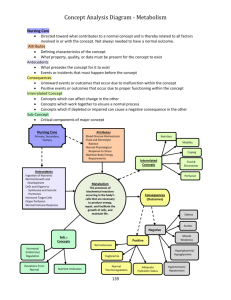
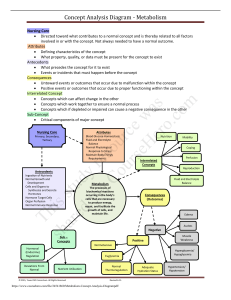
Syndrome characterized by decreased tissue perfusion and impaired cellular metabolism - Sudden and generalized ischemia to all body parts - Demand for oxygen and nutrient is the same but the body is not able to provide What is shock? - Results from some type lead to a decrease in tissue perfusion which causes cell hypoxia and eventually multiple organ destruction syndromes (MODS)... death. - Types - Septic (infection) - Hypovolemic (fluid loss) - Cardiogenic (weak heart) - Anaphylactic (allergic) - Neurogenic (neuro damage) - Obstructive (impeding blood flow) - Stages - Initial - Cell switch from aerobic to anaerobic. - Metabolism = LACTIC ACID - CO is LOW → Can’t support tissue perfusion and O2 demand - S/S are subtle - Lactic acid builds up in the blood (acid-base imbalance) damages cells even more - Normal serum lactate < 1mmol/L - Lactic acidosis > 4mmol/L - Compensatory (reversible) - Biochemical, neural, and hormonal team (vasoconstriction) to fight effects of anaerobic metabolism - Tries to increase BP, CO → increase perfusion - Baroreceptors: stimulates the SNS = release epinephrine and norepinephrine = vasoconstriction (increase BP & HR) - Increased perfusion to vital organs (brain and heart) shunted from non-vital (GI, skin, lungs, kidneys) - kidneys will activate RAAS → increases BLOOD VOLUME - More blood return to the heart - Due to aldosterone (kidneys keeping Na+ and water) urine will have high osmolality - GI System: risk for paralytic ileus - Skin: cool, moist, pale - EXCEPT! Septic shock: vasodilation, hot, flushed - Lungs: increased RR, hyperventilation - Decrease in arterial pressure = decrease in hydrostatic pressure - Progressive - Body systems are failing - Progressing to MODS/ death - - No more compensation → drop in CO → decreased O2 to cells → HYPOXIC INJURY = increase capillary permeability = LOSE blood volume and MASSIVE EDEMA - Neuro: MAP < 60mmHg, slow speech, confused, agitated, decreased reaction - Lungs: ARDS, increased RR, decreased O2, resp failure - Heart: muscle cells die, AMI, dysrhythmias - Kidneys: acute tubular necrosis, renal failure, decreased UOP, increased waste, increased creat & BUN - Gut: GI bleeding and ulcers - Liver: increased ammonia and bilirubin - DIC: micro clots in vessels, wastes platelets and clotting factors, bleeding everywhere - Need fast dynamic treatment Refractory (irreversible, not manageable) - All organs will shut down - Everything that happened in the previous stage is getting worse Diagnostic studies - Blood studies - Lactate - Base deficit - 12 lead ECG, continuous ECG - CXR - Hemodynamic monitoring