 ±0.400V Glc 0.500 ±0.100V ― Lac 0.500 ±0.100V ― TH0 0.100V and less 2.800 ±0.300V TH1 1.150 ±0.300V 1.150 ±0.300V TH2 0.850 ±0.300V 0.850 ±0.300V TH3 0.500 ~ 2.500V 0.500 ~ 2.500V TH4 0.850 ±0.300V 0.850 ±0.300V TH5 0.850 ±0.300V 0.850 ±0.300V BP 4.000 ±0.300V 4.000 ±0.300V FS-P(A) ON 3.000 ±1.000V 1.000V and less FS-L ON 3.000 ±1.000V 1.000V and less FS-M ON 0.100V and less 1.000V and less FS-R ON 0.100V and less 1.000V and less FS-W ON 3.000 ±1.000V 3.000 ±1.000V FS-P(A) OFF 0.500V and less 0.500V and less 51 FS-L OFF 0.500V and less 0.500V and less FS-M OFF 0.500V and less 0.500V and less FS-R OFF 0.500V and less 0.500V and less FS-W OFF 0.500V and less 0.500V and less FS-P(B) ON 1.500 ±1.000V 3.000 ±1.000V FS-P(B) OFF 0.500V and less 0.500V and less Draw out Liquid from Flow System All remained solution needs to be removed immediately when instrument is stopped. Security code 9120 can remove the solution from the flow system. Please follow below procedure to safely stop the instrument. Item should be prepared CAL cartridge filled with water. Flush bottle filled with water. Waste bottle 1. Access to the security code(Password entry) screen. 2. Remove CAL cartridge and Flush bottle. Load CAL cartridge filled with water and Flush bottle filled with water. Replace waste bottle with new one. 3. Enter security code 9120. Instrument feed the distilled water inside the flow system. Whole cycle takes 5minutes. 4. Remove CAL cartridge filled with water and Flush bottle filled with water. Do not remove waste bottle. 5. Enter security code 9120. Instrument draws the distilled water from liquid path and 52 leads to the waste bottle. Whole cycle takes 5minutes. Perform twice at least for this procedure. 6. Remover waste bottle, electrodes, sample nozzle and sample port from the instrument 7. Access to System shot down at Others from Function menu. Select Shut down. 8. Turn off the battery power when below screen appears. Remove AC power code. 53 System Rebooting In GASTAT-700 Model, Single Board Computer (SBC) and Solid State Drive (SSD) are loaded on CPU/SBC Unit. Since this small computer looks at enormous amounts of data in Solid State Drive, the Single Board Computer needs to cool down and reset all Internal Chips (IC) on the board by rebooting. Therefore, the instrument automatically reboots once a day to maintain proper condition for Single Board Computer. Instrument completely reboot once in 1 week. Only the G700 Model application reboots every day to reset the communication with CPU board. Time for rebooting Automatic rebooting can be performed after the internal cleaning. If you change internal cleaning schedule, the rebooting time must be changed accordingly. Enter security code 48 to change the time of rebooting to adapt to internal cleaning time. Automatically changes the value of security code 48 when calibration schedule has changed. Security code 48 0 a.m. 1 a.m. 2 a.m. 3 a.m. 4 a.m. 5 a.m. 6 a.m. 7 a.m. 8 a.m. 9 a.m. 10 a.m. 11 a.m. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 0 p.m. 1 p.m. 2 p.m. 3 p.m. 4 p.m. 5 p.m. 6 p.m. 7 p.m. 8 p.m. 9 p.m. 10 p.m. 11 p.m. 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Example 1. If the internal cleaning schedule is set at 4 a.m. as shown on below picture, enter 4 in security code 48. In this case, reboot will be performed at 4 a.m. 2. If the Internal cleaning is set more than twice in a day (e.g. 0 a.m. and 4 a.m.), set security code 48 as either one of internal cleaning time. (0 or 4 in this case) The reboot will be 54 performed at the time entered in security code 48. If the security code 48 is set at 4, reboot will be performed 4 a.m. CAUTION If the rebooting schedule does not set at same time as internal cleaning schedule, the system may start rebooting suddenly after any error message pops up (e.g. replacement of Cal cartridge etc…). NOTE ・AQC cannot be performed at the time of internal cleaning and system rebooting. Therefore, configure AQC time in different time. However, AQC can be performed at the time of internal cleaning only. i.e.) If the Internal cleaning is set 0 a.m. and 4 a.m. and rebooting time is set 0 a.m., do not configure AQC time at 0 a.m. 55 Calibration Calibration is the correction process by testing and adjusting the electronic signal of electrode based on known concentration of reagent. The calibration is performed in two different ways, which are by manual and automatic. Calibrations are mandatory process to operate the instrument. Calibration Report To understand the status of instrument, calibration report needs to be observed. Below procedure describes procedure to print out calibration report. 1. Select Calibration from Function. Select Electrode condition. 2. Past calibration result will be displayed. Press Detail output to print calibration report. 56 Below figure shows calibration report. Instrument is designed to report last ten calibration report. It is possible to change the number of calibration report printing by accessing security code 554, if you need more than ten calibration results or less. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Symbol Item 1 Calibration date & time 2 Sequential number 3 Calibrator type 4 Calibration error flag 5 Time of signal respond 6 Slope for calibration curve 7 Gap between current results and previous results 8 Voltage signal 9 Ref and dark values for Hb flow cell 10 Voltage signal after introducing clean an GlcLac electrode 57 Calibration Error Threshold In case calibration result is out of the following range, specific electrode shows calibration failure. Drift error When the value in DRIFT is out of below range, instrument shows as the Drift error. Item CAL1 CAL2 pH ±0.015 ±0.015 pCO2 (Torr) ±3.0 ±5.0 pO2 (Torr) ±5.0 + cNa (mmol/L) ±2.5 ±2.5 cK+ (mmol/L) ±0.25 ±0.25 cCl- (mmol/L) ±3.0 ±3.0 + cCa2 (mmol/L) ±0.15 ±0.15 cGlucose (mg/dL) ±15 cLactate (mg/dL) ±4.05 Slope error When the value in SLOPE is out of below range, instrument shows as the Slope error. Item Upper limit Lower limit pH 70.0 30.0 pCO2 70.0 30.0 pO2 2.3 0.5 cNa+ 100.0 20.0 cK+ 70.0 20.0 cCl-20.0 -70.0 cCa2+ 40.0 18.0 cGlucose cLactate F.C. Level error When the value in V is out of below range, instrument shows as the Level error. Item Upper limit Lower limit pH 4.4224 0.5576 pCO2 4.6193 0.7416 pO2 2.5 0.3000 cNa+ 4.7002 1.2815 + cK 4.4800 0.2423 cCl4.7995 0.1395 + cCa2 4.8674 0.1628 cGlucose cLactate F.C. 63000 20000 58 Expected value for Calibration Report Below chart describes the expected value for voltage, slope and count when the electrode is installed onto the instrument without any troubles. Expected value Item Expected voltage (CAL1) 1.7 to 3.5 Expected slope Expected Count 52 to 66 Below 16 pCO2 2.1 to 3.5 47 to 70 Below 45 pO2 0.7 to 1.5 1.0 to 2.1 Below 40 cNa+ 2.4 to 4.5 65 to 75 Below 16 cK+ 2.5 to 3.9 55 to 66.5 Below 16 cCl- 2.5 to 3.3 ‐45 to ‐55 Below 16 cCa2+ 2.5 to 3.3 25 to 38 Below 16 cGlucose 0.5 to 8.0 - 45 to 120 cLactate 0.2 to 9.5 - 47 to 140 FlowCell (Ref(peak) index val) 30000 to 60000 count - - FlowCell (Dark(peak) index val) for 710/720/730 9500 to 10500 count - - FlowCell (Dark(peak) index val) for 735 2000 to 3000 count - - pH 59 Calibration Error Flag In case of error, error status shall appear at ERR on the Calibration report. Error flag and its meanings are in the below chart. 0(Zero) in the error status area stands for “there is no error observed at the corresponding parameter”. If the error status area is not 0(Zero), it stands for “there are error at the corresponding parameter”. Slope leak Level Drift No end Flag Unstable error error error error point 000 001 ● 002 ● 003 ● ● 004 ● 005 ● ● 006 ● ● 007 ● ● ● 008 ● 009 ● ● 010 ● ● 011 ● ● ● 012 ● ● 013 ● ● ● 014 ● ● ● 015 ● ● ● ● 016 ● 017 ● ● 018 ● ● 019 ● ● ● 020 ● ● 021 ● ● ● 022 ● ● ● 023 ● ● ● ● 024 ● ● 025 ● ● ● 026 ● ● ● 027 ● ● ● ● 028 ● ● ● 029 ● ● ● ● 030 ● ● ● ● 031 ● ● ● ● ● 032 ● 033 ● ● 034 ● ● 035 ● ● ● 036 ● ● 037 ● ● ● 038 ● ● ● 60 039 040 041 042 043 044 045 046 047 048 049 050 051 052 053 054 055 056 057 058 059 060 061 062 063 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● 61 Count Report When the system measures sample, it verifies if sample is transferred to measurement module in predefined period and if the sample is containing air bubble. When TEST MODE is ON, status shall print on the top of the measurement result as a total count report. Total Count Total counts stands for time starting from sample detection of FS-P sensor to sample detected by FS-R sensor. Ecpected Total Count GASTAT-710 600 ~ 800 Error thershold Within 500 (GASTAT-710/720) Within 600 (GASTAT-730/735) GASTAT-730 600 ~ 800 Error message: Liquid remain detected (FS-R; FS COUNT ERR MIN) Flow check is performed after cleaning. Over 1200 (GASTAT-710/720) Over 1300 (GASTAT-730/735) GASTAT-730/735 700 ~ 900 Error message: sample not detected (FS-R; FS COUNT ERROR MAX) Flow check is performed after cleaning. NOTE: ・ The instrument stos measurement when total count error occurs. ・ Flow sensor shows an error when sample cannot be detected (FS-R;FS COUNT ERR MAX error). Slef diagnostic Flow is performed automatically after cleaning. 62 Sample Count Sample counts indicates portion of air bubble inside the sample.The instrument verifies if sample contains air bubble. Calculation formula is Total count over air detection time. Sample Count = group X ÷ Total Count If sample Count is more than 0.6, instrument shows “Caution! Sample volume is not enough.” It also prints following error message “Sample volume is not enough.” Sample Count Divided The instrument equally divides the total count in 4 segments, and verifies if each segment contains air bubble. If divided count exceeds predefined limit, it shows error. The arrow in the following illustration is the direction of the sample starting from FS3 sensor to the measurement unit. Group 2 Group 1 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Error message on the instrument and printed message by each segment is shown below. Hb line Group 2 pH~Lac line Group1 Group3 Group4 Group5 Normal Sample not enough Bubble detect Normal Normal Insufficient sample volume in tHb Air bubbles detected in tHb Sample not enough Insufficient sample volume in all parameters Insufficient sample volume in all parameters Insufficient sample volume in all parameters Bubble detect Air bubbles detected in measurement Air bubbles detected in measurement Air bubbles detected in all parameters module (pH~Lac) 63 module (pH~Lac) Insufficient sample volume in tHb Error flag for Count Report Bubble detected Group1,Group3,Group4,Group5 Error message : Air bubbles detected in measurement module (pH~Lac) Error print :※Bubble detected Bubble detected Group2 Error message : Air bubbles detected in tHb Error print : ※Air bubble detect trial NOTE: If air bubble was detected or Sample voleme is not enough, instrument print * in test result and screen. 64 Sample lack in Group1,Group3,Group4,Group5 Error message:Sample voleme is not enough Error print : ※Sample volume is not enough Sample volume is not enough 65 Error flag for Count Report Error flag appears on the top of the printed measurement result. Instrument continues measurement in Flag 1 and 2, whereas instrument stops measurement in Flag 3 and 4. Error flag is Meanings Operation 1 Bubble detected Measurement continue 2 Sample not enough Measurement continue 3 Total count is too small. Measurement stop 4 Total count is too big. Measurement stop Error flag 66 Procedure to Get Log File Engineers are not in front of instrument most of time when customer encouters the trouble. In this case, engineer needs to download the log to understand what happened when trouble occurred. Below are procedures to download calibration history. Calibration history This log will show all calibration results on past 50000. It is possible to find the instrument status when trouble had occurred. Item to be prepared: ・ USB memory After check for computer viruses before using USB memory, dispose it. Procedure: 1.Stick USB memory to USB inlet on rear panel. 2.Access security code 1072 and change the setting from "0" to "1". 3.Access security code 554 and change the setting to "50000". 4.Access security code 9003. 5.Calibration history will be transferred into USB memory by csv file. NOTE: ・ The calibration record is saved in the USB memory as csv file with name of downloaded date and time. i.e) Cal_YYYYMMDDHHMMSS.csv ・ Do not forget to set all security codes back to default. 67 AutoQC LOG This LOG will show the detail AQC result in the past. It is possible to analyze the AQC result with the Calibration history, AQC barcode, and Gastrol results. 1. Stick USB memory to USB inlet on rear panel. 2. Access “Function” ”Quality Control” ”Record” “Auto QC”and press “OK”. 3. Enter starting date at “starting date field” and the number of date at “extraction field”. 4. Press “USB save” to transfer Auto QC log into USB memory by csv file. 68 Data exchange Data can be exported / imported in GASTAT-700 Model. Press Function. Press Others. Press Data exchange. Press Data transfer or Data import. Data transfer (GASTAT-700 → USB memory) Press Data transfer. Select the data to be exported and Insert USB flush memory to the rear panel of instrument. Press OK. 69 The picture in the left shows the screen during data export. The picture in the left shows the screen when the data export completed. Remove USB flush memory. Data import (USB memory → GASTAT-700) Press Data import. Select the data to be exported and Insert USB flush memory to the rear panel of instrument. Press OK. 70 Log output This chapter describes how to get logs in USB flush memory. Press Function at home screen. Press Others. Press Log output. Enter the first day you want to extract the data in Start date field "YYYYMMDD" format in numerical keypad. Enter the last date of the extraction period. Check the data to be output and insert the USB memory into the device and press OK. The picture in the left shows the screen during log output. Progress bar stops when log output completed. The picture in the left shows the screen when log output completed. 71 MAINTENANCE Preventive Maintenance To keep the proper condition of instrument, TMC recommend performing the preventive maintenance of instrument accordingly. This prevents the accidental flow error in the instrument, short life of consumables, and accidental problem of software. Please follow below procedure properly to keep instrument in proper condition. External Cleaning This procedure is for cleaning measurement flow path lined in Figure 1 by liquid sodium hypochlorite provided by Techno Medica Co., Ltd. Please perform this cleaning procedure once in 2 weeks or once in 300 samples whichever comes earlier. This procedure will pre-long the life of electrodes (except REF, Glc, and Lac), consumables, and prevent the accidental flow error. Figure 1 72 Items to be prepared: # Item Comment 1. Cat #: 0083939 Name: Super Flush Set Hypochlorite tablet & 100ml empty container Price: JPY 1,000 2. Syringe Prepared by customer 3 Plastic glove This is to prevent your fingers To be damaged from hypochlorite. Procedure: A) Preparation of Super Flush Set Put a tablet and 100 ml distilled water to the black bottle to make up 3% hypochlorite solution. NOTE Do not cover the bottle after putting a tablet. Otherwise the bottle will burst. B) Perform external cleaning 1. Press “Function”, “Others”, “Self Diagnosis” 73 2. Remove the REF electrode, Glucose electrode and Lactate electrode 3. Insert the dummy electrode at the place of Reference electrode, Glucose electrode and Lactate electrode. NOTE If the old electrode is used as the dummy, make sure the membrane is not broken and flow path is not clogged. 4. Select back for 2 times to go to main menu. Then select cleaning and External cleaning. 74 5. Soak the hypochlorite acid and into the syringe. 6. Put the syringe on sample port. 7. The screen is automatically switched to the screen in the left. It goes to home screen when External cleaning sequence finished. 75 Hb Cleaning Hb cleaning should be conducted when measurement sample is clot inside Hb/OXY line and measurement value of Oxy parameter is not accurate. External cleaning solution should be used in Hb Cleaning. This procedure is for cleaning measurement flow path lined in Figure 2 by liquid sodium hypochlorite provided by Techno Medica Co., Ltd. Please perform this cleaning procedure once in 1 months or once in 150 samples whichever comes earlier. This procedure will pre-long the life of electrodes (except REF, Glc, and Lac), consumables, and prevent the accidental flow error. Figure 2 76 Items to be prepared: # Item Comment 1. Cat #: 0083939 Name: Super Flush Set Hypochlorite tablet & 100ml empty container Price: JPY 1,000 2. Syringe Prepared by customer 3 Plastic glove This is to prevent your fingers To be damaged from hypochlorite. Procedure: C) Preparation of Super Flush Set Put a tablet and 100 ml distilled water to the black bottle to make up 3% hypochlorite solution. NOTE Do not cover the bottle after putting a tablet. Otherwise the bottle will burst. Press Hb cleaning. The screen is automatically switched to the screen in the left. It goes to home screen when Hb cleaning sequence finished. Flush and 2P Calibration takes place automatically after Hb cleaning. NOTE: The picture in the left shows Cleaning selection screen when Flow Cell is not installed. No cleaning function is available. 77 Cleaning Waste Path It is recommended to clean waste path regularly (once per month or every 300 samples) to prevent blood clot in waste path. If the path is clogged at joint parts at waste path, flow sensor might have an error or reagent might overflow from Sample Port. If you face such problems, clean joint parts at waste path. This document describes the procedure of cleaning waste path. 78 Items to be prepared: # Item Comment 1. Cat#: 0083053 Name: Clog Remover Price: JPY 900 Used for connecting flow path 2. Cat #: 0083939 Name: Super Flush Set Hypochlorite tablet & 100ml empty container Price: JPY 1,000 3. Syringe Prepared by Distributor Procedure 1. Enter Security code 1982 2. Remove front panel (blue) and lower panel (white). 79 3. Remove Sample door. 4. Enter security code 9041 to move sample nozzle to initialize position. 5. Remove Sample port. 80 6. Remove Pump tube 3 and connect clog remove tube between two pins (red circle). 7. Soak the hypochlorite acid and into the syringe. 8. Mount syringe in sample port pin (front pin) and inject hypochlorite solution slowly to waste path. 9. Wait for 5min. 10. Remove clog remove tube and put Pump tube 3. Conduct manual flush cleaning 3 times. 81 Valve Cleaning Valve of GASTAT-700 Model needs to be tested once a year. If valve malfunction found during the test, it needs to be replaced immediately to prevent for flow sensor error, reagent leakage from flow path, or drift error on the calibration. Please follow below procedure for valve malfunction test. Items to be prepared # 1. Item Comment Syringe with the tube Prepared by Distributor Procedure 1. Access security code 1982 2. Remove Front panel (blue) and lower panel (white). 3. Remove CAL cartridge. Push both side of lock push the reagent needle cover in the back. And put tissue under the needle. 82 Warning: Pay attention not to injure your fingers by reagent needle in this procedure. 4. Remove Sample door. 5. Enter security code 9041 to move sample nozzle to initialize position. 83 6. Remove Sample port. 7. Fill Na hypochlorite acid solution (5%) in syringe. 8. Mount syringe in sample port pin (back pin). 9. Enter security code refer below to clean valve and flush solution to waste path slowly. And clean the flow path by water. 84 Valve No. Reagent S.C. (open) S.C. (close) All All (Initialization) 1 (NC) (small) CAL2 9051 9052 2 (NC) (small) AQC1 9053 9054 3 (NC) (small) CAL1 9055 9056 4 (NC) (small) AQC2 9057 9058 5 (NC) (small) AQC3 9059 9060 6(NC) (big) Clean 9061 9062 7 (NC) (big) Flush 9063 9064 8 (NO) (big) Flush/Waste/Air 9065 9066 9 (NO) (big) Flush/Waste/Air 9067 9068 10 (NO) (big) Waste/Air 9069 9070 11(NO) (big) Air 9071 9072 12(NC) (big) Air 9073 9074 9050 (Initialization) 10. Enter S.C.9050 to initialize all valves. 85 INSTRUMENT CHECK Instrument should be observed periodically to check for next consumable replacement. Below procedures describes how to check the next consumable replacement date and alert message. Consumable Amount Check 1. Access to Instrument condition at Fanction. 2. Amount of the consumables and next replacement date is displayed. NOTE: ・ Consumable replacement screen can be reached if you select specific consumable in Instrument condition menu. ・ Detailed replacement recorde can observed by access of Other in Record, Consumable replacement, Function. 86 Printing Consumable Amount Status Consumable amount can be print out by security code 9002. Maximum value printed on this result can be changed from below security code. Code Meanings Factory settings unit Message threshold 410 Flush sol. amount in the new Flush 550000 bottle *1μL 495mL 411 CAL 1 total volume in the new CAL 300000 cartridge *1μL 270mL 412 CAL 2 total volume in the new CAL 200000 cartridge *1μL 180mL 414 Internal cleaner total volume in the new 80000 *1μL 72mL *1μL 450mL time 6500 times CAL Cartridge 415 Waste bottle maximum capacity 500000 418 Sample port maximum life. A number 7000 of roundtrip of sample nozzle 1013 CAL 1 consumption 278 μL 1014 CAL 2 consumption 400 μL 1037 Cleaning pattern 1: Flush (no enzyme) 420 μL 1052 Cleaning pattern 16: Calibration 1 (no 247 enzyme) μL 1053 μL Cleaning pattern 17: Calibration 2 (no 465 enzyme) 87 Consumable replacement alert Below chart describes the threshold when alert message appears. Consumables Waste bottle Caution (yellow display) Threshold for alert Information (Recommend display) Expiry after installation 90% of waste in the bottle Depends on number of Calibration and Sampling. - Flush bottle 10% of Flush solution in the bottle. 15% of Flush solution in the bottle. Depends on number of Calibration and Sampling. CAL Cartridge (Auto QC) 10% of each solution left in the cartridge, or 5day before expiry 7days before expiry. 1month (30 days) which comes first. Sample Port 6500 roudtrip or 5days 14days before expiry. before expiry which comes first. 7000 roundtrip or, 3months (90 days). Pump Head 10days before expiry. 14days before expiry. 6months (180 days) Tubing kit - 1year (360days) 1year (360 Day) cause course from previous replacement. from previous replacement. Sampling Tube - 3months (90 days) course from previous replacement. 3months (90days) cause from previous replacement. Sampling Nozzle - 6months (180 days) course from previous replacement. 6months (180 days) cause from previous replacement. Joint Tube - 1year (360 days) course from previous replacement. 1year (360 days) course from previous replacement. Battery - 3years course from previous replacement. 3years course from previous replacement. 88 Printing paper check 1. Move up the Display. 2. Raise printer lever to open the printer. Check if printing paper is enough. When new thermal roll is installed, place the roll shown below. 3. Close the printer door until it gives click sounds. Check if printing side of paper is facing in front of the instrument. CAUTION ・Print head may be hot immediate after printing. Pay attention when you replace the thermal paper at that moment. ・Use TechnoMedica exclusive printing paper to avoid giving any damage to the printer. The printer may not be warranted by using of local thermal roll. 89 Self Diagnostic Instrument status can be checked by Self Diagnostic function. If instrument needs to be checked periodically, this function verifies the instrument is working fine. Please follow below procedure to perform each diagnostics. If problem found on any diagnostic, follow corresponding corrective action accordingly. Electrode check The system can check if each electrode establishes the circuit properly. The following sequence allows the system to verify the electric circuit including electrodes. Ensure to close the measurement module cover when Self disgnostic Electrode is performed. 1. Access to Self-diagnosis at Others from Function menu. 2. Press Electrode then Start. Average cycle time is 60sec. Instrument with Glc, and Lac parameter may take longer because of the longer cleaning. 3. Electrode self-diagnosis result shall be printed. Symbol Item 1 Voltage output result 2 Output voltage of previous calibration 90 1 2 Troubleshooting for error on Self Diagnosis: Electrode Probable cause Corrective action Bad contact between the pin of Remove affected electrode and push the pin up to the measurement module and check pin is workable. Then check the pin and electrode terminal. terminal of electrode contact well. Electrode terminal is oxidized. Remove rust with file Bubble inside electrode Check inner solution of electrode is enough. If bubbles are on the membrane or inner electrode, remove the bubble on affected electrode. Maximum intensity of flow cell Perform internal cleaning. is out of threshold. Perform Oxy-line cleaning. Below 20000 or over 63000 Perform external cleaning. NOTE Even if no problem found in electrode self-diagnosis, it does not prove that electrode is in good condition. # Comment (supplementary) Checkpoint 1 CAL1 is feeded to FS-P by P1. [ V3 ⇒ Sample port ⇒ FS-P ] V3 is opening to feed CAL1. And the head of the liquid segment is detected by FS-P. The movement is stopped temporarily at this time, and moves to the next step. (The trailing edge of the liquid segment remain V3 part). 2 CAL1 is feeded to FS-M by P1. [ FS-P ⇒ FS-M ] Suction of the liquid is resumed. And the head of the liquid segment is detected by FS-P. The movement is stopped temporarily at this time, and moves to the next step. (The trailing edge of the liquid segment is V3 part. ) 3 CAL1 is feeded to FS-R by P1. [ FS-M ⇒ FS-R ] Suction of the liquid is resumed And the head of the liquid segment is detected by FS-P. The movement is stopped temporarily at this time, and moves to the next step. (The trailing edge of the liquid segment is V3 part. ) Check if CALl is filled all electrode flow path. 4 CAL1 is feeded to FS-L by P2. The aspiration of the liquid is resumed, and the 91 [ FS-P ⇒ FS-L ] introduction into the Hb/OXY unit-side begins with the branch block of measurement module. The head of the liquid segment is detected by FS-L after passage. is Part V3 at this time. Check that CAL1 is filled in measurement module of the Hb/OXY unit. 5 Analysis is started in Check if Contamination of air bubbles checks what is shuttered to measurement electrode flow measurement module. Fill the electrode flow channel in path part. the EL case with chemical solution to evaluate the output of each electrode. ] 6 Analysis is started in Hb It is confirmed that there is no air bubbles entering the flow path portion of measurement electrode. module. The FC-channel in the [Hb-unit is filled with the chemical solution, and the output of the FC-photometric unit is evaluated. ] 7 Cleaning by Flush solution and Solution remaining checks what is absent to flow path part of a measurement system the part V3 eject. The flow path in the EL case, manifold. flow path in Hb, and the fluid flow path in the Hb unit and the chemical solution in the manifold section are process. ] 92 Flow check In this diagnostic, the system observes if the flow sensor ON/OFF within expected time by the following sequence. 1. Access to Self-diagnosis at Others from Function menu. 2. Press Flow and press Start. Average cycle time is approximately 100sec. 3. If error found, instrument displays an alert and prints. 93 Below is the result of self-diagnosis “flow”. 1 FS-L Normal Position of Flow sensor condition 2 Air / Threshold Air voltage (LED ON) / Threshold (lower limit) 3 Reagent / Threshold Reagent voltage (forward) / Threshold (upper limit) 4 Reagent (Re) / Threshold Reagent voltage (backward) / Threshold (upper limit) 5 Count / Threshold Counted Air voltage when checking Air voltage 6 Detect Times (ms) Detect times of reagent (forward) 7 (Re) Detect Times (ms) Detect times of reagent (backward) 94 Position of flow sensor FS-M FS-L FS-R FS-P FS-W 95 Sequence of flow check 96 Troubleshooting for error on Self Diagnosis: Flow General problem Probable cause Corrective action No O-ring or bad O-ring Install new O-ring. Bad installation of electrode Make sure electrodes are installed properly. Especially for Hb electrode. Clog in liquid path Remove clog Bad sample port position Correct position of sample port. Bad sample port rubber. Install new sample port. Bad installation of sampling Place sampling nozzle properly. nozzle Bad position of sample nozzle. Correct position of sample nozzle by adjusting the position of sample. 97 Sample nozzle is bent. Install new sample nozzle. Wrong tubing Install tube properly. Bad position of tubing. Correct position of tubing. Bad or old tubing Install new tubing. Bad position of pump tube. Correct position of tubing. Color of pump housing and color of tube should be matched. Old pump tube. Install new pump tube. Flush solution is installed with Remove the inner cap of flush solution. inner cap of flush solution. CAL cartridge or Flush bottle is Install new CAL cartridge or Flush bottle. empty. Specific problem Probable cause Corrective action Defected Pump unit Replace the pump unit Defected Valve Replace the valve # Comment checkpointed 1 Feed columns (air and Flush) from reverse direction before air Lv sampling To cleaning solutions segment, all FS internal flow path is in empty state. ] After that washing liquid segment that formed in V8sV9 was put into a sampling port direction(reverse direction), liquid feed pump is deactivated, and moves to the next step. Liquid in each flow path of FS's being status remains in is identified. 2 Measure the output of each FS as Air level, and Start air Lv sampling The output of the empty level evaluate. [ All FS is identified. ] The abnormals judgment when out of the specified range. 3 Feed Flush solution to FS-P After draining internal of the manifold, suction the after remaining solution eject Flush solution-liquid from V7 to FS-P, and temporarily stop transport when beginning of the process in manifold Until is detected by FS-P in Flush segment is passing through FS-P, and moves to solution, draw by the right the next step. (rotation of the right pump is CCW) pump. ] 4 Feed Flush solution to FS-M When the liquid suction is resumed and the head 98 Continuing in, and transferred of the liquid segment is detected by passing right pump to FS-M detecting set through FS-M, the transfer is temporarily stopped forth in the preceding paragraph. ] and the process proceeds to the next step. (rotation of the right pump is CCW) 5 Feed Flush solution to When the liquid suction is resumed and the head of the liquid segment is passed through FS-R, the FS-M(forward-direction) The last, and transferred right transfer is stopped and the next step is performed. pump to FS-R detecting set forth (rotation of the right pump is CCW) in the preceding paragraph. ] 6 Feed 7 Center pump rotation of CCW pump and left Feed Flush solution to FS-M is a liquid filled in FS-P, M, R, L pump detecting passage and eject with FS-W of to sampling port, and detects gas/liquid segment as CW. these in FS-W. ] 8 Feed 9 Feed Flush solution to FS-L(reverse-direction) Transfer Flush solution liquid from [ manifold to FS-L via central pump. ] to Starting aspiration of the liquid into the Hb/OXY-line, and when the head of the liquid FS-M(forward-direction) Continuing in, and transfer of segment passes through FS-L, the transfer stops FS-L in the central pump until the and the next step is entered. (CW is pump) liquid under the preceding paragraph is detected. ] Flush solution to Passing from V9 to right pump, and Flush solution is transferred from the case EL side to FS-R(reverse-direction) From manifold to right-hand stop transfer when FS-R is Detect and transferred, pump, and transfers the Flush and the flow proceeds to the next step. (rotation of solution to FS-R. ] the right pump is CW) Flush solution Passing from V8 through central pump, and the liquid Flush solution is transported from the pump module side, and the transfer is stopped when FS-L passes and is Detect, and the flow proceeds to the next step. (CCW is pump) Flush-segment that holds the internal flow path 10 Flush sample process and eject Measurement module and Hbflow for all FS and, in Hb/EL to is empty level is path unit. ] discharged All. Flush solution that stay after completion of process' absenting is identified. 99 FS (flow sensor) calibration check This section describes the procedure for correcting the flow sensor (FS)) in the flow system circuit. FS of GASTAT-700 is the Detect principle of the optical sensor, and therefore changes sensitivity due to degradation of the light source, stain/discoloration of the channel, etc. Each FS requires regular calibration. FS calibrations implementation according to following table. 1. Access to Self-diagnosis at Others from Function menu. 2. Press FS Calibration and press Start. Average cycle time is approximately 100sec. 3. If error found, instrument displays an alert and prints. 100 Below is the result of self-diagnosis “FS Calibration”. F.S-P:2 light receiving element and 1 LED 1 FS-L Normal Position of flow sensor condition 2 Air Air (Threshold) Air voltage (LED ON) voltage) 3 Reagent Reagent (Threshold) Reagent voltage (LED ON) Threshold (target voltage) 4 Dark Air voltage (LED OFF) Dark (Threshold) voltage) LED Control LED power (< 255) 5 Threshold (target Threshold (upper 101 Events requiring Subjects FS calibration Automatic/hand categories External cleaning All FS Auto calibration(automatic implementation after external cleaning) FS replacement All FS Auto calibration(after check FS attachment automatically implement) In time of flow check All FS abnormal Manual calibration(appropriate recovering from abnormal condition) when Steps of the FS calibration sequence are street of following table. # Comment checkpointed 1 Obtain all FS dark Lv (LED Check that all the internal flow paths of FS are empty. OFF) Off light source of all FS are turned, and acquires the line of the outputs of each FS. ] 2 All FS light intensity is Internal flow path of all FS's being air is identified. adjusted. *FS-P(PD2) is excepted. Light source of all FS is lit, and adjusts the maximum value of the output of each FS. ] 3 Feed Flush solution to FS-P It is confirmed that the Flush solution liquid after remaining solution eject supplied from the V7 passes through FS-P and then shifts to the next step. process in manifold Confirm that Flush solution liquid sucked from the [ manifold section can be detected by FS-P. ] 4 ?Feed Flush solution to FS-M Transferring the preceding Flush segment, and after adjusting P(PD2) intensity confirm the situation that if you enter following Transfer Flush solution 2 output step FS-M after passage. after check the output of Part FS-P, and make sure can be detected by FS-M. ] 5 ?Feed Flush solution to Transferring the preceding Flush segment, and confirm the situation that if you enter following FS-M(forward-direction) Transferring the Flush solution, step FS-R after passage and stop. 102 and make sure can be detected by FS-R. ] 6 Feed Flush solution to FS-M(forward-direction) [ Flush solution is transferred, and make sure can be detected by FS-L. ] Transferring the Flush segment in the Hb unit direction in the preceding paragraph, and confirm the situation that if you enter following step FS-L after passage and stop. 7 Feed Flush solution to FS-M Measurement channel solution Flush is referred to port reverse, and make sure can be detected by Flush solutions segment sol of preceding paragraph and preceding paragraph is referred to sampling port-direction reverse, and confirm the situation that if you enter following step FS-W FS-W. ] after passage and stop. 8 Feed Flush solution to FS-R(reverse-direction) Transferring the Flush solution, and make sure can be detected by FS-R. ] Passing from V9 to right pump, and Flush solution is transferred from the case EL side to stop transfer when FS-R is Detect and transferred, and the flow proceeds to the next step. (rotation of the right pump is CW) 9 Feed Flush solution to FS-L(reverse-direction) Transferring the Flush solution, and confirm the situation that can Passing from V8 through central pump, and the liquid Flush solution is transported from the pump module side, and the transfer is stopped when FS-L passes and is Detect, and the flow proceeds be detected in FS-L. ] to the next step. (CCW is pump) 10 Flush sample process and eject Drain Flush solution fluid from the [ measurement and Hb/OXY unit channels. ] Flush-segment that holds the internal flow path for all FS and, in Hb/EL to is empty level is discharged All. Flush solution that stays after completion of process' there is no is identified. 103 Valve check This section describes procedures for evaluating the operating status of electromagnetic valves in manifold modules. The valve check is performed under conditions that flow check is not in flow sensor error). Because the valve check works by the operation of the chemical pump and flow sensor in the operation of the valve check, if have a wrong flow check, check the valve check to remove the cause of the flow check. # Comment checkpointed 1 Valve 2 open and feed AQC AQC solution segments' then passes to the next step after reaching FS-P are identified. L1 to FS-P and eject ) Skip for AQC no function. 2 Valve 4 open and feed AQC The AQC chemical segment is checked to reach the next step after reaching FS-P. L2 to FS-P and eject ) Skip for AQC no function. 3 Valve 5 open and feed AQC The AQC chemical segment is checked to reach the next step after reaching FS-P. L3 to FS-P and eject ) Skip for AQC without function. 4 Valve 3 open and feed CAL1 CAL solution segments' then passes to the next step after reaching FS-P are identified. to FS-P and eject 5 Valve 1 open and feed CAL2 CAL solution segments' then passes to the next step after reaching FS-P are identified. to FS-P and eject 6 Valve 6 open and feed The Cleaner chemical segment is checked to Cleaner solution to FS-P and reach the next step after reaching FS-P. eject 7 Valve 7 open and feed Flush Flush is transferred to FS-L after the Flush-liquid segment reaches FS-P, and make solution to FS-P and eject sure you go to the next step. 8 After aspirate Flush solution To in the process that the head of the Flush to FS-P, open valve 11, and is segment in the preceding paragraph reached FS-L, check that the flow path between the V11 transferred to FS-L. and sampling ports is empty. 9 Flush sample path and eject Flush-segment that holds the internal flow path for all FS and, in Hb/EL to is empty level is discharged All. Flush solution that stays after completion of process' there is no is identified. 104 Valve position 2 way valve (Small): 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 2 way valve (Big): 6, 7, 11, 12 3 way valve: 8, 9, 10 Name Details Valve 1 CAL2 Valve 2 AQC1 Valve 3 CAL1 Valve 4 AQC2 Valve 5 AQC3 Valve 6 Clean Valve 7 Flush Valve 8 Flush / Waste / Air Valve 9 Flush / Waste / Air Valve 10 Waste / Air Valve 11 Air Valve 12 Air 105 Temperature check Procedures to check thermistor elements condition instrument. TH1, 2, 4, 5 are embedded within heater block of each part. Self diagnostic determines by comparetive the output temperature of each TH sensor with expended range. 1. Access to Self-diagnosis at Others from Function menu. 2. Press FS Calibration and press Start. Average cycle time is approximately 100sec. 3. If error found, instrument displays an alert and prints. 106 Position of Thermistor TH0 TH4 TH1 TH2 TH5 TH3 is on the main board inside instrument.Name Location (function) Allowable temperatur e range (℃) TH Electrode (Reference temperature sensor) 35.0 - 40.0 TH1 Block EL (Thermostat sensor) 35.0 – 40.0 TH2 Pre-heater 1 (Thermostat sensor) 35.0 - 40.0 Board in instrument Room temperature - 45.0 TH0 TH3 (Sensor to move air-cooled fan) Target temperatur e (℃) when Description analisis Within - 37 ± 0.1℃. - Within - 37 ± 0.1℃. the When TH3 senseor detect over 30℃, fan moves. If H3 sensor detect 45 ℃ , displayed. TH4 TH5 Hb/OXY block (Thermostat sensor) 35.0 - 40.0 Pre-heater 2 (thermostat sensor) 35.0 – 40.0 Within error is - 37 ± 0.1℃. Within - 37 ± 0.1℃. 107 Troubleshooting for error on Self Dignostic: Temperature Temp sensor TH0 TH sensor Expected value Probable cause and corrective action 35.0 ~ 40.0 ・Measurement module is cold. Wait for 30 minute at least to warm up ・Bad installation of TH sensor. Ensure TH sensor is loaded in measurement module correctly. ・Bad TH sensor. Replace new TH electrode. ・Bad correction factor on the security code 361 and 362. ※ S.C. 361 and 362 are factory setting. TH1 Measureme nt module 35.0 ~ 43.0 ・Measurement module is cold. Wait for 30 minute at least to warm up. ・Temperature at installation site is not proper. Ensure the installation place is air-conditioned. ・Bad Thermistor in measurement module. Please replace the measurement module. TH2 Preheater 1 35.0 ~ 43.0 ・Instrument is cold. Wait for 30 minute at least to warm up. ・ Temperature at installation site is not proper. Ensure the installation place is air-conditioned. ・Bad Thermistor in preheater1 module. Replace the preheater module. TH3 20.0 ~ 45.0 Temp inside instrument ・Installation environment is not in proper temperature. Make sure to have room air condition. TH4 35.0 ~ 43.0 Oxy module ・Instrument is cold. Please wait for 30 minute at least to warm up. ・Dust on the fan filter. Clean or replace the fan filter. ・No spaces next to the fan. At least 10 cm space is required in the fan. ・ Installation environment is not in proper temperature. Ensure the installation place is air-conditioned. ・ Bad Thermistor in Co-oxy module. Replace the Co-oxy module. TH5 Preheater 2 35.0 ~ 43.0 ・Instrument is cold. Please wait for 30 minute at least to warm up. ・ Installation environment is not in proper temperature. Ensure the installation place is air-conditioned. ・Bad Thermistor in preheater2 module. Replace the preheater2 module. 108 GND check Below chart described procedure to check the instrument electrical insolution state. 1. Inside instrument (4) (1) Pass criteria (2) (1) (2) 1Ω and less (3) (4) Uunder10Ω (5) No conduction (O.F is displaied) (3) (5) No. Position 1 ~ Position 2 1 Power GND ~ Sampling module metal Standard 1Ω and less 2 Hb module rear metal 3 Printer module rear metal 4 Electric coating surface Under 10Ω 5 Measurement module rear metal O.F 109 2. Front module (6) Pass criteria (6) 10Ω and less (7) (7) 1Ω and less No. Position 1 ~ Position 2 Standard 6 Screw on Printer module ~ Electric coating surface of rear mesurement module 10Ω and less Mnifold metal 1Ω and less 7 (8) (11) Pass criteria (9) (8) (9) No conduction (10) (11) (O.F is displaied) (12) (12) (10) 110 No. Position 1 ~ Position 2 Standard 8 Center screw on Printer module ~ Screw of Pre-heater 2 (brack) O.F 9 Screw of Pre-heater 1 (brack) 10 Sample port block 11 Pump 1 connecter in right side 12 Electrode block pin 3. Electrode terminal (14) (13) Pass criteria (14) (15) Under 3Ω No. Position 1 ~ Position 2 Standard 14 Ref electrode terminal (G710 ~G720) TH electrode terminal (G730) ~ Measurement module rear cover metal Under 3Ω 15 Electrode block pin 111 Flow cell check (Hb unit) Procedure to check if Flow cell installs in Hb unit. Press security code 9000. And check that “Spectroscope flow cell” change Yes or No (red frame) by the presence or absence of flow cell. (Check if movement of the microswitch to determine flow cell is inserted is correct) 112 Flow cell check (OXY unit) Procedure to check if Flow cell installs in OXY unit. Press security code 9000. And check that “Spectroscope flow cell” change Yes or No (red frame) by the presence or absence of flow cell. (Check if movement of the microswitch to determine flow cell is inserted is correct) 113 Sensor of CAL Cartridge and Bottle check procedure to check sensor of reagent bottle. Press security code "9000", and indicates the left figure. Check that the inside of the red frame varies depending on the presence or absence of each container. (Smooth operation of probe plug) (Supplementary) Below figure is manifold unit. The red circle in the figure indicates the position of each sensor. Flush Waste Cartridge Left figure is figure that looks at bottle sensor from the back side. The left side sensor in the figure shows bottle Detect status and right side sensor indicate bottle detection status. ON OFF 114 Printer check Procedure to check internal printer. 1465 ① Press security code “1465” and print the test pattern. Below test patern is printed out. 115 Software version check Procedure to check the software version. ① Press “Maintenance” ⇒ “Other” ⇒ “Securty code” and enter password (1982). ② Enter the Secrity code “9997” to print the current software version information. Below software version is printed out. SBC‐Ver(PROGRAM): 1.11 SBC‐Ver( SET_SH ) :1.11 SBC‐Ver(SET_INT): 1.11 SBC‐Ver(MESSAGE): 1.11 SH‐Ver( S) :730AQC Ver1.11 YY/MM/DD RMS( PROGRAM) :2.0.3.0 RMS( DLL) :2.0.3.0 ③ Check if all version above are unified. 116 FLOW SEQUENCE Below diagram illustrates overview frlow system of instrument. See below table to learn meaning and name used in the diagram. Overview FS-L FS-P FS-M Pump 2 FS-R Pump 3 Pump 1 Air inlet FS-W Air inlet 117 Description of valve, sensor and motor Item Description V1 2ways valve to allow CAL 2 to introduce into the flow system. V2 2ways valve to allow QC level1 to introduce into the flow system. V3 2ways valve to allow CAL 1 to introduce into the flow system. V4 2ways valve to allow QC level2 to introduce into the flow system. V5 2ways valve to allow QC level3 to introduce into the flow system. V6 2ways valve to allow internal cleaner to introduce into the flow system. V7 2ways valve to allow Flush sol to introduce into the flow system. V8 3ways valve to control Flush solution, waste, air. V9 3ways valve to control Flush solution, waste, air. V10 3ways valve to control waste and ambient air. V11 2ways valve to allow ambient air to introduce into the flow system. V12 2ways valve to allow ambient air to introduce into the flow system. P1, P2, P3 Pumps which draw liquid or ambient air into the liquid path or feed them into the waste. FS-P, FS-L, FS-M, Flow sensors which detects the presence of the liquid. FS-R, FS-W 118 Tube Diagram The following illustrates the tube specification and their location. 14:G735 12: G710/720 13: G735 5 8 0 10: G710/720 11: G735 9 2 7 No. Cat logue 0171052 6 1 Item Name Number 0 3 4 Connection - position 1 Sampling Connection Length position 2 Sampling nozzle - Preheater 1 130mm tube 1 0171051 Tubing kit Pump base 5 - Manifold 50mm 2 0171051 Tubing kit Pump base 2 - Manifold 50mm 3 0171051 Tubing kit Pump base 6 - Preheater 2 55mm 4 0171051 Tubing kit Pump base 4 - Manifold 50mm 5 0171051 Tubing kit Preheater 2 - Pipe bush 35mm 6 0171051 Tubing kit Pump base 5 - Preheater 55mm 7 0171051 Tubing kit Sample port - Manifold 45mm 8 0171053 Joint tube Preheater 1 - FS - P 23mm 9 0171051 Tubing kit Sample port - FS - W 55mm 10 0171051 Tubing kit FS - L - Pump bace 1 200mm (G710 and G720) 11 0171051 Tubing kit FS - L - Pump bace 1 250mm (G735) 12 0171051 Tubing kit Electrode block - Hemolysis unit 120mm (G710 and G720) 13 0171051 Tubing kit Electrode block - OXY unit (G735) 80mm 14 0171051 Tubing kit Hemolysis unit - OXY unit (G735) 40mm 119 Sequence Diagram Item Nozzle Description Position of nozzle varies from each movement. (H) = Home/CAL position (R) = Replace position (F) = Flush position (S) = Syringe position (M) = Micro mode position Pump (W) = Waste position (C) = Capillary position (P) = Port flush position CW: clockwise, CCW: counterclockwise F = Fast speed, M = Middle speed, S = Slow speed i.e.) P2F CW = Pump 2 moves clockwise in Fast speed P1M CCW = Pump 1 moves counter clockwise in middle speed. 120 Regular Flush Sequence No. Nozzle 1 W F Pump Movement 1.P3F CW 1. Nozzle in waste position, V10 and V12 opens, and +P1M CW V11 closes, P1 and P2 moves with middle speed. +P2M CCW P3 moves with fast speed to flow back (from measurement module to sample port) 18 flush/air column by and opening and closeing V8 and V9. Feed it for 10 seconds. 2.P3F CW (Refer to “Figure F-1. Creat Flush/air column. ) 2. After pump stop, flush/air colums come out from the nozzle, P3 moves to discharge the colms. 3.P1F CW +P2F CCW 3. Nozzle moves to flush position. P1 and P2 moves with fast speed to hold flush solution in sample port and to clean sample port. (Refer to “Figure F-2. 4.P3F CW Hold flush solution in port”.) 4. P3 moves with fast speed to discharge Flush solution. (Refer to “Figure F-3. Discharge flush 5.P1F CCW +P2F CW solution”.) 5. Flush solution moves from port to measurement module to make high performance of cleaning. *Make procedure above 3. to 5. as sample port cleaning. 6. Discharge flush solution from flow path. F C W H 6.P3F CW +P1M CW +P2M CCW 7. V10 connects waste line, V11 opens, and V12 7.P3F CW closes, P2 moves with middle speed. P3 moves with +P2M CW fast speed. Nozzle moves to Home/CAL position after moves from flush position to capillary position to remove remaining solution in port. 121 Figure F-1. Creat flush/air column :Flush solution(Blue arrow) 122 Figure F-2. Hold flush solution in port :Flush solution(Blue arrow) 123 Figure F-3. Discharge flush solution :Flush solution(Blue arrow) 124 Calibration sequence No . 1 Nozzle H Pump Movement 1.P3M CW 1. Nozzle moves to Home/CAL position. P1 +P1F CCW moves with fast speed to removes remaining solution in the measurement module path. *If check the flow, calibration retry and CAL2 is not provided. 2.P3F CW +P2M CW 2. P2 moves in middle speed with opening and (P1M closing V11 and V3 (CAL1) or V1 (CAL2) to CCW) make CAL/air column. After the creation of CAL/air column, V3 (CAL1) or V1 (CAL2) closes and V11 opens to feed CAL/air column to Hb direction (CAL1) or measurement module direction (CAL2). (Refer to “Fig. Creation CAL/air column and feed ”.) 3.P3M CW +P2M CW CL-1. 3. V11 closes. V3 (CAL1) or V1 (CAL2) opens. P2 moves to draw CAL to FS-P. (Refer to “Fig. CL-2. CAL Introduction to FS-P”. ) 4.P1L CW +P2L CW 4. V3 closes. P1 and P2 moves to discharge CAL solution to Hb direction. (Refer to “Figure CL-3 Discharge CAL solution”. ) 5.P3M CW +P2L CW 5. V11 opens. P2 moves to feed CAL to Hb direction. (Refer to “Figure CL-4 Feed CAL to Hb direction”. ) 6.P3M CW +P1L CCW +P2L CW 6. P1 and P2 moves to feed CAL to FS-M. (Refer to “Fig. CL-5. Feed CAL to FS-M”. ) 125 No . 2 Nozzle Pump Movement H 7.P3M CW +P1M CCW 7. P1 moves to feed CAL to FS-R. (Refer to “Fig. CL-6. Feed CAL to FS-R”. ) 8. P1 moves to feed CAL to enzyme electrode (or 8.P3M CW +P1F CCW dummy electrode). (Refer to “Fig. CL-7. Feed CAL to enzyme electrode”. ) 9.P3M CW 9. P2 moves to feed CAL to FS-L. *(Refer to “Fig. CL-8 Feed CAL to FS-L” . ) +P2F CW 126 Figure CL-1 Creation CAL/air column and feed :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 127 Figure CL-2 Feed CAL to FS-P :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 128 Figure CL-3 Discharge CAL solution :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 129 Figure CL-4 Feed CAL to Hb direction :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 130 Figure CL-5 Feed CAL to FS-M :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 131 Figure CL-6 Feed CAL to FS-R :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 132 Figure CL-7 Feed CAL to enzyme electrode :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 133 Figure CL-8 Feed CAL to FS-L :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 134 FLUSH cleaning sequence after Calibration No . 1 Nozzle H Pump 1.P3F CW +P1M CCW +P2L CW Movement 1. Nozzle moves to the Home/CAL position. P1, P2 and P3 moves with opening and closing V7 and V11 to feed flush/air columns. (Refer to “Figure CLW-1 flush/air columns sequence”. ) 2.P3F CW 2. Eject out flsh/air columns from the flow path. +P1F CCW +P2F CW 135 “Figure CLW-1 flush/air columns sequence” :Flush solution(Blue arrow) 136 Syringe Measurement sequencee No . 1 Nozzle Pump Movement H C S 1.P3M CW +P2M CW 1. P2 and P3 moves to aspirate remaining solution in port. Nozzle moves from Home/CAL position to Capirally positon. Stop P2 and P3. 2.P3M CW 2. Nozzle moves to Syringe position. P1 and P2 +P1L CCW moves to feed sample to FS-P. (Refer to +P2L CW “Fig.BS-1. Feed blood sample to FS-P” .) Waste position 3.P3M CW 3. P1 and P2 moves to feed sample to FS-M. +P1L CCW +P2L CW (Refer to “Fig.BS-2. Feed blood sample to FS-M” .) 4.P3M CW +P1M CCW 4. Nozzle moves waste position. P1 moves to feed sample to FS-R. (Refer to “Fig.BS-3. Feed blood sample to FS-R”. ) 5. P1 moves to feed sample to enzyme electrode 5.P3M CW +P1F CCW 6.P3M CW +P2M CW (dummy electrode). (Refer to “Fig.BS-4. Feed blood sample to enzyme electrode”. ) 6. P2 moves to feed sample to FS-L. (Refer to “Fig.BS-5. Feed blood sample to FS-L”. ) 7. Conduct “Regular Flush Sequence”. 137 Fig.BS-1. Feed blood sample to FS-P :Sample(Red arrow) 138 Fig.BS-2. Feed blood sample to FS-M :Sample(Red arrow) 139 Fig.BS-3. Feed blood sample to FS-R :Sample(Red arrow) 140 Fig.BS-4. Feed blood sample to enzyme electrode :Sample(Red arrow) 141 Fig.BS-5. Feed blood sample to FS-R :Sample(Red arrow) 142 Capillary measurement sequence No . 1 Nozzle H C Pump Movement 1.P2L CW 1. V11 closes. P2 moves with moving nozzle from Home/CAL position to Capillary position. V11 opens. 2.P3M CW +P2L CW 2. P2 moves to feed sample to FS-P. (Refer to “Fig.BC-1. Feed blood sample to FS-P”. ) 3.P3M CW 3. P1 and P2 moves to feed sample to +P1L CCW T-bifurcation. (Refer to “Fig.BC-2. Feed +P2L CW blood sample to T-bifurcation”. ) 4.P3M CW 4. P1 moves to feed sample to FS-M. (Refer to +P1L CCW “Fig. BC-3. Feed blood sample to FS-M”. ) 5.P3M CW +P1M CCW 6.P1M CW +P2M CW 5. P1 moves to feed sample to FS-R. (Refer to “Fig. BC-4. Feed blood sample to FS-R”. ) 6. Afeter GAS and ISE measurement, Hb measurement starts with P1 and P2 moving and closing V11. After that, P1 and P2 stops with V11 opening. (Refer to “Fig.BC-5. Hb measurement”.) 7. “Regular Flush Sequence” conducts. 143 Fig.BC-1. Feed blood sample to FS-P :Sample(Red arrow) 144 Fig.BC-2. Feed blood sample to T-bifurcation :Sample(Red arrow) 145 Fig. BC-3. Feed blood sample to FS-M :Sample(Red arrow) 146 Fig. BC-4. Feed blood sample to FS-R :Sample(Red arrow) 147 Fig.BC-5. Hb measurement :Sample(Red arrow) 148 CRS measurement sequence No . 1 Nozzle Pump Movement H C 1.P3M CW +P2M CW 1. P2 and P3 moves to aspirate remaining solution in port. Nozzle moves from Home/CAL position to Capirally positon. Stop P2 and P3 S 2.P3M CW 2. Nozzle moves to syringe position. P1 and P2 +P1L CCW moves to feed CRS to FS-P. (Refer to “Fig. +P2L CW CR-1. Feed CRS to FS-R”.) 3.P3M CW W 3. P1 and P2 moves to feed CRS to FS-M. (Refer +P1L CCW to “Fig. CR-2. Feed CRS to FS-M”.) +P2L CW 4.P3M CW 4. Nozzle moves to waste position. P1 moves to +P1M feed CRS to FS-R. (Refer to “Fig.CR-3. Feed CCW CRS to FS-R”.) 5. P1 moves to feed CRS to enzyme electrode (5) P3M CW +P1F CCW (dummy electrode). (Refer to “Fig. CR-4. Feed CRS to enzyme electrode”.) 6. Afeter measurement, Sequence” conducts. “Regular Flush 149 Fig. CR-1. Feed CRS to FS-P :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 150 Fig. CR-2. Feed CRS to FS-M :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 151 Fig. CR-3. Feed CRS to FS-R :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 152 Fig. CR-4. Feed CRS to enzyme electrode :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 153 QC measurement sequence No . 1 Nozzle Pump Movement H C 1.P3M CW +P2M CW 1. P2 and P3 moves to aspirate remaining solution in port. Nozzle moves from Home/CAL position to Capirally positon. Stop P2 and P3 S 2.P3M CW +P2M CW 2. Nozzle moves to syringe position. P2 moves to 3.P3M CW 3. P2 moves to feed GASTROL to FS-L. (Refer to +P2M CW W feed GASTROL to FS-P. (Refer to “Fig. G-1. Feed GASTROL to FS-P”.) “Fig. G-2. Feed GASTROL to FS-L”.) 4.P2M CW 4. P2 moves to measure Hb. (Refet to “Fig. G-3. Hb measurement”.) 5.P1L CW +P2L CW 5. P1 and P2 moves to discharge GASTROL to 6.P3M CW 6. P1 and P2 moves to feed GASTROL to FS-M. Hb direction. (Refer to “Fig. G-4. Discharge GASTROL to Hb directions”. ) +P1L CCW (Refer to “Fig. G-5. Feed GASTROL to +P2L CW FS-M”.) 7.P3M CW +P1M 7. Nozzle moves to waste position. P1 moves to CCW feed GASTROL to FS-R. (Refer to “Fig. G-6. Feed GASTROL to FS-R”.) 8.P3M CW +P1F CCW 8. P1 moves to feed GASTROL to enzyme electrode (or dummy electrode). (Refer to “Fig. G-7. Feed GASTROL to enzyme electrode”.) 154 No . 2 Nozzle Pump Movement W 9.P3M CW +P2M CW 9. P2 moves to feed GASTROL to Hb direction. (Refer to “Fig. G-8. Feed GASTROL to Hb direction”.) 10. After measurement, Flush sequence conducts. 155 Fig. G-1. Feed GASTROL to FS-P :Sample(pink arrow) 156 Fig. G-2. Feed GASTROL to FS-L :Sample(pink arrow) 157 Fig. G-3. Hb measurement :Sample(pink arrow) 158 Fig. G-4. Discharge GASTROL to Hb directions :Sample(pink arrow) 159 Fig. G-5. Feed GASTROL to FS-M :Sample(pink arrow) 160 Fig. G-6. Feed GASTROL to FS-R :Sample(pink arrow) 161 Fig. G-7. Feed GASTROL to enzyme electrode :Sample(pink arrow) 162 Fig. G-8. Feed GASTROL to Hb direction : Sample (pink arrow) 163 AQC Measurement sequence No . 1 Nozzle Pump Movement H 1.P3M CW +P2M CW 1. Nozzle moves to Home/CAL position. P2 moves with opening and closing V11 and V2 to create AQC/air columns. V2 close and AQC/air columns Feed. *In the above, AQC Lv1 uses V2, AQC Lv2 uses V4, and AQC Lv3 uses V5. (Refer to “Fig. A-1. Feed AQC/air columns”. ) 2.P3M CW +P2M CW 2. V11 closes. P2 moves with opening V2 to feed AQC to FS-P. (Refer to “Fig. A-2. Feed AQC to FS-P”. ) 3.P3M CW +P2M CW 3. P2 moves to feed AQC to FS-L. (Refer to “Fig. A-3. Feed AQC to FS-L”. ) 4.P2M CW 4. P2 moves to measure Hb. (Refet to “Fig. A-4. Hb measurement”.) 5.P3M CW +P2M CW 5. V2 closes and V11 opens. P2 moves to feed AQC to Hb directions. (Refet to “Fig. A-5. Feed AQC to Hb directions”.) 6.P1L CW +P2L CW 6. P1 and P2 moves to discharge AQC to Hb directions. (Refet to “Fig. A-6. Discharge AQC to Hb directions”.) 7.P3M CW +P1L CCW 7. P1 and P2 moves to feed AQC to FS-M. (Refet +P2L CW to “Fig. A-7. Feed AQC to FS-M”.) 164 No . 2 Nozzle Pump Movement H 8.P3M CW +P1M CCW 8. P1 moves to feed AQC to FS-R. (Refet to “Fig. A-8. Feed AQC to FS-R”.) 9. P1 moves to feed AQC to enzyme electrode (or 9.P3M CW +P1F CCW dummy electrode). (Refet to “Fig. A-9. Feed AQC to enzyme electrode”.) 10. P2 moves to adjust AQC position to Hb 10.P3M direction. (Refet to “Fig. A-10. Adjust AQC CW +P2M CW position”.) 11. After measurement, conduct Flush cleaning sequence as same as “Flush cleaning sequence after calibration”. 165 Fig. A-1. Feed AQC/air columns : Sample (pink arrow) 166 Fig. A-2. Feed AQC to FS-P :Sample(pink arrow) 167 Fig. A-3. Feed AQC to FS-L (pink arrow): Sample 168 Fig. A-4. Hb measurement :Sample(pink arrow) 169 Fig. A-5. Feed AQC to Hb directions :Sample(pink arrow) 170 Fig. A-6. Discharge AQC to Hb directions :Sample(pink arrow) 171 Fig. A-7. Feed AQC to FS-M :Sample(pink arrow) 172 Fig. A-8. Feed AQC to FS-R :Sample(pink arrow) 173 Fig. A-9. Feed AQC to enzyme electrode :Sample(pink arrow) 174 Fig. A-10. Adjust AQC position : Sample (pink arrow) 175 Dialysate measurement sequence No . 1 Nozzle Pump Movement H C S 1.P3M CW +P2M CW 1. P2 and P3 moves to aspirate remaining solution in port. Nozzle moves from Home/CAL position to Capirally positon. Stop P2 and P3. 2. Nozzle moves to syringe position. P2 moves to 2.P3M CW +P2M CW 3.P1L CW +P2L CW 4.P3M CW +P2L CW W feed dialysate sample to FS-P. (Refer to “Fig. D-1. Feed dialysate to FS-P”. ) 3. P1 and P2 moves to discharge dialysate sample to Hb direction. (Refer to “Fig. D-2. Discgarge dialysate to Hb direction”. ) 4. P2 moves to feed dialysate sample to Hb direction for avoiding air bubble. (Refer to “Fig. D-3. Feed dialysate to Hb direction”. ) 5. P1 moves to feed dialysate sample to FS-M. 5.P3M CW +P1L CCW (Refer to “Fig. D-4. Feed dialysate to 6.P3M CW FS-M”. ) +P1M 6. Nozzle moves to waste position. P1 moves to CCW feed dialysate sample to FS-R. (Refer to “Fig. D-5. Feed dialysate to FS-R”. ) 7.P3M CW 7. P1 moves to feed dialysate sample to enzyme +P1F CCW 8.P3M CW +P2M CW electrode (or dummy electrode). (Refer to “Fig. D-6.Feed dialysate to enzyme electrode”.) 8. P2 moves to adjust dialysate sample position to Hb direction. (Refer to “Fig. D-7. Adjust dialysate position”. ) 9. After measurement is completed, conduct Flush cleaning sequence as same as “Flush cleaning sequence after calibration”. 176 Fig. D-1. Feed dialysate to FS-P :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 177 Fig. D-2. Discgarge dialysate to Hb direction :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 178 Fig. D-3. Feed dialysate to Hb direction :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 179 Fig. D-4. Feed dialysate to FS-M :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 180 Fig. D-5. Feed dialysate to FS-R :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 181 Fig. D-6.Feed dialysate to enzyme electrode :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 182 Fig. D-7. Adjust dialysate position :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 183 Micro mode measurement sequence No . 1 Nozzle H C (or M) Pump Movement 1.P3M CW 1. P2 and P3 moves to aspirate +P2M CW remaining solution in port. Nozzle moves from Home/CAL position to Capirally (or *Micro mode) positon. Stop P2 and P3. (*in syringe case) 2.P3M CW 2. P2 moves to feed blood sample to +P2L CW FS-P. (Refer to “Fig. MM-1. Feed blood to FS-P”. ) H 3.P3M CW 3. Nozzle moves to Home/CAL +P1L position. P1 and P2 moves to feed CCW blood sample to FS-M. (Refer to +P2L CW “Fig. MM-2. Feed blood to FS-M”. ) 4. P1 moves to feed blood sample to 4.P3M CW +P1L CCW FS-R. (Refer to “Fig. MM-3. Feed blood to FS-R”. ) 5. P1 and P2 moves with measurement Hb. (Refer to “Fig. MM-4. Hb measurement”. ) 5.P1M CW +P2MCC W 6. After measurement is completed, conduct Flush cleaning sequence as same as “Flush cleaning sequence after calibration”. 184 Fig. MM-1. Feed blood to FS-P :Sample(Red arrow) 185 Fig. MM-2. Feed blood to FS-M :Sample(Red arrow) 186 Fig. MM-3. Feed blood to FS-R :Sample(Red arrow) 187 Fig. MM-4. Hb measurement :Sample(Red arrow) 188 Self diagnostic (Electrode) sequence No . 1 Nozzle Pump Movement H 1.P3M CW +P2M CW 1. Nozzle moves to Home/CAL position. P2 moves with closing V11 and opening V3 to feed CAL1 to FS-P. (Refer to “Fig. CA-1. Feed CAL1 to FS-P”. ) 2.P1L CW +P2L CW 2. P1 and P2 moves to discharge CAL1 to Hb direction. (Refer to “Fig. CA-2. Discharge CAL1 to Hb direction”. ) 3.P3M CW 3. P1 and P2 moves to feed CAL1 to FS-M. +P1L CCW (Refer to “Fig. CA-3. Feed CAL1 to FS-M”. ) +P2L CW 4.P3M CW 4. P1 moves to feed CAL1 to FS-R. (Refer to +P1M “Fig. CA-4. Feed CAL1 to FS-R”. ) CCW 5. P1 moves to feed CAL1 to enzyme electrode 5.P3M CW (or dummy electrode). (Refer to “Fig. CA-5. +P1F CCW Feed CAL1 to enzyme electrode”. ) 6.P3M CW +P2F CW H 6. P2 moves to feed CAL1 to FS-L. (Refer to “Fig. CA-6. Feed CAL1 to FS-L”. ) 7. Measure pH, pCO2, pO2, and ISE items. 8. After measurement finish, Flush cleaning conducts. 189 Fig. CA-1. Feed CAL1 to FS-P :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 190 Fig. CA-2. Discharge CAL1 to Hb direction :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 191 Fig. CA-3. Feed CAL1 to FS-M :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 192 Fig. CA-4. Feed CAL1 to FS-R :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 193 Fig. CA-5. Feed CAL1 to enzyme electrode :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 194 Fig. CA-6. Feed CAL1 to FS-L :CAL 1(Blue arrow) 195 Self diagnostic(flow) sequence No . 1 Nozzle Pump H W Movement 1. Nozzle moves from Home/CAL position to waste position. 2.P3F CW +P1M CW +P2M CCW 3.P3F CW 2. V10 and V12 opens, and V11 closes, P1, P2 and P3 moves to flow back (from measurement module to sample port) 3 flush/air column by and opening and closeing V8 and V9. Discharge columns to remove remaining solution. +P1M CW +P2M CCW 3. P1, P2 and P3 moves with checking flow sensor air level. All valves initialize. H 4.P3F CW +P2M CW 4. Nozzele moves to Home/CAL position. P2 moves to remove remaining solution. 5. V11 closes and V7 opens, P1 moves to feed 5.P3M CW +P1M Flush solution to PS-P. (Refer to “Fig. CF-1. Feed Flush to FS-P”. ) CCW 6. V7 closes and V11 opens, P1 moves to feed 6.P3M CW +P1M CCW Flush solution to FS-M. (Refer to “Fig. CF-2. Feed Flush to FS-M”. ) 7. P1 moves to feed Flush solution to FS-R. (Refer to “Fig. CF-3. Feed Flush to FS-R”. ) 7.P3M CW +P1M CCW 8. P2 moves to feed Flush solution to FS-L. (Refer to “Fig. CF-4. Feed Flush to FS-L”. ) 8.P3M CW +P2M CW 196 No . 2 Nozzle W Pump 9.P3F CW +P1M CW +P2M CCW Movement 9. Nozzle moves to waste positon. V10 and V12 conects to air line. P1, P2 and P3 moves with checking flow sensor reagent level of FS-W. Discharge Flush solution. After discharged solution, V10 and V12 connects waste line. (Refer to “Fig. CF-5. Feed Flush to FS-W”.) 10.P3M CW +P1M CW 11.P3M CW +P2M CCW 10. V9 opens. P1 moves to aspirate Flush solution in reverse direction. V9 closes and V10 and V12 connects air line to feed Flush solution to FS-R. (Refer to “Fig. CF-6. Feed Flush to FS-R”.) 11. V8 opens. P2 moves to aspirate Flush solution in reverse direction. V8 closes and V10 and V12 connects air line to feed Flush solution to FS-L. (Refer to “Fig. CF-7. Feed Flush to FS-L”.) 12. P1 and P2 moves to discharge Flush solution from flow path. 12.P3M CW +P1F CCW +P2F CW 197 Fig. CF-1. Feed Flush to FS-P :Flush solution(Blue arrow) 198 Fig. CF-2. Feed Flush to FS-M :Flush solution(Blue arrow) 199 Fig. CF-3. Feed Flush to FS-R :Flush solution(Blue arrow) 200 Fig. CF-4. Feed Flush to FS-L :Flush solution(Blue arrow) 201 Fig. CF-5. Feed Flush to FS-W :Flush solution(Blue arrow) 202 Fig. CF-6. Feed Flush to FS-R :Flush solution(Blue arrow) 203 Fig. CF-7. Feed Flush to FS-L :Flush solution(Blue arrow) 204 Self diagnostic (flow sensor calibration) sequence No . 1 Nozzle Pump H Movement 1. Nozzle moves to Home/CAL position. 2.P3M CW +P1M CCW +P2M CW 2. P1, P2 and P3 moves to discharge remaining solution. Check flow sensor dark (LED OFF) level. Adjust sensor level. *without FS-P (refer to below 5.) 3.P3F CW 3. P2 moves to remove remaining solution to Hb direction. +P2M CW 4.P3M CW +P1M CCW 5.P3M CW +P1M CCW 4. V11 closes and V7 opens. P1 moves to feed Flush solution to FS-P. 5. V7 closes and V11 opens. P1 moves to fill solution in FS-P. Adjust sensor level of FS-P. (Referr to “Fig. CC-1. Feed to Flush to FS-P”. ) 6. P1 moves to feed Flush solution to FS-M. 6.P3M CW +P1M CCW 7.P3M CW +P1M CCW 8.P3M CW +P2M CW 7. P1 moves to feed Flush solution to FS-R. 8. P2 moves to feed Flush solution to FS-L. 205 No . 2 Nozzle W Pump Movement (8) P3F 8. Nozzle moves to waste positon. V10 and V12 CW conects to air line. P1, P2 and P3 moves with +P1M CW checking flow sensor reagent level of FS-W. +P2M Discharge Flush solution. After discharged CCW solution, V10 and V12 connects waste line. 9.P3M CW 9. V9 opens. P1 moves to feed Flush solution in reverse direction. V9 closes and V10 and V12 connects air line to feed Flush solution to FS-R. +P1M CW 10.P3M CW +P2M CCW 10. V8 opens. P2 moves to feed Flush solution in reverse direction. V8 closes and V10 and V12 connects air line to feed Flush solution to FS-L. 11. P1 and P2 moves to discharge Flush solution in the path. 11.P3M CW +P1F CCW +P2F CW 206 Fig. CC-1. Feed to Flush to FS-P :Flush solution(Blue arrow) 207 Self diagnostic (Valve) sequence No . 1 Nozzle Pump H Movement 1. Nozzle moves to Home/CAL position. 2.P3M CW +P2M CW 2. V11 closes and V2 opens. P2 moves to feed reagent to FS-P. V2 closes V11 opens. Check to take time to detect reagent by FS-P. *Checking V2, V4, and V5 is for AQC type. (Refer to “Fig. CV-1. Feed reagent to FS-P”. ) 3.P3M CW +P2M CW 3. P2 moves to feed reagent to Hb direction. (Refer to “Fig. CV-2. Feed reagent to Hb direction”. ) 5.P3M CW +P2M CW 4. Above 2. and 3. operation is carried out repeatedly in order of V2, V4, V5, V3, V1, V6. *Checking V2, V4, and V5 is for AQC type. 5. V11 closes and V7 opens. P2 moves to feed Flush solution to FS-P. V7 closes V11 opens. Check to take time to detect Flush solution by 6.P3M CW +P2M CW 7.P3M CW +P2M CW FS-P. (Refer to “Fig. CV-3. Feed Flush to FS-P”. ) 6. V11 closes and V7 opens. P2 moves to feed Flush solution to FS-L. V7 closes V11 opens. Check to take time to detect Flush solution by FS-L. (Refer to “Fig. CV-4. Feed Flush to FS-L”. ) 7. P2 moves to feed Flush solution to Hb direction. 208 No . 2 Nozzle Pump Movement H 8.P3M CW +P2M CW 8. V11 closes and V7 opens. P2 moves to feed Flush solution to FS-P. V7 closes V11 opens. Check to take time to detect Flush solution by FS-P. 9.P3M CW +P2M CW 10.P3M CW +P2M CW 9. P2 moves to feed Flush solution to FS-L. Check to take time to detect Flush solution by FS-L. 10. P2 moves to feed Flush solution to Hb direction. 11. If valve check is OK, Flush cleaning sequence conducts. After CAL! measures. 209 Fig. CV-1. Feed reagent to FS-P :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 210 Fig. CV-2. Feed reagent to Hb direction :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 211 Fig. CV-3. Feed Flush to FS-P :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 212 Fig. CV-4. Feed Flush to FS-L :SAMPLE(Blue arrow) 213 Internal cleaning introduction sequence No . 1 Nozzle Pump H Movement 1. Nozzle moves to Home/CAL position. 2.P3M CW +P2M CW 2. V11 closes and V6 opens. P2 moves to detect cleaner by FS-P. After FS-P detects, feed cleaner to FS-L. (Refer to “Fig. CW-1. Feed cleaner to FS-P and FS-L”. ) 3.P3M CW 3. V6 closes and V11 opens. P1 moves to feed +P1L CCW cleaner to FS-M. (Refer to “Fig. CW-2. Feed cleaner to FS-M”. ) 4.P3M CW 4. P1 moves to feed cleaner to FS-R. (Refer to +P1L CCW “Fig. CW-3. Feed cleaner to FS-R”. ) 5.P3M CW 5. P1 moves to feed cleaner to enzyme electrode +P1L CCW (dummy electrode). (Refer to “Fig. CW-4. Feed cleaner to enzyme electrode”. ) 6.P3M CW 6. P2 moves and feed cleaner to remove cleaner +P2M CW in manihold path to Hb direction. (Refer to “Fig. CW-5. Feed cleaner to Hb direction”. ) 7. Nozzle moves to Home/CAL position. Cleaner fill all path for 180 seconds. 214 Internal cleaning sequence No . 1 Nozzle Pump Movement H 1. P3F CW +P2M CW 1. Nozzle moves to the Home/CAL position. P2 moves with opening and closing V7 and V11 to feed flush/air 5 columns in forward direction. 2. Nozzle moves to the waste position. V10 and V12 conncets air line. P3 moves with opening and closing V8 and V9 to feed flush/air 30 columns in reverse direction for 10 seconds. 3. After pump stop, flush/air colums come out from the nozzle, P3 moves to discharge the W F 2.P3F CW +P1M CW +P2M CCW 3.P3F CW colms. 4.P1F CW 4. Nozzle moves to flush position. P1 and P2 +P2F CCW moves with fast speed to hold flush solution in sample port and to clean sample port. 5.P3F CW 5. P3 moves with fast speed to discharge Flush solution. 6.P1F 6. Flush solution moves from port to CCW measurement module to make high +P2F CW performance of cleaning. *Make procedure 3times above 4. to 6. as sample port cleaning. 7.P3F CW +P1M CW +P2M CCW 8.P3F CW +P2M CW F C W 7. Discharge flush solution from flow path. 8. V10 connects waste line, V11 opens, and V12 closes, P2 moves with middle speed. P3 moves with fast speed. Nozzle moves to Home/CAL position after moves from flush position to capillary position to remove remaining solution in port. 9. After clean completion the 2-point calibration conducts. H 215 Fig. CW-1. Feed cleaner to FS-P and FS-L :Cleaner (Blue arrow) 216 Fig. CW-2. Feed cleaner to FS-M s :Cleaner (Blue arrow) 217 Fig. CW-3. Feed cleaner to FS-R :Cleaner (Blue arrow) 218 Fig. CW-4. Feed cleaner to enzyme electrode :Cleaner (Blue arrow) 219 Fig. CW-5. Feed cleaner to Hb direction :Cleaner (Blue arrow) 220 External cleaning introduction sequence No . 1 Nozzle Pump H S Movement 1. Nozzle moves to the Syringe position. 2.P3M CW +P2M CW 2. P2 moves to detect reagent by FS-P. P2 moves to feed reagent to FS-L. (Refer to “Fig. EW-1. Feed to FS-P and FS-L”.) 3.P3M CW 3. P1 moves to fill reagent in measurement +P1L CCW module. (Refer to “Fig.EW-2.Fill reagent in measurement module”.) 4. Nozzle moves to the Home/CAL position. Fill reagent in measurement module for 180 seconds. 221 External cleaning sequence No . 2 Nozzle H W Pump Movement 1.P3F CW +P1M CW +P2M CCW 1. Nozzle moves to the waste position. V10 and V12 conncets air line. P1, P2 and P3 moves with opening and closing V8 and V9 to feed flush/air 30 columns in reverse direction for 10 seconds. 2.P3F CW 2. After pump stop, flush/air colums come out from the nozzle, P3 moves to discharge the colms. F 3.P1F CW +P2F CCW 3. Nozzle moves to flush position. P1 and P2 moves with fast speed to hold flush solution in sample port and to clean sample port. 4.P3F CW 4. P3 moves with fast speed to discharge Flush 5.P1F solution. CCW +P2F CW 5. Flush solution moves from port to measurement module to make high F C W H performance of cleaning. *Make procedure 3times above 3. to 5. as sample port cleaning. 6.P3F CW +P1M CW +P2M CCW 7.P3F CW +P2M CW 6. Discharge flush solution from flow path. 7. V10 connects waste line, V11 opens, and V12 closes, P2 moves with middle speed. P3 moves with fast speed. Nozzle moves to Home/CAL position after moves from flush position to capillary position to remove remaining solution in port. 8. After clean completion the 2-point calibration conducts 222 Fig. EW-1. Feed to FS-P and FS-L :Ex. cleaner(Blue arrow) 223 Fig.EW-2.Fill reagent in measurement module : Ex. cleaner (Blue arrow) 224 Replacement Periodic replacement part The replacement of parts described in the Consumables replacement menu of the apparatus instrument shall be performed according to the user manual. In top-quality dried bonito, be described in replacement procedures of other tubes, and batteries. As caution on replacements of these part, individual precautions and others are performed according to description of the term. Other tubes [Parts] Tubing kit set : 1 set (Use genuine part) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery (OFF) in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ ④ ⑤ ⑥ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. Replace tubes according to piping diagram. Remove the pump module and waterproof plate to replace tube rear of the module. Below is pump module rear of pump module. ⑦ Reinstall waterproof plates and pump module. ⑧ Connect AC addapter. ⑨ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery and check flow path by self-diagnostic. 225 Battery In top-quality dried battery replacement exchanging procedure of the power supply unit of the apparatus is described. [Parts] Battery : 1 piece (use genuine part) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery (OFF) in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove the rear of instrument plate and pull the CPU/PC-BOX. ⑤ Screw the battery bracket and replace battery (red circle). (Check connector for battery) ⑥ Reinstall CPU/PC-BOX. ⑦ Connect AC adapter. ⑧ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery. 226 Unscheduled replacement part In top-quality dried bonito, be described in replace non regular replacement part for instrument. As caution on replacements of these part, collect of configuration parameters and data may be led to need in advance. Individual precautions and others are performed according to explanation of each term. Sampling port door In this section, be described in replacement procedures of sample instrument module flap. [Parts] Door : 1 piece (use genuine part) [Procedure] ① Pull the door show in the figure below. ② Replace door along the axis of cutting position until sounds click. 227 Fuse This section describes procedure of replacement the fuse of the power supply filter unit of the apparatus. [Parts] Fuse : 2 (use genuine parts) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery (OFF) in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Up-and-down switch unit using hollow so that be shown in figure, and derive fuse box of oranges. ⑤ ⑥ ⑦ ⑧ Replace 2 new fuses. Reinstall fuse box. (the back face plate and orange edges are flat) Connect AC addapter. Turn on the power ( | ) and battery. Fuse 228 Sampling nozzle In this section, be described in sample instrument module nozzle replacement procedures. [Parts] Nozzle : 1 piece (use genuine part) [Procedure] ① If instrument is turned off, move nozzle in direction of blue arrow (upper end position) in the following below.(next is ⑤) ② If instrument is turned on, press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "Security code". ③ Enter security code "1982". ④ Enter security code "9041" and move nozzle orign position in the following figure. ⑤ Remove sampling port. ⑥ Remove nozzle guides and nozzles at the same time in direction of red arrows. ⑦ Isolate nozzle guide and nozzle and reinstall nozzle guide after cleaning nozzle. ⑧ Reinstall nozzle guid and nozzle. ⑨ Press security code "9046" and "9041" to check nozzle movement. 229 Flow sensor In this section, be described in replacement procedures of flow sensor with each instruments(screw fixed). [Parts] Flow sensor : 1 unit (Use genuine part) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery (OFF) in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove screws on flow sensor (red circle) as shown below. Pull flow sensor from body with connections and contacts. Replace flow sensor and reinstall connections. ⑤ Connect AC adapter and turn on the power. ⑥ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery and check flow path by self-diagnostic. 230 Touch panel display module In this section, procedure of exchanging a display module of the apparatus is described. [Parts] Display module : 1 unit (Use genuine part) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove the display cover from the rear of instrument and replace new one. ⑤ Remove the cables of power, USB and DVI. ⑥ Connect AC adapter and turn on the power. ⑦ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery. 231 Printer unit In this section, be described in instrument printer module replacement procedures. [Parts] Printer module : 1 piece (use genuine part) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove the plate in rear of instrument.Remove and replace printer module in the following figure. ⑤ As caution on fastening of the module fixing screw after replacement, roller platen(printer cover) is attached to print head in status that is a printer paper, and performs the tightening. ⑥ After assembling the procedure in reverse procedure, it is possible to turn on the power supply and confirm that the print is properly performed(roll paper meandering, print, and paper feeding failure). 232 Hb unit & lighting source In this section, be described in OXI module replacement procedures of instrument. [Parts] Hb module : 1 piece (use genuine part) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove the panel in rear of instrument. Remove the preheater unit and replace Hb module. ⑤ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery and check calibration and QC. 233 234 OXY unit, hemolysis unit and light source In this section, procedure for exchanging the OXI module of the apparatus is described. [Parts] OXI module : 1 unit (Use genuine part) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove the panel in rear of instrument. Remove the preheater unit and replace Hb module. ⑤ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery and check calibration and QC. 235 236 237 Electrode module unit In this section, be described in EL module replacement procedures of instrument. [Parts] Electrode module : 1 piece (use genuine part) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove the electrode module from the body and replace new one as shown below. ⑤ Replacement Pipe bush and the ring from both sides of the electrode presser plate, as shown in the next page and replace the new parts. ⑥ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery and check flow path by self-diagnostic. 238 Sampling module In this section, procedure of exchanging a sample module of the apparatus is described. [Parts] Sampling module: 1 piece (use genuine part) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove the sample module from body and replace new one as shown below. Reinstall sampling port, the nozzle and tubings. ⑤ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery and check flow path by self-diagnostic. 239 Manifold unit & Valve In this section, describe how to exchange instrument manifold modules and valves. [Parts] Manifold module : 1 piece (use genuine part) Normal close 2 electromagnetic valve (small) : 5 pieces (V1, V2, V3, V4, V5) Normal close 2 electromagnetic valve (large) : 2 pieces (V6, V7, V12) Normal open 2 electromagnetic valve (large) : 1 piece (V11) 3 electromagnetic valve (large) : 3 pieces (V8, V9, V10) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove tubes connected to Manifold module. ⑤ Remove the manifold module and replace new one as shown below. Turn on the power ( | ) and battery and check valve by self-diagnostic. ⑥ If replace the valve individually, take care to replace the direction and type of the valves. (the following figure shows a view from the back side) 240 Below is the connection of each valve to the relay board. Valve CN Valve CN 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 8 9 10 11 12 8 9 10 11 12 13 241 Below is the valve position view on manifold module from rear side. 242 Barcode scanner unit This section describes how to exchange instrument barcode scanner unit. [Parts] Barcode scanner unit : 1 piece (use genuine part) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove the barcode scanner unit from body and replace new one as shown below. ⑤ Turn on the power. ⑥ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery and check if new barcode reader can scan consumable barcode. Installing the bar - code scanner unit from the viewpoint of the bottom side panel) 243 Preheater unit In this section, be described in preheater unit replacements procedures. [Parts] Preheater unit 1 : 1 unit (Use genuine part) Preheater unit 2 : 1 units (Use genuine parts) [Procedure] ⑦ Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ⑧ Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ⑨ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ⑩ Remove the preheater unit from body (red circle) and replace new one. ⑪ Connect AC adapter. ⑫ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery and check Temperature by self-diagnostic. 244 CPU/PC-BOX (remain SBC) In this section, be described in instrument power box module replacement procedures. [Parts] CPU/PC-BOX : 1 unit (use of genuine part) NOTE: SSD is not implanted, setting file and DataBase migration process are executed in advance. [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove the CPU/PC-BOX and replace new one. ⑤ Reinstall new CPU/PC-BOX ⑥ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery. ⑦ "Maintenance" when instrument completes startup ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "security code" is clicked. 245 ⑧ Security code "****" is inputed. ⑨ Security Code "○○ ○ ○" is inputed, and MAC address is checked. (Re-set of IoT maintenance is needed. Note the memo. ) NOTE: For IoT maintenance set procedures, services manual "8.15 modem check" is viewed. 246 SBC In this section, be described in procedures of SBC that are mounted on instrument power box module internal. [Parts] SBC : 1 unit (Use genuine parts) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove the CPU/PC-BOX to replace SBC. ⑤ Replace new SBC and reinstall CPU/PC-BOX. ⑥ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery. ⑦ Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "Security code". ⑧ Enter security code "1982". ⑨ Enter security code “1538” and enter MAC address (In the case of using Iot). 247 NOTE: Please refer to the service manual "8.15 modem check"for procedure of set IoT maintenance. 248 fan In this section, be described in unit's cabinet and supply box module internal fan replacement procedures. [Parts] Enclosure fan (large) : 1 unit (Use genuine parts) Power box fan (Small) : 3 units (Use genuine parts) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Pull the CPU/PC-BOX from bodyand dismantle it to access the fan (small). ⑤ Replace new fan and reinstall CPU/PC-BOX. 249 ⑥ Replace new fan (Be careful not to drop the nut). ⑦ Reinstall CPU/PC-BOX. 250 Pump unit In this section, be described in instrument pump module and replacement procedures of pump motor. [Parts] New pump module (use genuine parts) new pumps motor (use genuine parts) [Procedure] ① Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down" ⇒ "Shut down". ② Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ③ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ④ Remove the screws ( ) and motor. (do not loosen the screws of the mark( (defend to Liquid delivery from the pump)) 🚫 ). ⑤ Replace new pump module. Check that connector box is riding at upper right position to ragged edge of fitting as shown below. ⑥ Install Pump module. ⑦ Connect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ⑧ Turn on the power ( | ) and battery. [ back-view of pump unit ] Connecter box 🚫 🚫 🚫 🚫 🚫 🚫 251 SSD In this section, be described in procedures of SSD that become instrument storage device. [Parts] SSD (software installed) USB flush memory (Maximam 32GB) [Procedure] ① If the instrument does not work, check unique parameter from S/N.( next is ⑧). ② If the instrument works, press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "Data exchange" ⇒ "Data transfer". ③ Insert USB flush memory to USB port to get back up of the instrument. Check mark “Setting file” and “Data base” and press "OK". ④ If IoT function is valid, export 3 setting files (FTP related association, mail relationship and service reservation) to USB flush memory. (refer to services manual chapter 5). ⑤ After checking transfer procedures completing and remove USB flush memory. ⑥ Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down"⇒ "shut down". ⑦ Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ⑧ Disconnect AC addapter in rear of instrument. ⑨ Remove the screws on the lower left of the rear of instrument as shown below. And loosen the screws on the SSD bracket and remove SSD with bracket. ⑩ ⑪ ⑫ ⑬ Disconnect the SATA cable and power source cable from SSD. Replace new SSD. Connect AC addapter in rear of instrument and turn on the power ( | ) and battery. Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "Data exchange" ⇒ "Data inport". ⑭ Insert USB flush memory to USB port to get back up of the instrument. Check mark “Setting file” and “Data base” and press "OK". ⑮ If IoT function is valid, export 3 setting files (FTP related association, mail relationship and service reservation) to USB flush memory. (refer to services manual chapter 5). ⑯ After checking transfer procedures completing and remove USB flush memory. ⑰ Press "Function" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "System shut down"⇒ "shut down". ⑱ Turn off (0) the power and battery in rear of instrument after power LED color become "orange". ⑲ Turn on the power ( | ) and batter. 252 253 Troubleshooting chart In top-quality dried bonito, a procedure for solving the problem to be able to recover the problem from the state of the apparatus and to be able to recover the problem is shown in the flowchart. Problem factors those that is attributed to I/F systems system those that is due to flow path system or is roughly. "9.5.2 if it corresponds to the symptoms indicated in the bottom diagram. When proceed with analysis of I/F-system, and do not apply, 9.5.1. proceed to flow chart flowchart. START - Display lights (hide display). - Display color abnormal. - Starting up and display delays. Either applies or similar phenomena occur. - Abnormal coordinate of touch-panel. - Error window display of Windowsyou see. None of them are Analysis of Flow path Analysis of the I/F system 254 Flow path flowchart START (Interviewing) How long have you abnormal occurred? Abnormal [Check point] 1. Maintenance record of consumables. Cleaning flow ⇒ inspects the success of treatment. 2. Check the clog inside the flow path. ⇒ Remove a clot. Normal (Interviewing) Abnormal How long have you abnormal occurred? [Check point] Calibration flow 1. Calibration report 2. Maintenance report of consumable. Normal ⇒ inspects the success of treatment. 3. Check the clog inside the flow path. ⇒ Remove a clot. 4. Air bubble in calibration solutions. ⇒ Fix flow path constriction or air leakage, etc. Abnormal AQC flow (Interviewing) How long have you abnormal occurred? [Check point] 1. AQC record Normal 2. Maintenance report of consumable. ⇒inspects the success of treatment 3. Check the clog inside the flow path. ⇒ Remove a clot. 4. Air bubble in calibration solutions. ⇒ Fix flow path constriction or air leakage, etc. Next page 255 (Interviewing) How long has the problem occurred? Abnormal QC flow [Check point] 1. QC record 2. Maintenance report of consumable. ⇒inspects the success of treatment Normal 3. Check the clog inside the flow path. ⇒ Remove a clot. 4. Air bubble in calibration solutions. ⇒- Fix flow path constriction or air leakage, etc. Abnormal (Interviewing) How long has the problem occurred? Sample flow [Check point] 1. Measurement record Normal 2. Maintenance report of consumable. ⇒inspects the success of treatment 3. Check the clog inside the flow path. ⇒ Remove a clot. 4. Air bubble in calibration solutions. ⇒- Fix flow path constriction or air leakage, etc. Abnormal Reproducibility of CAL (Interviewing) How long has the problem occurred? [Check point] Normal 1. Measurement record 2. Maintenance report of consumable. ⇒inspects the success of treatment 3. Check the clog inside the flow path. ⇒ Remove a clot. 4. Air bubble in calibration solutions. Next page ⇒ Fix flow path constriction or air leakage, etc. 256 (Interviewing) How long has the problem occurred? [Check point] Abnormal 1. AQC record 2. Maintenance report of consumable. AQC data ⇒inspects the success of treatment interpretation 3. Check remaining amount of AQC. Normal ⇒Remove a clot. 4. Air bubble in calibration solutions. ⇒ Fix flow path constriction or air leakage, etc. (Interviewing) How long has the problem occurred? Abnormal QC data [Check point] 1. QC record interpretation 2. Maintenance report of consumable. ⇒inspects the success of treatment Normal 3. Check the QC target value. 4. Check the QC measurement procedure and environment. ⇒- Fix flow path constriction or air leakage, etc. Abnormal Sample data determination (Interviewing) Why do you deem the result has deviation? How long has phenomenon occurred? [Check point] 1. Measurement record 2. Maintenance report of consumable. ⇒inspects the success of treatment 3. Check a clog inside container. ⇒Remove a clot. END 4. Reproducibility of the problem 5. Check the procedure. Before sample measures. 257 I/F system flow chart (Interviewing) START How long has the problem occurred? [Check point] Abnormal 1. Check the signal cable. 2. Bad touch panel reaction. Touch panel ⇒ Refer to 8.11. 3. Bad response speed Normal ⇒ Refer to 8.11 (Interviewing) Abnormal Color/brightness of display How long has the problem occurred? [Check point] 1. Check electric voltage of screen 2. Check the brightness/tint setting Normal 3. Check the signal cable 4. Check the backlight ⇒ Check the color change from the cold. Yes Windows error (Interviewing) How long has the problem occurred? [Check point] 1. Inspection of internal storage Non ⇒Check the OS file 2. Check internal communication. ⇒ Check the internal cables. 3. Check for virus infection. ⇒ Virus removal file was implemented. Next page 258 (Interviewing) Abnormal Boot up speed How long has the problem occurred? [Check point] 1. Check the restart time 2. Evaluating access speed for storage Normal 3. Storage capacity 4. Check SMART info. 5. Check Temporary folder and delete files that is no longer used. Yes Blue back screen (Interviewing) How long has the problem occurred? [Check point] ① Storage capacity No ② Check SMART info see. ③ Storage restoration process. ④ Check the SBC there (Interviewing) Restart repetition How long has the problem occurred? [check point] ① Storage use capacity Ther e is ② Check SMART info. ③ Storage restoration process. ④ Check the SBC END 259 Standby Screen Checking When instrument has an error, the following symbol/message appears on the display. Field Instrument status Symbol/Message Description Some parameters cannot be analyzed due to calibration/QC and AQC error or consumable replacement date is coming soon. Analysis cannot be conducted due to flow system error or some consumables are expired. Printer cover is open. Maintenanc e Status Comsumables replacemet date is coming soon. Details information is displayed when △icon is pressed. Error code and message are displayed. Corrective action appears when Navigation is pressed. Electrode status Pre-caution Details information can be checked when ! icon is pressed. AQC error occurd Details information can be checked when △ icon is pressed. Analysis cannot be conducted. Details information can be checked when × icon is pressed. 260 "○ Ready " status Currently, instruments can not measurement some parameters, or the replacement deadline of Consumables is close to caution state. If display this alarm sg, the following is the reason. - Calibration error of some parameters(electrode) - AQC error of some parameters (electrode) - The regulars consumable replacement Expiration date Procedures to check clause of electrode conditions error troubleshooting. "× Measurement " Unable status It is status that currently warns that instrument is unable to measurement. If this caution is displayed, there is an abnormal in instrument and a recovery procedure is required. As possible main cause, possible those are as follows. - If the previous calibration is invalid - Sky or expired date CAL Cartridge - Waste full - It is Flush solution empty liquid - Limit of use or expired date other consumable QA - The possibility of the set of parameters of maintenance part - System temperature occurrence of an abnormality - Occurrence of an abnormality of flow system The treatment confirms the error and check terms. 261 Errors Displays in Instrument Status Field This chapter describes troubleshooting for errors displays in the instrument status field. Message Corrective action Printer cover open Close the printer cover No printer paper notification Load thermal roll paper 262 Errors Displays in Electrode Status Field When parameters have error for Calibration, AQC, GASTROL, ISE CRS and Dialysis, electrode status shows ! or △ or ×. Press electrode status icon to know further details. Check method of Electrode condition Details of Electrode condition 263 Display × Pop up example Description Calibration failure ・ Calibration passed but electrode voltage and slope Electrode Voltage Slope pH 1.3 – 3.9 50 – 68 pCO2 1.3 – 4.1 40 – 72 pO2 0.5 – 4.1 0.7 – 2.2 Na 1.4 – 3.8 60 – 80 K 2.3 – 4.1 48 – 68 Cl 2.3 – 3.9 -57 - -40 Ca 2.3 – 3.5 20 - 40 Glc Lower limit 0.12 Lac Lower limit 0.0825 Flow cell Lower limit 25000 △ (Hb module) Flow cell Lower limit 25000 (CO-OXY module) values are out of the following range. ・ AQC out of range. ・ Calibration passed electrode voltage, slope values and count are out of the following range. Electrode Voltage Slope Count (sec) ! pH 1.7 – 3.5 25 – 66 Over 40 pCO2 2.0 – 3.6 47 – 70 Over 65 pO2 0.7 – 1.5 0.9 – 2.1 Over 60 Na 2.4 – 3.4 65 – 78 Over 40 K 2.5 – 3.9 55 – 66.5 Over 40 Cl 2.5 – 3.3 -55 - -45 Over 40 Ca 2.5 – 3.3 25 - 38 Over 40 Glc Lower limit 0.15 Lac Lower limit 0.095 Hb 30000 - 60000 (Hb module) Flow cell 30000 - 60000 (CO-OXY module) 264 ・ AQC is out of recommended range, abnormal result compared with previous results, abnormal trend and wide variation. ・ GASTROL is out of upper/lower limit value, recommended range, abnormal result compared with previous results, abnormal trend and wide variation. ・ CRS is out of upper/lower limit value, recommended range, abnormal result compared with previous results, abnormal trend and wide variation. ・ Dialysis is out of upper/lower limit value, recommended range, abnormal result compared with previous results, abnormal trend and wide variation. Print condition The latest calibration history and the AQC history are output. NOTE: From the date of calibrations of last time, when pass 1 point calibration and pass 2 point than 2 hours than 5 hours, the calibration of all the measurement parameters is disabled. (ア) Press (electrode condition) (イ) electrode condition is displayedState-of-the-art calibration status and AQC result is displayed 265 Press detailed output. AQC results of 3 batch are outputted print calibration record and past history of 10 batch past. Output case with details calibration history a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) Symbol Details a) Date ( YYYY/MM/DD HH:MM) b) Calibration date & ID c) Type of calibration (Cal1, Cal2) d) Electrode species e) Output voltage calibration time f) Drift value g) Slope value h) Count value i) Calibration error content in 266 Coping at calibration error Referring to calibration history and the AQC history, and process in following table. Case Calibration result AQC result Correspondence procedures 1 There is abnormal to whichever Paragraph 1 of pH/Na/K/Cl/Ca. Seeing [ 9.8.3.pH/Na/K/Cl/iCa troubleshooting procedures 2 To above whichever Paragraph 2 of pH/Na/K/Cl/Ca [9.8.4. Electrode troubleshooting procedures] Ref (see) →See [ 9.8.3: pH/Na/K/Cl/iCa there is abnormal. troubleshooting procedures ]. 3 There is abnormal to whichever Paragraph 1 of pCO2/pO2. See [ 9.8.5 pC22/p22 troubleshooting procedures ] 4 There is abnormal to all sections of pCO2/pO2. See [ 9.8.5 pC22/p22 troubleshooting procedures ] 5 There is abnormal to whichever Paragraph 1 of Glc/Lac. [9.8.6. Glc/Lac procedure ] 6 There is abnormal to all sections of Glc/Lac. [9.8.6. Seeing Glc/Lac troubleshooting procedures 7 Having abnormals to - [9.8.7. Hb/OXY troubleshooting Hb procedure ] 8 Having abnormals to OXY [9.8.7. Hb/OXY troubleshooting procedure ] 9 Abnormal corresponding to the plurality of the [9.8.8. Please troubleshooting stream troubleshooting refer to procedures the for 267 above-mentioned Case1-8 10 Normal Either Seeing [ 9.8.3.pH/Na/K/Cl/iCa pH/Na/K/Cl/Ca has troubleshooting procedures an abnormal in the 1 section. 11 Normal To whichever Paragraph above [9.8.4. Electrode troubleshooting procedures] Ref (see) 2 of →See [ 9.8.3: pH/Na/K/Cl/iCa pH/Na/K/Cl/Ca there is abnormal. troubleshooting procedures ]. 12 Normal There is abnormal See [ 9.8.5 pC22/p22 to whichever troubleshooting procedures ] Paragraph 1 of pCO2/pO2. 13 Normal There is abnormal Seeing to all sections of [ 9.8.5.pCO2troubleshooting pCO2/pO2. procedures 14 Normal There is abnormal [9.8.6. Glc/Lac to whichever procedure ] Paragraph 1 of Glc/Lac. troubleshooting 15 Normal There is abnormal [9.8.6. Glc/Lac to all sections of procedure ] Glc/Lac. troubleshooting 16 Normal Have abnormals in [9.8.7. Seeing Hb/OXY Hb troubleshooting procedures 17 Normal Have abnormals in [9.8.7. Seeing Hb/OXY OXY troubleshooting procedures 268 Calibration failure of pH/Na/K/Cl/Ca Conduct the following corrective action to clear the failure. When calibration failure occurs more than two parameters, follow 10.3.4. Calibration failure of Ref 1. 2. 3. 4. Shake the affected electrode down to babble the electrode’s sample path. Check for solution level of affected electrode. If small, dispose the solution to avoid concentration, and refill it. Shake Ref electrode so that Ref solution will reach to the sample path of the electrode. Check for solution level of Ref electrode. If small, dispose the solution, wash KCL crystal exists at the sample path with distilled water, and then refill the solution. 5. 6. 7. 8. Check if any solution leakage of the electrode. If necessary, wipe with dry cloth. Check if O ring of the electrode is in place. Check if O ring of the electrode holder is in place. Check the sample path for clots. If necessary, remove the other electrodes and clean the path. 9. Check if calibration solution stops at the measurement unit properly while calibration. Check for any air bubble. If problem found, check for pump tube, tubing, sample port and sampling nozzle. If necessary replace it. If calibration solution does not aspirated, CAL Cartridge should be replaced. 10. Replace affected electrode if not improved. 269 Calibration failure of Ref Conduct the following corrective action to clear the failure. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Shake Ref electrode so that Ref solution will reach to the sample path of the electrode. Check for solution level of Ref electrode. If small, dispose the solution to avoid concentration, and refill it. Check if any solution leakage of the electrode. If necessary, wipe with dry cloth. Check if O ring of the electrode is in place. Check if KCL crystal exists at the sample path. Wash the sample path by distilled water, and then refill the solution. Check the sample path for clots. If necessary, remove the other electrodes and clean the path. Check if calibration solution stops at the measurement unit properly while calibration. Check for any air bubble. If problem found, check for pump tube, tubing, sample port and sampling nozzle. If necessary replace it. If calibration solution does not aspirated, CAL Cartridge should be replaced. Replace affected electrode if not improved. 270 Calibration failure of pCO2 and pO2 Conduct the following corrective action to clear the failure. 1. Shake the affected electrode down to babble electrode’s sample path. 2. Check for solution reaches to the inner electrode of affected electrode. If small, shake the affected electrode down to move the solution to touch the inner electrode. If the solution is empty or the solution is discoloration, electrodes should be replaced. 3. Check if O ring of the electrode is in place. 4. Check the sample path for clots. If necessary, remove the other electrodes and clean the path. 5. Check if calibration solution stops at the measurement unit properly while calibration. Check for any air bubble. If problem found, check for pump tube assy, tubing, sample port and sample nozzle. If necessary replace it. 6. Replace affected electrode if not improved. 7. CAL Cartridge should be replaced if not improved. 271 Glc/Lac troubleshooting When an error occurs, perform the following measures. Check Flow during the calibration - Check stop position and flow sequence of Calibration. NG Check of Check flow system inner solution - Please confirm the amount of liquid by referring to the photograph. - 3. Liquid flow check of operation sequence for more information Perform 2 point Calibration NG Checking the Ref electrode, FS-R 2 point cal. pl ・ Check if flow path of Ref electrode is not crystalized and darken. ・ Clean flow path FS-R. NG Check GND in measurement module Perform 2 point Calibration NG Replace electrode Perform 2 point Calibration NG Replace CAL cartridge NG 272 Contact TMC NOTE: When instrument Flush is empty, and waste liquid fill up, the electrode flow path can not be kept wet when stopped by various errors, or the like, and the drying can be performedIn such case the electrode voltage decrease, or, electrode may deteriorateNote so that long instruments is not now status stopped 273 Hb/OXY troubleshooting performs the following operations to remove abnormal. Check Flow during the calibration - Check stop position and flow sequence of Calibration. NG Barcode reading check Flow of flow cell - Check output voltage of Reading. - 3. Liquid flow check with operation sequence Perform 2 point Calibration NG Implementation of oxy-line cleaning - Please practice with clean procedure. Replace flow cell NG Replace CAL cartridge NG Contact TMC 1 confirms whether the flow cell is attached correctly. 2 Self diagnostic → Checking light intensity values in test of electrical contacts up to. (1) If maximum light intensity value exceeded 63000, mounting bad of flow cell is thought. Flow cell is removed 1 degree, and again should be reattached. (2) If the maximum light intensity value was below 20000, contamination of flow cell is thought. Flush with flash clean and internal cleaners to removes dirt, and is self diagnostic, and test the electrode section. 3 Perform external cleaning for Oxy lines. If the above action does not improve the problem, replace and, flow cell with problem with new flow cell. 274 troubleshooting of flow path In time of occurrence of abnormal of flow path system implement the following measures 1 2 3 Check Calibrator is introduced to the measurement module properly, and there is no bubble generating. If the calibrator is not introduced properly, check pump tube, sampling tube, sample port, and sampling nozzle. If there is damage on these consumable, replace them Perform internal cleaning. Check the clog inside the flow path. Remove electrode and clean the flow path if needed. 275 troubleshooting of errors and navigation systems Message that is displayed on error display and check display and treatment is as shown in the table below. Error contents Meanings instrument temperature in turn is not Detecting abnormal instrument temperature control the proper temperature. Selecting the system. tick, and perform temperature control test. (P-FS) can not detect sample. Selecting the tick, and perform testing of a flow system. Left flow sensor(L-FS) can not detect sample. Selecting the tick, and check the flow system for. Center flow sensor(M-FS) can not detect sample. Selecting the tick, and tests the flow system. Right flow sensor(R-FS) can not detect sample. Selecting the tick, and perform testing of a flow system. Waste flow sensor(W-FS) can not detect sample. Selecting the tick, and check the flow system for. Measurement module cover open Determining electrodes class mounting conditions, and closes the cover. A flow cell is mounted. The correct setting flow cell, and close cover. WASTE bottle fullMaintenance OK, and either performs maintenance or press the check button. FLUSH bottle emptyMaintenance OK, and either performs maintenance or press the check button. CAL Cartridge emptyPress the maintenance button to perform 276 maintenance or press the check button. If is unable to get the measurement key, switch the battery switch to OFF, and should be the power switch OFF. Before taking the measurement pushes the calibration button. Beyond the expiration date of the calibration. Perform calibration before measurement. 277 Temperature Error (Error code 03600) Instrument is desgined to keep the same temperature. If temperature is out of range, it shows temperature error. Probable cause Corrective action Inside the instrument temperature is low because of right after; 1. the power is turned ON. 2. TH electrode is replaced. 3. Other electrodes are replaced. Wait 30 minutes and diagnosis (temeperature). Inside the measurement module 1. Close measurement module cover. temperature is unstable. 2. Wait 3 minutes and conduct Self diagnosis (temperature). Bad TH electrode installation ・ Check TH electrode in position. ・ Check if TH electrode terminal is not dirty. Room temperature is too high. 1. 2. conduct Self Check if room temperature is 10-30 centrigrade. Check if there is no obstacle in front of instrument fan. 1. Press Navigation. Self (temperature) starts automatically. diagnostics 278 2. Check if result of temperature shows Normal. Self diagnostic-printing 1 2 Item 1 Actual temperature 2 Appropriate temperature range 279 Flow sensor error Flow sensor is a liquid sensor which detects the presence of the liquid. If liquid could not be detected, instrument shows Flow sensor error. Probable cause ・ Liquid level is too high. ・ Air level is too low. Corrective action Conduct Self diagnosis (Flow). Conduct the following actions to release error. 1. Check if tubes are installed correctly. 2. Check if tubes are not dirty and scratch. Check if tubes are not caught between measurement module and measurement module cover. 3. Check if tube is correctly inserted with Flow Sensor. Also check if Flow Sensor cover is installed correctly. 4. Check if Sample port and Sampling nozzle are installed correctly. 5. Check if Sample port does not have clot. Also check if Sampling nozzle is not bent. 6. Check if O ring attached correctly. Also check if electrode is installed in correct position. 7. Check if liquid flows correctly in Self diagnosis. 280 Printing examples of Flow Self diagnostic Item 1 The area shows value that there is no liquid in sensor area. 2 The area shows value that there is liquid in sensor area. 3 The limited value that sensor conclude no liquid (Value is higher than the value it is normal) 4 The upper value that sensor conclude there is liquid (Value is lower than the value it is normal) 5 Flow sensor status 1 2 3 4 5 281 Measurement module cover is open Probable cause Corrective action ・ Measurement module cover is open ・ Close measurement module cover until it shouds “click”. ・ Measurement module cover is not closed due to bad electrodes ・ Check electrodes are installed in installation position. Flow cell installation error (Error code 03744) Probable cause Flow cell is not installed firmly Corrective action Insert Flow cell until it sounds “click”. 282 Waste bottle error (Error code 03703) Probable cause Corrective action Waste bottle is full Replace Waste bottle Flush bottle empty error (Error code 03731) Probable cause ・ Flush solution cannot be feed ・ Liquid inside Flush bottle insufficient Corrective action Replace Flush bottle is 283 CAL Cartridge empty error Probable cause ・ Calibration liquid cannot be feed ・ Liquid inside cartridge is insufficient Corrective action Replace CAL Cartridge 284 Battery error (03803) Below screen will appear on the display if instrument is running under battery mode. Probable cause Display does not respond Problem cause Battery is not enough. Restart instrument. 1. Turn OFF the battery switch. 2. Turn OFF the power switch. 3. Connect the AC code. the 4. Turn ON the power switch. 5. Turn ON the battery switch. 285 No calibration conduct error (Error code 03802) Probable cause Corrective action It has passed 2 hours after 1 point Conduct 1 point calibration calibration was conducted ・ It has passed 5 hours after 2 point Conduct 2 point calibration calibration was conducted ・ No calibration is conducted after turn ON the instrument 286 Flag 03803 Problem corrective action When display reacts due to 1. AC code connects to outlet with possible power supplies. pressing of keys: in addition Battery drive post after 30 2. If abnormal key response, restart the following procedure. classification pl passed over. ① SWOFF. ② dorsalPowerSWOFF. ③ AC code connects to outlet with enabling power supplies. ④ PowerSW ON the back is ON. ⑤ SWON. 03803 If display is not unresponsive: Auto-unrecoverable battery insufficient. state Restart. Procedures are as follows. for ① The battery SW on the rear side is OFF. ② dorsalPowerSWOFF. ③ AC code connects to outlet with possible power supplies. ④ dorsalPowerSWON. ⑤ SWON. 287 Calibration error display appears below at the time of following a) When no 1-point calibration is performed in 2hours or more b) 2-point calibration is not performed for 5 hours or more Before sample measurement press `` calibration '' Flag 03802 Problem corrective action Status that exceeds 2hours after the Point a " sg is carried out manually last 1-point calibration completed 03802 State exceeding 5 hours after Perform 2-point calibration manually completion of the previous 2 point calibration Not calibration status of startup/after reboot 288 Barcode Error Problem Corrective action No “Barcode Read OK” is printed Check if thermal roll paper has enough margins. Barcode cannot be read. ・ Check if barcode reader emits light. ・ Barcode label may be defective. Try to read spare barcode attached on its corresponding consumables box. Printer Error Problem No print at all Printing characters are not clear Corrective action ・ Printer door is open. ・ Printer is out of thermal roll paper. ・ Thermal roll paper is inside out. ・ Check if a number of printing sheets sets 0. Check if there is no obstacle around printer head and platen roller. Printing characters are not straight Printing characters are spread 289 Display Problem Problem Corrective action Nothing appears on display ・ Check if power is ON. ・ Check if power code is connected firmly. ・ Check if there is abstacle in front of human detect sensor. Display is OFF if the instrument does not detect human by the human detect sensor under display save mode. Misaligned display Conduct touch panel calibration ・ Bad light intensity ・ Bad coloring Adjust display setting 290 Touch-panel calibration procedure to calibrate the touch-panel unit. ① If USB-keyboard and mose is not used, see after ④. ② Connect USB-keyboard and mouse to G-700 Model USB port. ③ Press “Alt + Tab” to show the Windows display, and then proceeds to ⑤. ④ Press “Function” ⇒ “Other” ⇒ password “1982” ⇒ security code “65” swich ON. Press “Back” ⇒ “Shut down” ⇒ “APP shut down”. ⑤ Press DMC_MSTP (shortcut) on the desktop to execute. ⑥ Press “キャリブレーション(in Japanese)” of left figure. Click ⑦ Tach calibration screen shown left. Tach 1target on the corner and targets are changed to red and the next target point is displayed. Tach When finish taching calibration points, "OK" and "キャンセル" button comes along. When input can be made without problems, "OK" button is clicked. When mistake except calibration point, and press the, there is no that click the "cancellation" or anything Esc key you can press, and waits for 15 seconds. 15 When second, the previous calibration data is discarded, and no storage is saved in Windows. 291 Troubleshooting QC Analysis If you get bad GASTROL-QC results Check the following items if measurement value shows out of range. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Immediately before use, shake the ampoule vigorously for at least fifteen seconds to re-equilibrate the gases with the solution. Ampoule is single time use. Use exclusive adapter when measurement. When you open the ampoules, immediate measure otherwise, pH, pCO2 and pO2 value will be affected by room air. If the ampoule storage condition is not 22-28 degree, leave the ampoule in 22-28 degree for more than 60 minutes. If you have a constant-temperature bath, leave the ampoule in 25 degree for more than 10 minutes. Check if target value is properly memorized inside the quality control menu. Stir the ampoule gently to return the solution to the bottom of the ampoule. Allow bubbles to rise between shaking and before opening the ampoule. Pay attention for the expiry date. Pay attention for air bubble of ampoule. 10. Access Electrode condition to check calibration results. If there is parameter which was failure calibration, it should be solved before GASTROL-QC measurement. 11. Replace CAL Cartridge and conduct 2 point calibration. 12. Replace errouneous electrode and conduct 2 point calibration. NOTE: It will take approximately 30 minutes until electrode becomes stable after electrode replacement depends on its storage temperature. Repeat 2 point calibration manually until it is passed. 292 Auto QC Measured value error Check the following items if measurement value shows out of range. 1. Conduct AQC manually. 2. Access Electrode condition to check calibration results. If there is parameter which was failure calibration, it should be solved before AQC measurement. Measure GASTROL-QC and check if results are in range. Replace CAL Cartridge. Conduct 2 point calibration and AQC. Replace errouneous electrode. Conduct 2 point calibration and AQC. 3. 4. 5. NOTE: It will take approximately 30 minutes until electrode becomes stable after electrode replacement depends on its storage temperature. Repeat 2 point calibration manually until it is passed. 293 Q&A System Status Not movement at all. trouble Corrective action ・ Check if power code is connected. ・ Check if power switch is ON. Sample cannot be aspirated. ・ Check if there is clot inside syringe. ・ Check if there is air bubble inside syringe. ・ Check if syringe include anticoagulant. Instrument does not work at all Electric fuse may be damaged. suddenly, soon after thunder. Heed below to replace the fuse. 1. Turn OFF the battery switch. 2. Remove the power code from the electric outlet first, and then from the instrument. 3. Remove fuse box. 4. Replace two pieces of fuses. 5. Push fuse box until click sound is generated. 6. Connect the power code from the instrument first, and then from the electric outlet. 1. 7. Turn ON the battery switch. Message “Waste bottle is full” ・ Instrument may calculate wrongly. appears wven the waste bottle ・ Last replacement of waste bottle may not be properly is not full. operated. ・ Access to Waste bottle replacement to change the waste bottle with correct procedure. Message “Sample no detected” ・ Perform Flush cleaning. Check if there is no clot appears even the sample was inside container and eject a coule of drops of blood placed. to tissue. ・ Check if there is no clot inside flow path. ・ Perform flow check in Self diagnostics. ・ Check flow sensor level if the message appears even the sample is aspirated. Liquid leaks from the sample Sample port may be damaged or has a clot inside. port Replace the sample port or perform the procedure to remove the clot. Erroneous test results. Perform two point calibrations if there is any error on calibration. If no error, your blood sample may have an air bubble which may lead to erroneous test results. 294 Abnormal test results. Perform Flush cleaning. Check if there is no clot inside container and eject a coule of drops of blood to tissue. Perform two point calibrations if abnormal error still occurs. Measured parameter result is ・ Measured parameter is OFF. Change measured not shown. parameter from OFF to ON. Calculated parameter result is not shown. No printout for specific measurement item. Hb value is far from hematology analyzer. Measurement result is remarkably high and low. Measurement result for tHb and OXY parameter are unstable. ・ Check if sample type is correct. ・ Calculated parameter is OFF. Change calculated parameter from OFF to ON. ・ Measured parameter which is needed to calculate calculated parameter is OFF. Change measured parameter from OFF to ON. Measurement item may be deactivated. Active the measurement item. ・ Stir the sample well. ・ Check if Flow cell data sheet was scanned. ・ Check if Flow cell is installed correctly. ・ Check if specimen does not include clot or air bubble. ・ Check if specimen strage condition and strage time. ・ Check if specimen is diluted by anticoagulant. ・ Stir the sample well. ・ Check if Flow cell data sheet was scanned. **. * is printed out as Hb measurement result ・ Analysis range (2.0 to 23.0g/dL) is exceded. **. * is printed our as measurement result for calculated parameters. Message “Air bubble detected” appears. Message “Insufficient sample” appears. ・ Analysis range is exceeded. Flow sensor error occurs Measurement sample is aspirated continuously Sample is clogged inside sample path ・ Remove air bubble from container. ・ Remove air bubble from container. ・ Measure the samle by Micro mode is sample volume is small. ・ Perform flow check in Self diagnostics. ・ Replace sampling tube. ・ Remove air bubble from container. ・ Check flow sensor level. ・ Check if there is no clot inside flow path. ・ Perform flow check in Self diagnostics and check FS-P (Flow sensor P) level. ・ Check if blood is collected by anticoagulant syringes. 295 Inner cylinder of the syringe is Sample volume is insufficient. detected. Compared with other devices Measured value deviates. Na and K values are far from other instruments. ・ Calibration are Normal the End or Check. ・ Control is in Normal range or Check. ・ Sample are either Analysis or Check, in both devices in fresh blood to ten min immediately stir it. ・ Check if heparine litium is used as anticoagulant. ・ Check if sample is hemolyzed. Ca2+ (iCa) value is far from other instruments. Check if heparine litium is used as anticoagulant. Glc and Lac values are far from other instruments. Check if the sample is measured immediately. (Measurement result is changed due to metabolism.) 296 Function and utility Status Corrective action How to use keyboard and mouse Insert USB connector into the USB port. How to remote monitoring/control the analyzers in centralized Techno Medica has optional solution. Contact Techno Medical local representative. How to collect data for buckup Insert USB memory into the USB port. Measurement data and quality control data can be collected. Can security soft be installed? Security software is installed as a standard. What is the replacement Once per month. freqneucy for CAL Cartridge On board shelf life of CAL Cartridge can be extended maximum 2 months by save mode. Save mode cannot be applied by GASTAT-700Model with AQC and Glc/Lac. What is the replacement Depends on sample volume. frequency for FLUSH Solution What is the replacement frequency for Waste bottle Depends on sample volume. What is the replacement frequency for electrodes Access Electrode/Flow cell maintenance record to check next replacement schedule. What is the replacement Flow sensor needs to be replaced when sensor level is frequency for flow sensor decreasing. Expectation is once per 2 years. What is the replacement frequency for built-in battery Recommends once per 2 years. How to temporarily extend exchange date for consumables Yes not. If the replacement date is reached, replace the exchange. Is periodic software reboot necessary No. Instrument automatically reboots once per day. How to cancel consumables replacement record? Cancellation is not possible. How long measurement/QC There is no time limit. data can be kept 297 Communication error with HIS/LIS In top-quality dried bonito, when communicate the devices with the higher level, be described in way problem solving be generated by. Communication that instruments handle is classified into direction and bi-directional communication by the-means — sg. (see table below) Facility: mean Communications-direction Details LAN: TCP/IP interactive RS-232 C: Seriral Single-direction number Specification for communication with upper Specification for communication with upper Symptoms and actions of problem No. Means of Symptoms of problem Check items and corrective action communications 1 TCP/IP Check by "PING" is ① Operation of switching hub checks confirmed. what is correct. ② Cable disconnection's there is no is identified. ③ Cable connection checks what is correct. (Differentiation of LAN1/2) ④ Set including IP address and gateway address of your own machine checks what is correct. ⑤ Replace the SBC unit. 2 TCP/IP Can not be opened ① Host system's application is not (though ping can running or standby, and is not in confirm the the state. communication,) ② Port number of host system's matching set is identified. ③ A response to opening can not be received. 3 TCP/IP There is not response ① Host system appli are not status of sample ID receive was Accept. (including delay) Sample ID + attribute ② There is fraudulent fraud in host 298 reply system receive message. ③ Communication is delayed and retransmitted. 4 TCP/IP Response to sample ① There is fraudulent fraud in host ID receive error system receive message. Error in the response ② S-ID or barcode is improper. NW7 of the sample ID + Self-Verification of barcode in the attribute case of type. ③ There are protocol violations. 5 serial Communication ① Communication cable checks 9pin(scalpel)-9pin(scalpel) of cross(non-straight) specification with there saw and. ② communication set of Serial port setting(profile)'s is in agreement with the higher rank is identified. ③ Content that is sent from instrument with HyperTerminal or polling on separate PC's can be received according to communication specifications is identified. 6 serial Part P-ID of the ① P-ID transfer maintenance of message is blanked. sample barcode being effective is identified. ② Use sample barcode type being configured properly is identified. 7 common Data for AQC and QC ① Check that set that data for AQC is sent to the upper and QC to top be sent are turning level on. ② Sample identification codes for AQC and QC(facility sets)'s are set correctly is identified. 299 Status of the power This section describes the power supply status. Status trouble shooting Power on Outputs of the power are seen. Sure that power cable connection is made. Check the power fuse. DC output of Power board is seen. Failure/damage part replacement CPU(SH) power-driven device(nozzle, Cable connection between the Power board pump, and valve) does not operate. is identified that CPU board. Others respond. Cable connection of CPU board and power-related device is identified. Replacement of failure/break parts The Hb/Oxy module does not respond. Check the cable connection between the Otherwise respond. Hb/Oxy unit and the CPU-board. Hb/Oxy board and cable connection between the Power-boards is identified. Failure/damage part replacement hemolysis respond. unit responds. Others Cable connection between the US board is identified that US unit. US board and cable connection between the Power-boards is identified. Failure/damage part replacement Analog signals are Otherwise respond. not output. Checking the cable connections of the measurement module that CPU board. Cable connection of Power-board and measurement module is identified. Check the connection of the analog board of measurement module. Failure/damage part replacement Output to the built-in Otherwise respond. printer. Cable connection between Power board/printer is identified. Cable connection among Power board/SBC 300 is identified. Failure/damage part replacement barcode scanner does not respond. Check the presence of red light from the Otherwise respond. scanner section. Check cable connections of the scanner and the SBC unit. Failure/damage part replacement Do not see output on the display. Check the lighting of the power (blue) lamp. Others respond. Check the connection and voltage of the power cable. Sure that DVI cables connection is made. Failure/damage part replacement The touch-panel responds. Otherwise Power source(blue) lamp light is identified. respond. Check the USB cable connection of the panel and SBC unit. Replacement of failure/break parts Preheater does not. Others respond. Cable connection of CPU boards and pre-heater is identified. Replacement of failure/break parts 301 Software invocation ranking and troubleshooting This section describes the normal startup order of the software and the actions that occur when an error occurs or an abnormal startup. No. Normal state trouble shooting 1 Program launch of All power supplies are OFF and 10 seconds or more CPU(SH) and to confirm the initialization OF the pump and nozzle standby-SBC after the power supply is turned on. communications Program of CPU(SH) is overwritten. CPU(SH) is exchanged. 2 Start of BIOS of SBC All power source is OFF, is not more than 10 seconds, and confirms normal activation of BIOS after power is turned on again. Checks of SBC are performed. Replace SBC. 3 Starting WindowsOS Letting all power supplies be OFF, is not more than 10 seconds, and confirms normal activation of WindowsOS after power is turned on again. Check the cable and SSD power supply to SSD. Overwrite/replace SSD, and confirms. 4 Starting application of Consistency of software-version of GASTAT-700 is GASTAT-700 checked. Overwriting the SOFTWARE/update is performed. Replace SSD. 5 Delete unnecessary files GASTAT-700 application is on SSD in time of 1 overwrites/update the SBC file. 6 CPU(SH) forwarding If transfer is not completed before and after 5 parameters to seconds, exit the GASTAT-700 application, and SBC board(communication) file is updated overwrite/overwriting. from SBC 7 Interface connection of If transfer is complete after 5 seconds, the SBC and barcode GASTAT-700 application is terminated and the SBC reader file is overwritten/updated. 8 Read and movies file 9 Internal database and If connection to the internal database is not GASTAT-700 complete, the GASTAT-700 application is terminated application connection and the SBC file is overwritten/updated. play terminated, and of If the moving image is not displayed, the GASTAT-700 application is ended and the SBC file is overwritten/updated. 302 Adjustment Nozzle position Procedur to adjust the nozzle position below. ① Access security code 9041 to move the sample port and remove it. ② Remove Nozzle and nozzle guide, and check that the nozzle is bent, dirt and scratches. (If dirt and flaw are found on the surface of Nozzle and Nozzle guide, cleaning or replacement it.) ③ Fix Nozzle and nozzle guide. 303 ④ Press security code 9041. And check that the tip of nozzle from the edge of the nozzle guide fall within the range (-0.2-+0.0mm). (Adjust the position of the original sensor to the specified range as shown below) ⑤ Press security code 9043. And check that the hole of nozzle to flow reagent is exactly on the hole of sample port base. 304 ⑥ Enter security code 9046. And check if the gap between nozzle handle and nozzle guide fall within the range (0. 1 ~ 0.6 mm). ⑦ Enter security code 9047. And check that nozzle stopps with the limit sensor detection without noise. 305 Error code In this chapter, problem procedure is described based on the status of the flow of the apparatus, the info obtained from the display, print output, etc. Service error code In top-quality dried bonito, the error code for the service output from instrument is explained. The error code is written as follows, and the error code consists of error segments, sequence codes, and phenomenon codes. Error category Description on error category is as shown in the table below. Description System error Measurement error Flow error Maintenance error Interface error Error code form Configuring the error code (XXXXX). 306 Sequence code Combination of sequence code and sequence operation is as shown in the table below. Sequence operation Sequence operation Boot up CRS low Blood CRS middle Blood (Capillary) CRS high Blood (Micro mode) Dialysate control 1 Blood (Capillary + Micro mode) Dialysate control 2 Dialysate 1 Dialysate control 3 Dialysate 2 AQC L1 Dialysate 3 AQC L2 1 P calibration AQC L3 2 P calibration Self-diagnostic (Electrode) Flush cleaning Self-diagnostic (Flow) Internal cleaning Self-diagnostic (FS Calibration) External cleaning Self-diagnostic (Valve) Hb cleaning Self-diagnostic (Temperature) GASTROL L1 GASTROL L2 Standby scren GASTROL L3 307 Error code A unique numeric phenomenon code except for the case with "error category" of "1". "Error category" is combination of parameters and error content for "1", and phenomenon codes is determined. Error Code Explanation Internal setting reading 00101 file error Internal setting 00102 file error writing Default setting reading 00103 file error 00104 00105 Setting file reading error Setting file writing error Default setting reading 00106 file error 00107 Message file reading error Printer object 00108 creation error 308 Generation cause Corrective action Check if “G700_set_internal.xml” file Failed reading exists under D: ¥ TMC ¥ G7H ¥ setting. G700_set_internal.xml If there is not such file, install G-700M file at startup. software to create the file again. Failed accessing to G700_set_internal.xml file. Check if “G700_set_internal.xml” file exists under D: ¥ TMC ¥ G7H ¥ setting. If there is not such file, install G-700M software to create the file again. Check if “G700_set_internal_def.xml” Failed reading file exists under D: ¥ TMC ¥ G7H G700_set_internal_def. ¥ setting. xml file. If there is not such file, install G-700M software to create the file again. Check if “G7○○_set.xml” file exists Failed reading G7〇〇 under D: ¥ TMC ¥ G7H ¥ setting. _set file at startup. If there is not such file, install G-700M software to create the file again. Check if “G7○○_set.xml” file exists Failed writing G7〇〇 under D: ¥ TMC ¥ G7H ¥ setting. _set file. If there is not such file, install G-700M software to create the file again. Check if “G7○○_set_def.xml” file Failed reading G7〇〇 exists under D: ¥ TMC ¥ G7H ¥ setting. _set_def file. If there is not such file, install G-700M software to create the file again. Check if “G700_msg_○.xml” file exists under C: ¥ TMC ¥ G7H ¥ setting. G700_msg_ ○ file at If there is not such file, install G-700M startup. software to create the file again. Failed reading In time of starting confirms whether printer driver is instrument not The present. If is not, then the driver is printer driver. reinstalled. confirms the connection cable to the printer board. Boot up 00109 printing process error SH 00110 communication error 00111 DB connection error - - Check if internal H8 communication Failed communicating port (002,001) is "4" (COM4) in with SH. G700_set_internal.xml. Check if "G700DB.mdf" and "G700DB_log.ldf" files exists under D: Failed connecting with ¥ TMC ¥ G7H ¥ DATA. Data Bace at startup. As SQL Server may not have been activated correctly, restart the operation of OS. Check if "G700DB.mdf" and 00112 00113 DB error DB error reading writing Failed reading Bace. Failed writing Bace. Date "G700DB_log.ldf" files exists under D: ¥ TMC ¥ G7H ¥ DATA. Check the application version. Check if "G700DB.mdf" and Date "G700DB_log.ldf" files exists under D: ¥ TMC ¥ G7H ¥ DATA. Check the application version. Log file writing 00114 error checks whether the log file of the last Failed accessing to the minute is opened in the notepad behind log file. the application. Internal setting 00118 file back up creation error Failed creating back up Check if “G700_set_internal.xml” file file at internal set file under D: ¥ TMC ¥ G7H ¥ BackUp is rewritable. opened by memo pad. Setting file up 00119 back creation error Failed creating back up Check if “G7○○_set.xml” file file at set file under D: ¥ TMC ¥ G7H ¥ BackUp is rewritable. opened by memo pad. Nozzle home not 00200 sensor detected Failed detecting nozzle Check the nozzle parameters. in nozzle home Check the position nozzle and sensor. position. Nozzle 00201 sensor detected Failed detecting nozzle Check the nozzle parameters. in nozzle limit position. Check the position nozzle and sensor. 00202 limit not Nozzle index time out Time out communication in Check the connection with the nozzle with motor. 309 the nozzle motor. Nozzle limit sensor not 00203 detected (Nozzle index control) Limit sensor was Check the nozzle parameters. detected during the Check the position nozzle and sensor. nozzle driving. Pump 1 index 00204 time out Time out in Check the connection with pump motor communication with 1. the pump motor 1. Pump 2 index 00205 time out 00206 Pump 3 index time out the pump motor 2. Time out communication the pump motor 3. OXY spectroscope 00207 communication error 00208 Time out communication Small spectroscope communication error in Check the connection with pump motor with 2. in Check the connection with pump motor with 3. Failed communicating Check the connection with the with the OXY spectroscope board. spectroscope. Failed communicating Check the connection with the small with the OXY small spectroscope board. spectroscope. OXY ultrasonic vibrator 00209 communication error Failed communicating Check the connection with the OXY with the OXY ultrasonic vibrator unit. ultrasonic vibrator. OXY ultrasonic vibrator 00210 abnormal motion The ultrasonic vibrator Check the connection with the OXY unit did not work ultrasonic vibrator unit. normally. OXY ultrasonic 00211 vibrator abnormal stop The ultrasonic vibrator Check the connection with the OXY unit did not stop ultrasonic vibrator unit. normally. Semaphore time 00300 retrieve out Detected abnormal at Check the connection with SH. microcomputer control. Check the application version. 00301 Event Detected abnormal at Check the connection with SH. 310 flag 00302 retrieve waiting microcomputer control. Task Detected abnormal at Check the connection with SH. control error 40001 calibration -48191 errors (Red ☓) * Voltage caution 50001 stable level -58191 (output voltage-increasi * ng ▲) Slope caution 60001 criterion level -68191 (slope of the * slope yellow) Check the application version. microcomputer control. Check the application version. Calibration data was abnormal determination. (No end point /unstable /drift error /level error / lope error) (1) Check and remove (if needed) air bubbles in relevant parameter electrode. (2) Conduct External cleaning. (3) Replace relevant parameter electrode. (4) Replace CAL cartridge. Calibration voltage was (1) Check and remove (if needed) air bubbles in relevant parameter electrode. (2) Conduct External cleaning. (3) Refill inner solution of relevant below or exceeded the parameter electrode (pH,Na,K,Cl,Ca). alarm threshold. (4) Replace relevant parameter or Ref electrode. corresponding parameter. (5) Replace CAL cartridge. (1) Check and remove (if needed) air bubbles in relevant parameter electrode. I exceeded slope at (2) Conduct External cleaning calibration or less than (3) Replace relevant parameter caution threshold. electrode. (4) Replace CAL cartridge. 70001 Output voltage -78191 caution level * The output voltage (1) Refill inner solution of relevant during calibration was parameter electrode (pH,Na,K,Cl,Ca). below or exceeded the (2) Conduct External cleaning. Recommend threshold. 80001 Slope caution -88191 level * The slope of the calibration was below (1) Conduct External cleaning or exceeded the Recommend threshold. 90001 Count caution -98191 level * 40001 Out of -48191 measured range * The counting exceeds count the (1) Conduct External cleaning Recommend threshold. There were parameters below the upper and lower thresholds during measurement of the quality control (1) Check and remove (if needed) air bubbles in relevant parameter electrode. (2) Conduct External cleaning. (3) Replace relevant parameter electrode. 311 50001 Out of -58191 recommended range * substance. (4) Replace CAL cartridge. There were parameters under the Recommend threshold or exceeded when measurement the quality control substance. (1) Conduct External cleaning (2) Replace relevant parameter electrode. (3) Refill inner solution of relevant parameter electrode (pH,Na,K,Cl,Ca). Shift abnormal -68191 status * In certain precision-controlled (1) Conduct External cleaning. substance, the quality (2) Check if solution is leaked in control measurement sample path. Wipe out leakage if data of the preceding needed. party 6cases is all (3) Refill inner solution of relevant concentrated to one parameter electrode (pH,Na,K,Cl,Ca). side of the expected value. 70001 Abnormal -78191 change-with-ti me * Some of the 6 recent data in the quality (1) Conduct External cleaning. control material is (2) Refill inner solution of relevant continuously rising or parameter electrode (pH,Na,K,Cl,Ca). descending. 80001 Abnormal Big -88191 variation * In certain precision-controlled (1) Conduct Flow check. substance, the last value (2) Refill inner solution of relevant 2cases is away from the parameter electrode (pH,Na,K,Cl,Ca). expected value than set value 60001 90001 Abnormal -98191 result related to a few items * 312 In certain precision-controlled substance, when all 5 entries of pH,Na,K, Cl,Ca were diagnosed to be shift state. And, in (1) Replace Ref electrode. a group of(Na, K, Ca) group and(Cl, pH), the trend is the same trend for the group, and the groups are shifting in reverse tendencies. All parameters 02001 air bubble detected Air bubble was After remove air bubble from the detected in sample. sample container, try to analyze again. All parameters 02002 insufficient sample volume (1)Check if the sample volume is sufficient in sample container and Sample was aspirated analyze again. was insufficient. (2)Even if have sufficient sample volume, if there is an error, conduct flow check. 02003 No end Electrode unstable. Sample not 02004 detected (Sample door) 02005 Sample not detected (FS-P) Attempted to aspirate the sample, but the port After inserting container, press was not shaken by the “Analysis” button. vessel. (1)Check if the sample volume is sufficient in sample container and Sample was aspirated analyze again. was insufficient. (2)Even if have sufficient sample volume, if there is an error, conduct flow check. (1)Check if the sample volume is 02006 Sample not detected (FS-R) sufficient in sample container and Sample was aspirated analyze again. was insufficient. (2)Even if have sufficient sample volume, if there is an error, conduct flow check. Remaining 02007 solution detected (FS-R) After cleaning , the solution was detected at Conduct Flow check. FS-R. Waste bottle 02008 sensor error Waste bottle was removed during Load Waste bottle until beep sounds. measurement sequence. CAL cartridge 02009 sensor error Cal cartridge was removed during Load Cal cartridge until beep sounds. measurement sequence. Flush bottle 02010 sensor error Flush bottle was removed during Load Flush bottle until beep sounds. measurement sequence. 313 Temperature 02011 error 02012 Flow sensor error Measurement module cover 02015 open (Inproper electrode loading) Temperature of instrument is below the Conduct Temperature check. threshold. Flow sensor abnormal. was Conduct Flow check. Installation of electrode Check the installation of electrodes and is abnormal. close measurement module cover. Flow cell 02016 sensor error (OXY unit flow cell not loaded) Flow cell is not loaded. Check Flow cell installation. Remaining 02020 solution detected (FS-P) After cleaning, solution was detected in Conduct Flow check. FS-P. Syringe not 02025 removed The container is inserted into sample Remove syringe. port. No end + All (1)Electrode unstable. 02031 parameters air (2)Air bubble bubble detected detected. No endo + All parameters 02032 insufficient sample volume Flow cell sensor error 02034 (Small spectroscope not loaded) 02035 314 Sample not detected (FS-L) voltage (1)Remove air bubbles in electrode. (2)Remove air bubbles in electrode. was (3)Remove air bubble from the sample container and try to analyze again. (1)Remove air bubbles in electrode. (1)Electrode voltage (2)Remove air bubbles in electrode. unstable. (3)Check if the sample volume is (2)Sample was not sufficient in sample container and aspired sufficient. analyze again. Flow cell is not loaded. Check Flow cell installation. (1)Check if the sample volume is Sample was aspirated sufficient in sample container and was insufficient. analyze again. (2)Even if have sufficient sample volume, if there is an error, conduct flow check. Remaining 02036 solution detected (FS-L) After cleaning, solution was detected in (3)onduct Flow check. FS-L. Sample 02037 detected (FS-M) (1)Check if the sample volume is sufficient in sample container and Sample was aspirated analyze again. was insufficient. (2)Even if have sufficient sample volume, if there is an error, conduct flow check. not Remaining solution 02038 detected (FS-M) After cleaning, solution was detected in Conduct Flow check. FS-M. pH-Lac air 02039 bubble detected Air bubble was Check if the sample volume is sufficient detected during in sample container and analyze again. measurement sequence. OXY air bubble 02040 detected Air bubble was Check if the sample volume is sufficient detected during OXY in sample container and analyze again. measurement sequence. (1)Check if the sample volume is OXY 02041 insufficient sample pH-Lac air bubble detected 02042 +OXY insufficient sample volume sufficient in sample container and Sample was insufficient analyze again. during OXY (2)Even if have sufficient sample measurement sequence. volume, if there is an error, conduct flow check. (1)Air bubble was detected between pH and Lac. (2)Sample was insufficient during OXY measurement sequence. (1)Electrode voltage No end + unstable. air (2)Air bubble was 02043 pH-Lac bubble detected detected between pH and Lac. 02044 No end + OXY (1)Electrode (1)Remove air bubbles in electrode. (2)Check if the sample volume is sufficient in sample container and analyze again. (1)Remove air bubbles in electrode. (2)Refill inner solution of relevant parameter electrode. (3)Remove air bubble from the sample container and try to analyze again. voltage (1)Remove air bubbles in electrode. 315 air bubble unstable. detected (2)Refill inner solution of relevant (2)Air bubble was detected during OXY measurement sequence. (1)Electrode voltage No end + OXY unstable. (2)Sample was 02045 insufficient sample volume insufficient during OXY measurement sequence. (1)Electrode No end + Air bubble detected OXY 02046 + insufficient sample volume parameter electrode. (3)Remove air bubble from the sample container and try to analyze again. (1)Remove air bubbles in electrode. (2)Refill inner solution of relevant parameter electrode. (3)Check if the sample volume is sufficient in sample container and analyze again. voltage unstable. (2)Air bubble was detected during OXY measurement sequence. (3)Sample was insufficient during OXY measurement sequence. (1)Remove air bubbles in electrode. (2)Refill inner solution of relevant parameter electrode. (3)Check if the sample volume is sufficient in sample container and analyze again. (1)Remove air bubbles in electrode. (1)Electrode voltage (2)Refill inner solution of relevant No end + OXY unstable. parameter electrode. not (2)Sample was not 02047 sample (3)Check if the sample volume is detected detected during OXY sufficient in sample container and measurement sequence. analyze again. (1)Air bubble was pH-Lac ari detected between pH and bubble detected Lac. Check if the sample volume is sufficient 02048 + OXY sample (2)Air bubble was in sample container and analyze again. not detected detected during OXY measurement sequence. No end + (1)Electrode unstable. voltage pH-Lac air (2)Air bubble was 02049 bubble detected detected during + OXY sample measurement and OXY not detected measurement sequence. 02050 Abnormal 316 - (1)Remove air bubbles in electrode. (2)Refill inner solution of relevant parameter electrode. (3)Remove air bubble from the sample container and try to analyze again. - Sample not detected 02051 (1)Check if the sample volume is sufficient in sample container and (Lmeasurement s (FS2)) GASTROL, AQC Remaining solution Detect 02052 (L-FS(FS2)) GASTROL, AQC Sample was aspirated was insufficient. After cleaning, solution was detected at FS-L. (1)Electrode voltage No end + Oxy unstable. sample wrong (2)Remaining solution 02053 detect blood was detected at sample measurement module. analyze again. (2)Even if have sufficient sample volume, if there is an error, conduct flow check. Conduct Flow check. (1)Remove air bubbles in electrode. (2)Refill inner solution of relevant parameter electrode. Conduct flow check. pH-Lac air bubble detected 02054 + Oxy sample wrong detect blood sample (1)Air bubble was detected between pH and (1)Remove air bubble from the sample Lac. container and try to analyze again. (2)Sample was not (2)Conduct flow check. detected during OXY measurement sequence. No end + pH-Lac air 02055 bubble detected + OXY sample not detected (1)Electrode voltage unstable. (2)Air bubble was detected between pH and Lac. (3)Sample was not detected during OXY measurement sequence. Sample 02056 not detected (R-FS (FS4)) Micro mode Remaining 02057 solution Detect (R-FS (FS4)) (1)Remove air bubbles in electrode. (2)Refill inner solution of relevant parameter electrode. (3)Remove air bubble from the sample container and try to analyze again. (1)Check if the sample volume is sufficient in sample container and Sample was aspirated analyze again. was insufficient. (2)Even if have sufficient sample volume, if there is an error, conduct flow check. After cleaning, solution Conduct Flow check. was detected at FS-R. 317 Micro mode 12708 22708 12709 FS-P Abnormal FS-P (Air (Air Lv) < Threshold (1)Check the flow pat and conduct Flow Level) check. (2)Conduct external cleaning. (3)Conduct Flow sensor calibration. FS-P Abnormal FS-P (Liquid (Liquid Lv) > Threshold (1)Check the flow pat and conduct Flow Level) check. (2)Conduct external cleaning. (3)Conduct Flow sensor calibration. FS-L Abnormal FS-L (Air Lv) (Air (1)Check the flow pat and conduct Flow Level) check. < Threshold (2)Conduct external cleaning. (3)Conduct Flow sensor calibration. (1)Check the flow pat and conduct Flow 22709 FS-L Abnormal FS-L (Liquid (Liqid Lv) > Threshold Level) check. (2)Conduct external cleaning. (3)Conduct Flow sensor calibration. FS-M FS-M (Air 12710 Abnormal (Air < Threshold Lv) (1)Check the flow pat and conduct Flow Level) check. (2)Conduct external cleaning. (3)Conduct Flow sensor calibration. FS-M 22710 Abnormal (Liquid Lv) (1)Check the flow pat and conduct Flow Level) check. (2)Conduct external cleaning. (3)Conduct Flow sensor calibration. 12711 FS-M (Liquid > Threshold FS-R Abnormal FS-R (Air (Air Lv) < Threshold (1)Check the flow pat and conduct Flow check. Level) (2)Conduct external cleaning. (3)Conduct Flow sensor calibration.Perform flow sensor calibration. (1)Check the flow pat and conduct Flow 22711 FS-R Abnormal FS-R (Liquid (Liquid Lv) > Threshold FS-W FS-W (Air 12712 Abnormal (Air < Threshold Lv) 318 Level) check. (2)Conduct external cleaning. (3)Conduct Flow sensor calibration. Level) (1)Check the flow pat and conduct Flow check. (2)Conduct external cleaning. (3)Conduct Flow sensor calibration. FS-W 22712 Abnormal (Liquid Lv) (1)Check the flow pat and conduct Flow FS-W (Liquid > Threshold Level) check. (2)Conduct external cleaning. (3)Conduct Flow sensor calibration. 02733 Wrong tube set (FS-L) Tube might disconnected. be Install the tube and conduct Flow check. 12733 Wrong tube set (FS-R) Tube might disconnected. be Install the tube and conduct Flow check. 22733 Wrong tube set (FS-W) Tube might disconnected. be Install the tube and conduct Flow check. Wrong tube set Tube be Install the tube and conduct Flow (FS-L, FS-R) disconnected. 42733 Wrong tube set (FS-L, FS-W) Tube might disconnected. be Install the tube and conduct Flow check. 52733 Wrong tube set (FS-R, FS-W) Tube might disconnected. be Install the tube and conduct Flow check. Wrong tube set 62733 (FS-L, FS-R, FS-W) Tube might disconnected. be Install the tube and conduct Flow check. 32733 02100 02101 02102 Waste bottle set standby Flush bottle set standby CAL cartridge set standby Bottle detect OFF 02103 sensor standby might check. Waste bottle was removed under measurement or Load Waste bottle. calibration or cleaning sequence. Flush bottle was removed under measurement or Load Flush bottle. calibration or cleaning sequence. CAL cartridge was removed under measurement or Load CAL cartridge. calibration or cleaning sequence. Sample container was inserted into sample Remove the container that is inserting port under calibration into sample port. or cleaning. 319 Measurement 02104 module cover close standby Measurement cover was opened under Close measurement cover. measurement calibration or cleaning. Flow cell set 02105 standby Flow cell was removed under measurement Load Flow cell. calibration or cleaning. Flow cel for small 02106 spectroscope set standby Flow cell was removed under measurement Load Flow cell. calibration or cleaning. CAL cartridge replacement 03000 date notification 7 days until Prepare new Cal cartridge for replacement expiration replacement. date. CAL cartridge 03001 replacement date caution 5 day until replacement Replace Cal cartridge. expiration date. 03002 CAL cartridge expired 30 days have passed since last replacement Replace Cal cartridge. date (Saving mode is max 60 days). CAL cartridge 03003 remaining amount caution 03004 CAL cartridge empty Remaining amount is Replace Cal cartridge. 10 % or less. Cal cartridge is empty. Replace Cal cartridge. Flush bottle remaining 03010 amount notification Remaining amount is Prepare new Flush bottle for 15 % or less. replacement. Flush bottle 03011 remaining amount caution Remaining amount is Replace Flush bottle. 10% or less. 03012 Flush empty 03020 Waste bottle full caution 320 bottle Flush bottle is empty. Replace Flush bottle. Remaining amount is Replace Waste bottle. 10% or less. 03021 Waste full bottle Waste bottle is full. Replace Waste bottle. Pump head replacement 03030 date notification 14 days until Prepare new Pump head for replacement expiration replacement. date. Pump head 03031 replacement date caution 10 days until replacement expiration Replace pump head. date. Pump 03032 exired 180 days have passed since last replacement Replace pump head. date. tube Sample port replacement 03040 date notification 14 days until Prepare new Sample port for replacement expiration replacement. date. Sample port 03041 replacement date caution 10 days until replacement expiration Replace Sample port. date. Sample 03042 expired port 90 days have passed since last replacement Replace Sample port. date. Sample 03043 usage caution port count Sample 03044 exceed count port usage Remaining usage count Replace Sample port. is 500 or less. Usage count of Sample Replace Sample port. port is upper limit. Tubing kit 03050 replacement recommended 360 days have passed since last replacement Prepare new Tubing kit for replacement. date. Sampling tube 03051 replacement recommended 90 days have passed since last replacement Replace Sampling tube. Joint tube 03052 replacement recommended 360 days have passed since last replacement Replace Joint tube. date. 03053 Nozzle replacement date. 180 days have passed Replace Sampling nozzle. since last replacement 321 recommended date. pH electrode 03100 replacement recommended 360 days have passed since last replacement Replace the pH electrode. date. pCO2 electrode 03101 replacement recommended 270 days have passed since last replacement Replace the pCO2 electrode. date. pO2 electrode 03102 replacement recommended 270 days have passed since last replacement Replace the pO2 electrode. date. Na electrode 03103 replacement recommended K electrode 360 days have passed since last replacement Replace the Na electrode. date.. 270 days have passed 03104 replacement recommended since last replacement Replace K electrodes. date. Cl electrode 03105 replacement recommended 180 days have passed since last replacement Replace the Cl electrode. date. iCa electrode 03106 replacement recommended 270 days have passed since last replacement Replace the iCa electrode. Glc electrode 03107 replacement recommended 90 days have passed since last replacement Replace the Glc electrode. date. Lac electrode 03108 replacement recommended 90 days have passed since last replacement Replace the Lac electrode. date. Ref electrode 03109 replacement recommended 180 days have passed since last replacement Replace the Ref electrode. date. Flow cell 03110 replacement recommended 360 days have passed since last replacement Replace the Flow cell. date. Conduct external 03111 cleaning (FS-P (PD1) low V 322 date. FS-P (PD1 (Air level)) Conduct external cleaning. < Threshold output) Conduct external 03112 cleaning (FS-P (PD2) low V output) Conduct external 03113 cleaning (FS-L low V output) 03114 Conduct external cleaning (FS-M low V output) FS-P (PD2 (Air level)) Conduct external cleaning. < Threshold FS-L (Air < Threshold level) FS-M level) (Air < Threshold Conduct external cleaning. Conduct external cleaning. Conduct FS-R (Air < Threshold level) Conduct external 03116 cleaning (FS-W low V output) FS-W (Air < Threshold level) External 03200 cleaning recommended 30 days have passed since last replacement Conduct external cleaning. date. 03115 03201 external cleaning (FS-R low V output) Hb cleaning recommended Battery 03300 replacement recommended No printer 03400 paper notification Conduct external cleaning. Conduct external cleaning. 30 days have passed since last Hb cleaning Conduct Hb cleaning or external or external cleaning cleaning. date. 3 years have passed since last replacement Replace the battery. date. There is not printer Replace the printer paper. paper. Measurement 03500 module cover open Measurement module Close measurement module cover. cover is opened. 03600 Abnormal Instrument temperature (1) Just startup instrument 323 temperature < Threshold Instrument is cold. Please wait for 30 minute at least to warm up. (2)Not just startup instrument Conduct Temperature check. Replace the TH sensor. Abnormal 03601 temperature inside analyzer (1)Check if the fan works. Instrument temperature (2)Open up spase at side of instrument. > Threshold (3)Reduce temperature of air conditioning. 03701 CAL cartridge not detected Cal cartridge is not Load Cal cartridge. loaded. 03702 Flush bottle not detected Flush bottle loaded. is not Waste Waste is not 03703 bottle not detected loaded. Measurement 03715 module cover open 03716 Flow cell not loaded FLUSH 03731 solution aspiration error Flow cell (small 03744 spectroscope) not loaded 03801 Container detected Load Waste bottle. Measurement module Close measurement module cover. cover is opened. Flow cell is not loaded. Flush solution cannot be aspirated. Flow cell spectroscope) loaded. Load Flow cell. (1)Check remaining amount of Flush bottles. (2)Check if tubes is connected. (small is not Load Flow cell (small spectroscope). Container is inserted Remove the container from sample port. into sample port. Not calibrated 03802 error 03803 Switching the battery 05000 Fail to conect to HOST 324 bottle Load Flush bottle. of Calibration is not conducted for a certain Conduct calibration. time. Switched to drive mode. (1) Power failure battery Shut down the instrument. (2) AC adapter is removed Connect the AC adapter. Failed comunicating to (1) Check the communication setting HOST. with HOST. (2) Check if LAN cable is connected. (3) Check the IP address. 05001 Disconnected by HOST The receive message Check the communication setting from HOST is 0 bytes. with HOST. No patient attribute 05002 inquiry from HOST There is a response to the patient attribute Check the communication setting query from HOST after with HOST. barcode reading. No patient demographic 05003 transmit from HOST For the time after Check the communication setting waiting for patient info with HOST. receive on the HOST 05004 Fail to capture patient attribute Something exception generated patient Check the communication setting attributes received in with HOST. process. 05005 Error response from HOST Communication status code from the Check the communication setting HOST-side(or the with HOST. response code) was received on abnormal. Telegram length that Wrong 05006 string HOST 05008 data from Failed to log-in FTP server Failed to file 05009 upload on FTP server 05010 Failed mail tosend has been sent from Check the communication setting HOST was improper. with HOST. For ASTM-1 end was not "L|1|N<CR>". confirms basic device info. Failed to process confirms the connection of the M2M logging into the FTP adapter. (physical connection, set IP server. address, setting M2M adapter) confirms basic device info. Failed to File upload confirms the connection of the M2M process to FTP server adapter. (Physical connection, set IP on FTP server address, M 2 M adapter configuration) confirms mail settings. confirms the connection of the M2M Failed to Mail Sending adapter. (Set up physical connections, Process. configuring the IP address, and M2M adapter settings) 325 Check the mail settings. 05011 Failed to receive mail 90 days to IoT 05020 system contract expiry 60 days to IoT 05021 system contract expiry Be later 30 date to IoT system 05022 contract expiration IoT system 05023 contract expired Failed to process mail confirms the connection of the M2M receiving. adapter. (physical connection, set IP address, setting M2M adapter) As a relatively only notification no Remaining until correspondence is required. expiration of the IoT If there is update of the contract, the contract, and was 90 contract termination date should be days before. extended accordingly. As a relatively only notification no Remaining until correspondence is required. expiration of the IoT If there is update of the contract, the contract, and was 60 contract termination date should be days before. extended accordingly. As a relatively only notification no Remaining until correspondence is required. expiration of the IoT If there is update of contract, the contract, and was 30 contract termination date should be days before. extended accordingly. As a relatively only notification no correspondence is required. The IoT Period expires. If there is update of the contract, extend the contract end date according to for. Supplement: Msg mail notification, inc ◎ notifies the user and server, and sign-to notify the server. <S/C #>S/C number that/that contains the Send content without switchingyou see. -Notification is notified. *Division: in addition If any abnormal is found in each parameter, the following "0"bit in the table below is used ⇒ represent as 1", 2 binary number of this 13 digit into 10 type pl is converted, and output as integral number of 0000 to 8191. pH pCO2 pO2 Na K Cl iCa Glc Lac Hb Oxy tHb tBil 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 The upper bit low - order bits E.g: pO2,tBil,tHb,Oxy error(1031) 326 pH pCO2 pO2 Na K Cl iCa Glc Lac Hb Oxy tHb tBil 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 = 4096×0 + 2048×0 + 1024×1+ 512×0 + 256×0 + 128×0 + 64×0 + 32×0 + 16×0 + 8×0 + 4×1+ 2×1+ 1×1 = 1031 327 Hardware error This section describes the error code output from hardware. PCB error The error code can be identified by the emission signal of LED on PCB. Signal details are as shown in the table below. PCB LED Status Corrective action CPU (SH) Green LED Normal (1)Lighting on : Flash ROM Ready (2)Lighting off : Flash ROM Busy (Writing mode) Lighting on is normal after power is turned on. (3)Blinking : Abnormal Abnormal (4)Lighting off is abnormal after (1)Check after the program power is turned on. is reinstalled. (2)Replace PCB. Power D6 (Yellowish green LED) Lighting on : AC adapter Lighting off : Battery drive Confirm that the power supply is matched to electrode status supply. D7 (Yellow LED) Confirming the situation Lighting on : Battery level remaining that be matching status of amount Lighting off : Battery drive ≧5.6V If D7 is not turned off, abnormal BAT remaining amounts in use. Replace BAT to confirm. PCB is exchanged. ⇒ Confirm that the power supply is matched to D8(orange) LED lights off ⇒ BAT electrode status supply. non-charging D8(orange) LED charging BAT '' light up After BAT drive D8 does not light. Check ON/OFF OF the BAT switch. Replacing BAT, confirms. PCB is exchanged. D9(red) LED light up ⇒ abnormal temperature D9 328 (red) LED Off and BAT When D9 continues to be lit: in addition ⇒ BAT Replace BAT to confirm. Temperature Normal Printer 1 0 1 0 0 PCB is exchanged. 2 3 4 LED(0: lights off,1: lights on) Status of the printer and the LED signal's is in 1 1 1 In initialization agreement is identified. 1 0 1 Flush memory is Printer mechanical is being rewritten identified. 0 0 0 Head error 0 1 0 Head temperature PCB is exchanged. error 0 1 0 0 Vp voltage error Vp initializes voltage error 0 1 1 0 Presenter paper jam error Mark detect during paper jam error 1 0 0 0 Presenter paper feeding error 1 1 0 0 Pallet fork create error 1 1 1 0 Out-of-paper error 1 0 0 1 In print 0 0 0 1 Print possible 329 Spare parts Main module and cover Class A: Expected replacement term over a year (sensor, nozzle) B: Expected replacement term over 3 years (motor, valve) C: Expected replacement term over 5 years (herness, board) I exploded view: number of figure gives each part number. Drawing No. Product Code 02-000 0171154 EL (Electrode) Module 03-000 0171240 Manifold Module (without AQC Model) 03-000 0171241 Manifold Module (with AQC Model) 04-000 0171180 Sample Port Module 05-000 0171242 Pump Module 06-000 0171243 Preheater1 Module 07-000 0171244 Preheater2 Module 08-000 0171245 Display Module 09-000 0171189 Power Module 10-000 0171246 Hb Module 11-000 0171247 OXY Module 12-000 0171248 Printer Module 13-000 0171229 BC Scanner Module 01-001 0171151 Thermal Cover ASM 01-002 0171152 Printer Cover 01-003 0171153 FRM FAN 330 Product Name Remarks Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71105 Excluding Finger Gard, including Herness and Connector CA14 331 EL Module Drawing No. 332 Product Code Product Name Remarks 02-001 0171155 Flow Sensor (TypeA Ir) FS-P Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71820 02-002 0171156 Flow Sensor (TypeB) FS-M 02-003 0171157 Flow Sensor (TypeC) FS-R 02-004 0171158 Photo Interrupt Sensor 02-005 0171159 Hinge 02-006 0171160 LED Board 333 Manifold Module Drawing No. Product Code Product Name Remarks 03-001 0171162 Flow Sensor(W) FS-W Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71821 03-003 0171164 Bottle Nozzle 2pcs per unit 03-004 0171165 Needle ASM 3-6pcs per unit Including harness and connector 03-005 03-006 0171166 0171167 Valve1 Valve3 Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71101 Including harness and connector Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71103 Including harness and connector 03-007 03-008 03-009 0171168 0171169 0171170 Valve6 Valve7 Valve8 Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71206 Including harness and connector Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71207 Including harness and connector Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71308 03-010 334 0171171 Valve9 Including harness and connector Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71309 03-011 03-012 03-013 03-014 03-015 0171172 0171173 0171174 0171175 0171176 Valve10 Including harness and connector Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71310 Valve11 Including harness and connector Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71511 Valve12 Including harness and connector Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71512 Valve2 Including harness and connector Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71102 Valve4 Including harness and connector Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71104 Including harness and connector Resigtration No. to manage replacement record is 71105 03-016 0171177 Valve5 03-018 0171180 Valve Div Board 02-004 0171158 Photo Interrupt Sensor 3pcs per unit 335 336 Sampling Module Drawing No. Product Code Product Name 04-002 0171183 Nozzle Motor 04-003 0171184 Timing Belt 04-004 0171602 Nozzle 04-005 0171186 Bearing 04-008 0171404 Flap 02-004 0171158 Photo Interrupt Sensor Remarks Including harness and connector CA42 6pcs per unit 3pcs per unit 337 338 Pump Module Drawing No. Product Code Product Name Remarks 05-001 0171186 Tube Pump 3pcs per unit 05-002 0171187 Pump Cover ASM Including pipe 339 Display Module Drawing No. Product Code 08-001 0171196 340 Product Name Touch Monitor Remarks Power Supply Module Drawing No. Product Code Product Name Remarks Including harness and connector CA7 Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71401 09-002 0171191 Battery 09-003 0171192 SSD 09-004 0171193 SBC FAN Including harness and connector CA31 09-005 0171194 SWR FAN Including harness and connector CA11 09-006 0171195 PWR FAN 09-007 0171196 SBC 09-008 0171197 SWR 09-009 0171198 PWR Board 09-010 0171199 CPU Board 09-011 0171200 PSR Board Including harness and connector CA12 341 342 HB Module Drawing No. Product Code Product Name Remarks 10-001 0171201 Flow Sensor(L) FS-L Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71817 10-002 0171202 Hb Micro Switch Including thermistor and connector CA58 10-003 0171203 HB Board 10-004 0171204 HB Meter Board 10-005 0171205 HbLED Board 343 344 OXY Module Drawing No. Product Code Product Name Remarks 11-001 0171201 Flow Sensor(L) FS-L Registration No. to manage replacement record is 71817 11-002 0171207 OXY Micro Switch Including thermistor and heater CA60 11-003 0171208 OXI Fiber 11-004 0171209 Spectroscope Head 11-005 0171210 Neon Driver Board 11-006 0171211 Oxy Meter Board 11-007 0171212 Oxy LED Board 11-008 0171213 Neon Light Board 11-009 0171214 Ultrasonic Unit 345 346 Printer Module Drawing No. Product Code Product Name 12-001 0171215 Thermal Printer 12-002 0171216 Printer Board Remarks 347 Barcode Reader Modules Drawing No. Product Code Product Name 13-001 0171217 Motion sensor 13-002 0171218 CCD Scanner 348 Remarks Including harness and connector CA41 PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and connection point CPU (Central Processing Unit) PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point 3 RS-422 4 PSR Board 5 Ultrasonic Unit 6 Photo Interrupt Sensor Motion sensor 7 Hb(OXY) Module 8 Nozzle Motor 9 PSR Board 10 Valve Div Board 11 LED Board Full Anarog Board Hb(OXY) Board Preheater1 Module Preheater2 Module Description Sample Port Module BC Scanner Module Sample Port Module 12-002 12-001 349 PSR (Photo Solder Resist) PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point 1 SBC Board 2 Display Module BC Scanner Module 3 SBC Board 4 Power Board 5 CPU Board 6 Printer Board 7 SBC Board 8 Display Module 9 SBC Board 10 CPU Board 11 Power Board 350 Description Full Analog PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point Description 1 - debug 2 CPU Board 3 CPU Board 4 CPU Board 351 LED PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point Description 1 CPU Board 2 Heater, Thermistor Electro module 3 Flow Sensor(TypeA Ir) Electro module 4 Photo Interrupt Sensor Electro module Hb Meter PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point Description 3 - Debug 4 CPU Board 5 Hb Board 6 Hb LED Board 7 Micro Swich Hb Module Flow Sensor(TypeA Gr) Hb Module Heater, Thermistor Hb Module 8 352 CPU Board Hb PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point 1 Hb Meter Board Description Hb LED PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point 1 Hb Meter Board Description 353 OXY Meter PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point Description 2 Spectroscope Head OXY Module 3 OXY LED Board 5 - 6 CPU Board 7 CPU Board 8 Micro Swich OXY Module Neon Light Board OXY Module Flow Sensor(TypeA Gr) OXY Module Heater, Thermistor OXY Module Debug Neon Driver PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connect tips 2 Neon Light Board 3 OXY Meter Board 354 Description OXY LED PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point 1 OXY Meter Board Description Neon Light PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point 1 Neon Driver Board Description CN1 355 Power PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point Description 1 SWR Power Module 2 Battery SW Power Module 3 Battery Power Module 4 PSR Board 5 PSR Board 6 SWR FAN, PWR FAN Power Module 7 FRM FAN Main Module CN1 CN7 CN5 CN4 CN6 CN2 CN3 356 Valve Div PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point 1 CPU Board 2 Valve1 3 Valve2 4 Valve3 5 Valve4 6 Valve5 7 Valve6 8 Valve7 9 Valve8 10 Valve9 11 Valve10 12 Valve11 13 Valve12 Description 14 15 Photo Interrupt Sensor Flash Bottle 16 Photo Interrupt Sensor Waste Bottle 17 Photo Interrupt Sensor Cassette 18 Flow Sensor(TypeA Gr) Manifold Module CN1 357 Printer PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point 1 Thermal Printer 2 PSR Board 3 PSR Board 4 SBC Board 358 Description SBC PCB (Printed Circuit Board) CN Connection point 1 DC in 2 - 3 LAN1 4 LAN2 5 CPU FAN 8 - 9 SATA 10 - 11 - 13 DVI 14 - 16 USB 17 USB 18 Serial A 19 Serial B 20 Serial C 21 - 22 - 24 USB 29 - 30 SBC FAN 31 Li battery 32 - 33 - 34 SATA Power 35 - 36 - 37 - Description Display Module 359 360 TROUBLE SHOOTING Calibration failure Calibration failure happens when below condition are observed during the calibration. Take the proper action to fix the instrument. Error Error Meanings NO END POINT ERR Electrode does not reach stable reading within number 001 predefined time limit. 002 UNSTABLE ERR Electrode output is not stable reading because of electric noise. Eventually it does not reach stable reading within predefined time limit. 004 DRIFT ERR Electrode drift is beyond predefined limits during a one-point or a two-point calibration compared with previous calibration result. 008 LEVEL ERR Electrode output is beyond predefined limits during a one-point or a two-point calibration. 032 SLOPE ERROR Electrode SLOPE is beyond predefined limits during a one-point or a two-point calibration. 361 Trouble Shooting Flow Calibration Error shows on screen Select Detail output in Electrode condition of Calibration to print out calibration history. No Error on the all parameter Yes See 4.1.6 Error on all parameter. Error on pCO2/pO2 (gas) parameter Check 4.1.3 Error on GAS parameter Error on pH/Na/Cl/K/Ca (ISE) parameter Check 4.1.2 Error on ISE parameter Error on Glc/Lac (enzyme) parameter Check 4.1.4 Error on Enzyme parameter Error on tHb/Oxy (CO-Oxy) parameter Check Troubleshooting for Co-Oxy Unit Error on Hb parameter Check 4.1.5 Error on Hb parameter 362 Error on ISE parameter Check Flow during the calibration Check stop position of calibrator. NG Check if errors occur on plural parameters Check Ref electrode Check Flow Check electrode shown as error Check inner solution ・ Check bubble inside the electrode Check crystal at flow path ・ Check inner solution Check flow path is not dark ・ Shake electrode well to remove bubble Shake electrode well to remove bubble Perform 2 point Calibration NG Check GND in measurement module Perform 2 point Calibration NG Replace electrode Perform 2 point Calibration NG Replace CAL cartridge Perform 2 point Calibration NG Contact TMC 363 Error on plural parameter 1. Check Calibrator is introduced to the measurement module properly, and there is no bubble generating. If the calibrator is not introduced properly, check pump tube, sampling tube, sample port, and sampling nozzle. If there are damage on these consumable, replace them 2. Check O-ring next to the electrode is installed properly. If there are solution or sample remains at O-ring, remove them. 3. Shake the electrode very well to make adapt inner solution well with membrane. 4. Check the inner solution of Ref electrode. If the inner solution level is lower than black line on the tank, add the inner solution and shake it well. 5. Check the flow path of Ref electrode is not darken, or crystallized. If it is darken or crystallized, replace Ref electrode. 6. Check electrode is installed at proper place. 7. Check the clog inside the flow path. Remove electrode and clean the flow path if needed. 8. If error is not solved by above procedure, replace the electrode for error parameter. Error on specific parameter 1. Check inner solution of each electrode. If the there are few solution remaining, replace the inner solution. Do not refill the inner solution. Clean inside of electrode well with new inner solution and fill new inner solution. 2. Shake the affected electrode/Ref electrode down to remove bubble the electrode’s sample path. 3. Check electrode is installed at proper place. 4. Check O-ring next to the electrode is installed properly. If there are solution or sample remains at O-ring, remove them. 5. Check Calibrator is introduced to the measurement module properly, and there is no bubble generating. If the calibrator is not introduced properly, check pump tube, sampling tube, sample port, and sampling nozzle. If there is damage on these consumable, replace them. 364 Error on GAS parameter Check Flow during the calibration Check stop position and flow sequence of Calibration. NG Check errors on plural parameter Shake electrode well to remove bubble Check inner solution Check Flow Perform 2 point Calibration NG Check GND in measurement module Perform 2 point Calibration NG Replace electrode Perform 2 point Calibration NG Replace CAL cartridge Perform 2 point Calibration NG Contact TMC 365 1. Check Calibrator is introduced to the measurement module properly, and there is no bubble generating. If the calibrator is not introduced properly, check pump tube, sampling tube, sample port, and sampling nozzle. If there are damage on these consumable, replace them 2. Check O-ring next to the electrode is installed properly. 3. Shake the electrode very well to remove the bubbles on membrane. 4. Check amount of inner solution. If the inner solution is not attaching the membrane, shake electrode to move the remained inner solution on the membrane. 5. Check the clog inside the flow path. Remove electrode and clean the flow path if needed. 6. Check resistance inside the measurement module. If the resistance is higher than 30 ohms, check there are any leaks on the measurement module and remove them. 7. If problem is not solved by above, replace problematic electrode to new electrode. 8. If problem is not solved by above, replace CAL cartridge. 9. If problem is not solved by above, contact TMC. 366 Error on enzyme parameter Check Flow during the calibration Check stop position and flow sequence of Calibration. NG Check errors on plural parameter Check Flow Check inner solution Perform 2 point Calibration NG Check Hb and Ref electrode Check if flow path of Ref electrode is not crystalized and darken. Clean flow path of Hb electrode. Perform 2 point Calibration NG Check GND in measurement module Perform 2 point Calibration NG Replace electrode Perform 2 point Calibration NG Replace CAL cartridge Perform 2 point Calibration NG Contact TMC 367 Replacement notice of Glc electrode When the Calibration was performed, system alerts the Glc electrode replacement coming soon if the CAL1 voltage shows lower than threshold value. This is the condition of output of electrode is getting lower. Please replace the electrode if needed. Alert display Error display Glc 0.15 V 0.12 V Lac 0.095 V 0.0825 V Error by lack of cleaning membrane During the cleaning process, system monitors the output of enzyme electrodes to check the membrane is cleaned. If the membrane is not cleaned enough because of high Glc or Lac sample measurement, display shows as an error. In this case, check the Electrode condition in Calibration at Function. If the display shows need Perform Flush cleaning. Please perform the flush cleaning several times to clean the membrane. NOTE System monitors the membrane condition even in conditioning. If the output of the Glc or Lac electrode shows under threshold at condition, error will disappear. 368 Error on Hb parameter Check Flow during the calibration Check stop position and flow sequence of Calibration. NG Clean Flow path of Hb electrode Check Flow Check inner solution Perform 2 point Calibration NG Replace Flow cell Perform 2 point Calibration NG Contact TMC Error on all parameter 1. Check Calibrator is introduced to the measurement module properly, and there is no bubble generating. If the calibrator is not introduced properly, check pump tube, sampling tube, sample port, and sampling nozzle. If there is damage on these consumable, replace them 2. Perform internal cleaning. 3. Check the clog inside the flow path. Remove electrode and clean the flow path if needed. 369 Bad QC result Ampoule QC error Check Calibration condition NG Check Flow Check 4.1 Calibration error for troubleshooting Check stop position and flow sequence of Calibration Perform 2 point Calibration and retry the QC Perform QC with correct protocol NG Replace consumable and clean flow path Clean flow path and replace consumable if needed Perform 2 point Calibration and retry the QC NG Replace electrode Perform 2 point Calibration and retry the QC NG Replace CAL cartridge Perform 2 point Calibration and retry the QC NG Check the Unique factor Security code 88, 911, and 912 Perform 2 point Calibration and retry the QC NG Contact TMC 370 1. Agitation of ampoule is not enough. Shake the ampoule more than 15 seconds to homogenize the liquid. 2. Bubble inside the ampoule. 3. Do not hold the ampoule with palm to not to warm up. 4. Do not re-use the ampoule once it is used. 5. Ensure to use exclusive adapter. 6. Immediate use after opening the ampoule. Room air gives bad impact to pH, pCO2 and pO2. 7. Check if target value is properly set with use of datasheet. This is very important if lot number of control has been changed. 8. The measurement should be performed in 20 to 25 Celsius to get the best value. 9. Do not use the expired ampoule for measurement. Auto QC error Check Calibration condition NG Check Flow Check 10.1 Calibration error for troubleshooting Check stop position and flow sequence of Calibration Perform 2 point Calibration and perform Auto QC manually NG Perform 2 point Calibration and perform ampoule QC Perform QC with correct protocol NG Perform 2 point Calibration, Check Ampoule QC error for troubleshooting And perform Auto QC manually Replace Cal cartridge and perform Auto QC manually. Check the unique factor security code 88, 911, and 912 and perform Auto QC. NG Contact TMC 371 G-700M AQC barcode explanation AQC Data GASTAT-700 Exp. 2020.09 Lot. ○○○○○○ 71933 2009 0001 210 635 420 410 400 950 610 185 1350 1 2 3 4 5 5 Seq. No 1 Position Length (Digit) 1–5 5 2 6–9 4 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Total 10 - 13 14 -16 17 - 19 20 - 23 24 - 26 27 - 29 30 - 33 34 - 36 37 - 39 40 - 43 4 3 3 4 3 3 4 3 3 4 43 372 6 7 8 6 9 10 11 12 9 Meaning Example Value Cat. No. Expire date (YYMM) S/N pH pCO2 Level 1 pO2 pH pCO2 Level 2 pO2 pH pCO2 Level 3 pO2 71933 71933 2009 Sep 2020 0001 210 635 420 410 400 950 610 185 1350 0001 7.21 63.5 torr 42 torr 7.41 40 torr 95 torr 7.61 18.5 torr 135 torr AQC default setting Parameter Unit Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 pH ±0.05 ±0.05 ±0.05 pCO2 ±7 ±6 ±5 Torr pO2 ±12 ±14 ±16 Torr Na K Cl Ca 110 ~ 120 2.40 ~ 2.80 85.0 ~ 95.0 1.55 ~ 2.05 134 ~ 146 3.80 ~ 4.40 100 ~ 110 0.90 ~ 1.30 153 ~ 167 6.90 ~ 7.90 118 ~ 132 0.45 ~ 0.95 mmol/L mmol/L mmol/L mmol/L Glc 32.0 ~ 62.0 (2.21 ~ 3.45) 82.5 ~ 117.5 (4.59 ~ 6.53) Lac Hb 0.50 ~ 1.50 15.5 ~ 18.5 2.00 ~ 4.00 10.5 ~ 13.5 165 ~ 235 mg/dL (9.16 ~ 13.04) (mmol/L) 6.20 ~ 10.2 5.5 ~ 8.5 mmol/L g/dL 373 Touch Panel Calibration When touch reaction of G700Model is bad, it is necessary to calibrate the point of touch on panel. Please note that calibration application appears with Japanese. This manual describes the position where to select. Tem to be prepared USB Key board USB mouse 1. Connect the USB Key board and the mouse to the G-700 USB port. 2. Press “Alt + TAB” on home display to move windows display. 3. Click “DMC_MSTP” to open touch calibration application. 4. Click ”キャリブレーション”. 5. Press target on the 4 coners for a short period. 6. Press “OK” after calibration is completed. Touch 4 points Press “G700Lancher” to start G700 application. 374 Software upgrade (procedures to upgrade SH (Micro computer)) This chapter describes fow to install the software. Item to be prepared USB memory Install “VersionUo” folder in USB memory. (VersionUp folder must be place directly under the USB memory without changing the name of folder.) Do not plug any other memory device while installing the software. Do not use the USB memory with Security lock Do not use the USB memory which has virus protection. VersionUp folder mot file (main_V○R_○○_YYYY_MM_DD) SW2 USB Do not change the name. (VersionUp) Check version the mot file. V1R11 = version 1.11 375 Enter security code 65 to switch ON Test mode and shutdown application. 376 Remove the rear panel by 4 screw. Stick USB memory on USB inlet. Switch SW2 on CPU board inside instrument to change writing mode. Switch SW1 near SW2 to re-start windows. 1 Normal mode SW2 Writing mode 2 SW1 “Pi- Pi- Pi-“ 377 Open “G700ShUpdate” Click “Select” and open mot file (main_V○R_○○_YYYY_MM_DD) Select “my computer” ⇒ “removal disk” ⇒ “VersionUp” ⇒ “main_V○R_○○ _YYYY_MM_DD”. Click “Start” to start overwriting process. It will take approx. 6 minutes. Click “×” mark on right coner to close “G700ShUpdate”. 2 Click “G700ShUpdate” 1 3 SUCCES ○ 分 (minutes) ○ 秒 Switch SW2 on CPU board inside instrument to change normal mode. Switch SW1 near SW2 to re-start windows. 1 Writing mode SW2 Normal Normal mode 2 SW1 “Pi- Pi- Pi-“ 378 Click “G700ShLancher” on Windows. Click “G700ShLancher” 1 2 Click “OverWrite Launcher”. Restart and start G700Lancher again. Check all mark ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 3 Click “Over Write” 4 Click “Over Write and Run Exe” G700 application woll be started up automatically after “OverWrite and Run Exe”. Remove USB memory from USB inlet. Enter security code “9997” to check if software update was completed. “9997” SBC‐Ver (PROGRAM) : 1.11 SBC‐Ver (SET_SH) :1.11 SBC‐Ver (SET_INT) : 1.11 SBC‐Ver (MESSAGE) : 1.11 SH‐Ver (S) :730AQC Ver1.11 17/08/25 RMS( PROGRAM) :2.0.3.0 RMS( DLL) :2.0.3.0 G700Lancher : 1.15 379 Interface setting Set up Instrument G700 Model can interface between HOST PC or G700 Model as below. Follow the procedure to setup the instrument properly. A: Communication between the LIS and G700 Model GASTAT-700Model HUB HOST PC B: Communication between LIS with plural number of G700 Model GASTAT-700Model (Central) GASTAT-700Model (Teminal) HUB GASTAT-700Model (Teminal) C: Communication between the G700 Model (In this case, no need to create the interfacing program.) GASTAT-700Model (Central) GASTAT-700Model (Teminal) HUB GASTAT-700Model (Teminal) Please follow below procedure to setup interface for G700 Model. 380 HOST PC Network settings This chapter describes how to set up communication of local area network (LAN) Specifications / details of interface should be discussed about between customer and information system vendor and Techno Medica service representative. Contact Techno Medica local service representative to configure LAN communication setting. Press Function at home screen. Press Others. Press Network settings. Press each icon to configure settings in the ➊ ➋ ➌ ➍ field ➊-➍. Press Switch in the field ➋ to configure the communication protocol. Press Switch in the field ➌ to configure the central-terminal unit setting. The message changes from None→Central unit→Terminal unit by repeat. Press Switch in the field ➍ to configure port number setting for GLAN Server. The message changes from Without → With in repeat. 381 The details of each item are described in the table. Item Description Configuration IP address IP address of GASTAT-700 Model XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX (Default: 0.0.0.0) Subnet mask Subnet mask of GASTAT-700 255.255.XXX.XXX Model (Default 0.0.0.0) Gate way Gate way address of GASTAT-700 XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX Model (Default: Blank) Host IP IP address of Host (HIS/ LIS) XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX (Default 0.0.0.0) Host port No. Port number of Host (HIS/ LIS) Default: 1001 Switch(➋) Selecting a protocol for host Refer to interface manual of communications GASTAT-700 model. Central unit IP IP address of Central unit XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX (Default 0.0.0.0) Port number Subnet mask of Central unit Default: 1002 Switch(➌) Activating/deactivating Central/Terminal communication Selecting from "none", "Central unit", "Terminal" Remote port No. Port number for remote control Default: 1003 operation Switch(➍) Activating/deactivating control operation 382 remote Selecting from "With", "Without" Communication Specification 1. TMC’s Coverage Instrument Host TMC Cable connection 2. Standard IEEE802.3 10BASE-T 3. Interface TCP/IP 4. Transmission method Socket communication 5. Socket type Stream socket(TCP) 6. Server/Client GASTAT is a client and LIS is a server 7. Transmission code JIS8 8. Text length Fixed length 9. Port number 1024~65535 When installing multiple clients, please give 1 port per 1 client. 10.Gate Way Should be determined by Host 11.Instrument IP Address Should be determined by Host 12.Host IP Address Should be determined by Host 13.Computer name When installing multiple units on the same network, please set the computer name as follows. 1st:GASTAT-1 2nd:GASTAT-2 3rd:GASTAT-3 ・ ・ th n :GASTAT-n 383 Barcode Configuration 1. Available barcode of the container (12 types) ・Code 39 ・Industrial 2/5 (ITF) ・Interleaved 2/5 ・Matrix 2/5 ・MSI/Plessy ・Codabar (NW7) ・UPCA ・UPCE ・EAN-8 ・EAN-13 ・Code 93 ・Code 128 2. Maximum digits recognized by instrument are 20. NOTE The following Code128 type of barcode is not usable because they are already registered for instrument operation purpose. ①Barcode starting with ”7193” (The first 4 digits) ②Barcode starting with ”2893” (The first 4 digits) ③Barcode starting with ”7105” (The first 4 digits) ④Barcode starting with ”7160” (The first 4 digits) ⑤Barcode starting with ”838” (The first 3 digits) ⑥Barcode starting with ”839” (The first 3 digits) ⑦Barcode starting with ”718” (The first 3 digits) ⑧Barcode starting with ”711 ~ 715” (The first 3 digits) ⑨Barcode starting with ”G700” (The first 4 digits) ⑩Barcode starting with ”0192” (The first 4 digits) ⑪Barcode starting with ”7192” (The first 4 digits) ⑫Barcode starting with ”7194” (The first 4 digits) ⑬Barcode starting with ”7195” (The first 4 digits) ⑭Barcode starting with ”7196” (The first 4 digits) ⑮Barcode starting with “?????” (The first digits) “?????” is the same configuration with S.C. 577, 578 and 579. It can be neglected in case their configuration is 0 (Default settings) 3. Barcode Reader Specification Scannable width:Depends on barcode resolution Scannable depth:Depends on barcode resolution Degradative ability:0.1mm 384 4. Confirmed operation system Windows7 (Winsock2 should be installed in Windows) 385 Data Flow Normal flow GASTAT LIS ① Session bind request ② Session bind permission ③ Specimen ID ④ ACK string ⑤ Specimen ID + Patient demographic ⑥ ACK string ⑦ Specimen ID + Patient demographic + Test results ⑧ ACK string ⑨ Session terminate request ① GASTAT sends “Session bind request” to LIS. ② GASTAT receives “Session bind permission” from LIS. ③ GASTAT sends “Specimen ID” to LIS. ④ GASTAT receives “ACK string” from LIS. ⑤ GASTAT receives “Specimen ID and Patient demographic” from LIS. ⑥ GASTAT sends “ACK string” to LIS. ⑦ GASTAT sends “Specimen ID and Patient demographic and Test results” from LIS when measurement. ⑧ GASTAT sends “ACK string” to LIS. ⑨ GASTAT sends “Session terminate request” to LIS. NTOE1: Timing of sending Session bind request (①) is occasional. NOTE2: When Send button is pressed on the "Measurement data", the process from 3 to 6 are omited. 386 Flow when error occurs GASTAT LIS ① Session bind request ② Session bind permission ③ Specimen ID ④ ACK string ⑤ Specimen ID + Patient demographic ⑥ ACK string ⑦ Specimen ID + Patient demographic + Test results ⑧ ACK string ⑨ Session terminate request 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. If GASTAT could not receive either one of ②,④,⑧ from LIS, GASTAT re-sends ①,③,⑦ maximum 5times for every 3seconds. If there was no container barcode, GASTAT do not send ①. If there was no Patient demographic corresponds to container barcode, LIS should send “Space(20H)” as a Patient demographic at ⑤. In such case GASTAT sends “Space(20H)” as a Patient demographic at ⑦. In case two or more different barcode are read before measurement, last one will be acknowledged as specimen ID. GASTAT sends ⑨ whenever in the following occasions. (a) In case container barcode was read after “START” key, GASTAT sends ⑨ and start again from ①. (b) In case “FUNCTION” key was pressed before “START” key, GASTAT sends ⑨ (c) In case “STOP” key was pressed while measurement or after measurement(before test report print out), GASTAT sends ⑨. 387 String Format ③Specimen ID from GASTAT to LIS Byte Location Item Details 2 1-2nd byte String ID It should be always 80. 3 3-5th byte Data length It should be always 80. 20 6-25th byte Specimen ID Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. 1 26th byte CR ④ACK String Byte Location Item Details 2 1-2nd byte String ID It should be always 80. 3 3-5th byte Data length It should be always 004. 2 6-7th byte Communication error status Refer to NOTE 1 2 8-9th byte 00 (Dummy) It should be always 00. 1 10th byte CR NOTE: 1 00: Normal 02: Bite length 01: Abnormal 03: Time out ⑤Specimen ID + Patient demographic from LIS to GASTAT Byte 388 Location Item Details 2 1-2nd byte String ID It should be always 60. 3 3-5th byte Data length It should be always 342. 20 6-25th byte Specimen ID Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. Single byte character only 20 26-45th byte P-ID Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. Single byte character only 20 46-65th byte Patient name Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. Single byte character only 20 66-85th byte Dummy Should be always covered by “Space (20H)” 5 86-90th byte Height (cm) Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (5H)”. Single byte character only 5 91-95th byte Weight (kg) Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (5H)”. Single byte character only 1 96th byte Sex M (Male) / F (Female) 3 97-99th byte Age Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (3H)”. Single byte character only 10 100-109th byte Date of birth YYYY / MM / DD 10 110-119th byte Department name Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (10H)”. 128 120-247th byte Comments Left justify. Blank should be covered “Space (128H)”. part by 20 248-267th byte Space 1 Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. 20 268-287th byte Space 2 Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. 20 288-307th byte Space 3 Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. 20 208-327th byte Doctor ID 10 328-337th byte Birth weight (g) Right justify. 10 328-347th byte Gestation period (week) Left justify. 1 308th byte CR ⑥ACK String 389 Byte Location Item Details 2 1-2nd byte String ID It should be always 80. 3 3-5th byte Data length It should be always 004. 2 6-7th byte Communication error status Refer to NOTE 1 2 8-9th byte 00 (Dummy) It should be always 00. 1 10th byte CR NOTE: 1 00: Normal 01: Abnormal 02: Bite length 03: Time out ⑦Specimen ID + Patient demographic + Test results from GASTAT to LIS Byte Location Item Details 2 1-2nd byte String ID It should be always 82. 3 3-5th byte Data length It should be always 829. 20 6-25th byte Specimen ID Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. 20 26-45th byte P-ID Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. 20 46-65th byte Patient name Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. Single byte character only 390 20 66-85th byte Dummy Should be always covered by “Space (20H)” 5 86-90th byte Height (cm) Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (5H)”. Single byte character only 5 91-95th byte Weight (kg) Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (5H)”. Single byte character only 1 96th byte Sex M (Male) / F (Female) 3 97-99th byte Age Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (3H)”. Single byte character only 10 100-109th byte Date of birth YYYY / MM / DD 10 110-119th byte Department name Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (10H)”. 128 120-247th byte Comments Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (128H)”. 20 248-267th byte Space Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. 20 268-287th byte Space Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. 20 288-307th byte Space Left justify. Blank part should be covered by “Space (20H)”. 10 308-317th byte Date YYYY / MM / DD 8 318~325 th byte Time HH:MM:SS 5 326~330 th byte pH Unit:None 『 9.999 』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Upper limit: 8.000 Lower limit: 6.000 (Non-Corrected value by entered temperature) 5 331~335 th byte pCO2 Unit: Torr 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Upper limit: 200.0 Lower limit: 10.0 (Non-Corrected value by entered temperature) 5 336~340 th byte pO2 Unit: Torr 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Upper limit: 760.0 Lower limit: 10.0 (Non-Corrected value by entered temperature) 5 341~345 th byte Na Unit: mmol/L 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Upper limit: 200.0 Lower limit:80.0 5 346~350 th byte K Unit: mmol/L 『99.99』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Upper limit: 20.0 Lower limit: 1.0 5 351~355 th byte Cl Unit: mmol/L 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered 391 with 0. Upper limit: 200.0 Lower limit: 50.0 392 Ca Unit: mmol/L 『99.99』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Upper limit: 5.00 Lower limit: 0.50 5 356~360 th byte 5 361~365th byte Glc 5 366~370 th byte La Unit: mmol/L 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Upper limit:30.0 Lower limit: 0.4 5 371~375 th byte Hb Unit: g/dL 『99.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Upper limit: 23.0 Lower limit: 2.0 Oxy type: Space all 5 376~380 th byte SO2 Unit: % 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. 5 381~385 th byte FO2Hb Unit: % 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. 5 386~390 th byte FCOHb Unit: % 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. 5 391~395 th byte FMetHb Unit: % 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. 5 396~400 th byte FHHb Unit: % 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. 5 401~405 th byte Bil Unit: mg/dL 『99.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Upper limit: 58.5 Lower limit: 0.0 5 406~410 th byte tHb Unit:g/dL 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Upper limit: 23.0 Lower limit: 2.0 Without Oxy type: space all 5 411~415 th byte Barometic Pressure Unit: Torr 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Unit: mmol/L 『99.99』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Upper limit: 66.6 Lower limit: 1.1 4 416~419 th byte Patient Temp Unit: ℃ 『99.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. 5 420~424 th byte FiO2 Unit: % 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. Upper limit: 100.0 Lower limit: 0.0 5 425~429 th byte Respiratory volume Unit:l/min 『999.9』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. 3 430~432 th byte Breathing rate Unit:b/min 『999』 Right justify. Blank part will be covered with 0. 20 20 20 433~452 th byte Measure appliance 453~472 th byte Sample type 473~492 th byte Sample area Right justify. 00:Syringe 01:Capillary 11:Others Left justify. 00:Non 01:Arterial blood 02:Venous blood 03:Mixed venous blood Space all excepting measement blood Left justify. 00:Not specified 01:Left upper arm 02:Right upper arm 03:Left thigh 04:Right thigh 05:Left radial artery 06:Right radial artery 07:Umbilical cord blood 08:Heel 09:Earlobe 10:Finger Space all excepting measement blood 20 493~512 th Operater ID Left justify. 393 byte 394 20 513~532th byte Doctor ID Left justify. 10 533~542th byte Sampling date YYYY/MM/DD 5 543~547th byte Sampling time HH:MM 10 548~557th byte Birth weight (g) Left justify. 10 558~567th byte Pregnancy period (week) Left justify. 5 568~572th byte AG 5 573~577th byte AG(K) 4 578~581th byte HCO3-act 4 582~585th byte HCO3-std 5 586~590th byte MCHC Space all. 5 591~595th byte BE Space all. 5 596~600th byte BE(ecf) 5 601~605th byte BE(B) 4 606~609th byte BB 5 610~614th byte ctCO2 4 615~618th byte ctCO2(P) 5 619~623th byte ctCO2(B) 5 624~628th byte CO2/dry air 4 629~632th byte Hct 5 633~637th byte pH(T) Space all. Space all. pH (Corrected value temperature) by 5 638~642th byte pH(P,st) Space all. 5 643~647th byte H+ Space all. 5 648~652th byte PCO2(T) pCO2 (Corrected value by entered temperature) 5 653~657th byte PO2(T) pO2 (Corrected value by entered temperature) 5 658~662th byte sO2(est) 5 663~667th byte ctO2 Space all. 5 668~672th byte ctO2(Hb) Space all. entered 5 673~677th byte BO2 5 678~682th byte p50 5 683~687th byte p50(T) 5 688~692th byte p50(st) 5 693~697th byte O2sat(est) 5 698~702th byte PO2/FIO2 5 703~707th byte Ca++(7.4) 5 708~712th byte PO2(A,T) 5 713~717th byte PAO2 5 718~722th byte PO2(A-a) 5 723~727th byte PO2(A-a)(T) 4 728~731th byte PO2(a/A) 5 732~736th byte PO2(a/A)(T) 4 737~740th byte RI 5 741~745th byte RI(T) 4 746~749th byte ctO2(a) 5 750~754th byte ctO2(B) 5 755~759th byte ctO2(v) 5 760~764th byte ctO2(a-v) 5 765~769th byte ctO2([a-v]/a) 5 770~774th byte VO2 5 775~779th byte DO2 5 780~784th byte Qt 5 785~789th byte Qsp/Qt 5 790~794th byte Qsp/Qt(est) 5 795~799th byte OER 15 800~814th byte Space 20 815~834th byte Parameter stauts 1 835th byte Space all. Space all. NOTE3) Refer Parameter status CR NOTE: 395 1.If specific measured/derived parameter is set to OFF, GASTAT sends corresponding number of “Space (20H)”. 2. In case there is measurement failure on specific measured parameter, relative derived parameter will be “*”. ie) If tHb has an measurement failure, GASTAT sends “**.*” as a Hb value to the LIS. Hct value becomes “**.*” NOTE3: Parameter status Byte 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Parameter pH pCO2 pO2 Na K Cl Ca Glc Lac Hb Byte 11 12 13 Parameter SO2 14 15 O2Hb COHb MetHb HHb 16 17 18 19 20 Bil tHb 0 0 0 fixed fixed fixed Error code describes the error status of all of the measurement parameter. It may help LIS to determine if test results is reliable/not reliable. The following chart gives an information about the location of the each parameter and error code details. Error code Status 0 Test finished without problem. 1 Bubble detect 2 Sample too small 3 Measurement failure 4 Result exceed the upper limt of measurement range. 5 Result underrun the lower limit of measurement range. 6 Result exceed the upper limit of normal value. 7 Result underrun the lower limit of normal value. Measurable range and Normal Range Normal Parameter 396 Measurement Range (Default Range setting) Related calculated parameters pH 6.000 – 8.000 7.380 – 7.460 HCO3-,O2SAT,BE,SBE,TCO2,BB,O2CT,SBC pCO2 10.0 – 200.0 32.0 – HCO3-,BE,SBE,TCO2,BB,SBC,AaDO2,RI,a/A Torr 46.0 pO2 10.0 – 760.0 Torr 74.0 – 108.0 O2SAT,O2CT,SBC,AaDO2,RI,a/A Na 80.0 – 200.0 mmol/L 139.0 – 147.0 AG K 1.00 – 20.00 mmol/L 3.30 – 4.70 AG Cl 50.0 – 200.0 mmol/L 102.0 – 110.0 AG Ca 0.50 – 5.00 mmol/L 1.00 – 1.30 AG,cCa Glc 1.1 – 66.6 mmol/L 3.30 – 7.80 0.4 – 30.0 Lac mmol/L 0.4 – 1.8 tHb 2.0 – 23.0 g/dL 12.0 -18.0 SO2 0 -100 % 92.0 98.5 O2Hb 0 -100 % 94.0 97.0 COHb 0 -100 % 0 - 10.0 MetHb 0 -100 % 0 - 10.0 HHb 0 -100 % 0 - 5.0 Bil 0 -58.5 mg/dL 0.2 – 1.2 Hct Even though results exceed the upper limt or underrun the lower limit, the instrument sends obtained values to Host. (ie) If the result of Ca is 0.01 (The value underruns lower limit), the instrument sends 0.01 ⑧ACK String Byte Location Item Details 2 1~2th byte String ID It should be always 82. 3 3~5th byte Data Length It should be always 004. 2 6~7th byte Communication status 2 8~9th byte 00 (Dummy) 1 10th byte CR error Refer to NOTE 1 It should be always 00. 397 NOTE: Communication error status 00: Normal 01: Abnormal 398 02: Bite length 03: Time out G700 Model trouble report format DDMMYYYY Error classification Mandatory information Flow error (1), (2-1), (2-2), (2-5), (3), (4), (5), (8) Calibration failure (1), (2-1), (2-2), (2-5), (3), (4), (5), (8) Manual QC is out of target range / The (1), (2-1), (2-2), (2-5), (3), (4), (5), (6) instrument shows abnormal results. AQC is out of target range (1), (2-1), (2-2), (2-3), (2-4), (2-5), (3), (4), (5), (6) A customer makes a complaint that test (1), (2-1), (2-2), (2-5), (3), (4), (5), (6), (7), (8) results varies from another instrument. 1. Basic Information Service date DDMMYYYY Company name Engineer name who trouble reported Hospital name Installation place Instrument model name G710 G710aqc G720 G730 G720aqc G735 G730aqc G735aqc Instrument serial number Instrument version (Security code : 9997) 399 2. Log file required for troubleshooting 1. Calibration history Stick USB memory to USB inlet on rear panel. Access security code 1072 and change the setting from "0" to "1". Access security code 554 and change the setting to "50000". Access security code 9003 Calibration history will be transferred into USB memory by electric file. 2. Flow check results Perform “Flow” in Self Diagnosis. Then Perform “Valve” in Self Diagnosis. Send printed result by PDF file. 3. Auto QC log Stick USB memory to USB inlet on rear panel. Access “Function” “Quality Control” ”Record” “Auto QC” and press “OK”. Enter starting date at “Start date” and the number of date at “Extraction field”. Press “USB save”. Auto QC log will be transferred into USB memory by electric file. 4. AQC barcode Take a picture of AQC barcode shown behind the CAL cartridge. Send the picture file with Auto QC log. 5. Setting log Stick USB memory to USB inlet on rear panel. Access “Function” “Others” ”Data exchange” “Data transfer” Put check mark at “Setting file” and “Data base” and press “OK” Setting file will be transferred into USB memory by electric file. 3. Action taken Trouble description Action taken by field service engineer 400 4. Electrode Information Lot number pH PCO2 Lac Flow cell PO2 Ref Na K Cl Ca Glc pH: pCO2: pO2: Ref: Na: K: Cl: Ca: Glc: Lac: Flow cell: Installation date pH: pCO2: pO2: Ref: Na: K: Cl: Ca: Glc: Lac: Flow cell: 401 5. Reagent / consumable information Cal cartridge: Pump tube: Lot number: Lot number: Installation date: Installation date: Sample port & Nozzle: Tubing kit: Lot number: Lot number: Installation date: Installation date: Sampling tube: Flush solution: Lot number: Lot number: Installation date: Installation date: 402 6. Quality control information GASTROL / GASTROL-ISE Put check mark and enter batch number of ample. GASTROL Batch number: L1: L2: L3: GASTROL-ISE Batch number: L1: L2: L3: Level 1 pH PCO2 PO2 Na K Cl Ca Glc Lac pH PCO2 PO2 Na K Cl Ca Glc Lac pH PCO2 PO2 Na K Cl Ca Glc Lac Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Level 2 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Level 3 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 403 7. Test result of Blood Sample 8. Enter the value obtained from your GASTAT and competitor in below chart for comparison: Competitor’s model name: Bayer 850 (For example) pH PCO2 PO2 Na K Cl Ca Glc Sample1 Gastat Sample1 Competitor Sample2 Gastat Sample2 Competitor Sample3 Gastat Sample3 Competitor Sample4 Gastat Sample4 Competitor 9. Container information Type of container Heparin type Manufacturer name Syringe Disposable plastic syringe for blood gas analysis Local syringe Capillary Disposable plastic capillary Glass capillary 404 (ie) Liquid sodium heparin Volume Lac