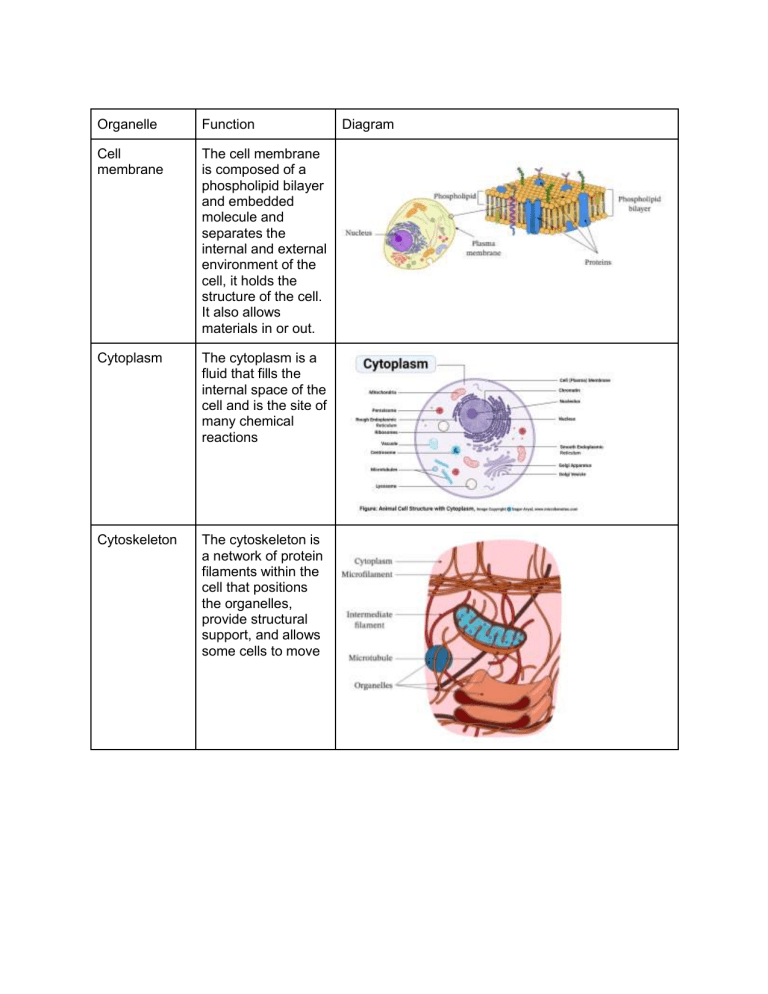
Organelle Function Cell membrane The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded molecule and separates the internal and external environment of the cell, it holds the structure of the cell. It also allows materials in or out. Cytoplasm The cytoplasm is a fluid that fills the internal space of the cell and is the site of many chemical reactions Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments within the cell that positions the organelles, provide structural support, and allows some cells to move Diagram Nucleus The nucleus is a key component of eukaryotic cells and is the organelle that stores and protects the DNA Ribosomes Ribosomes are non membranous structures that act as the site of protein synthesis in the cell Rough endoplasmic reticulum The rough endoplasmic reticulum is a series of folded membranes, or flattened sacs, that is covered with ribosomes and is associated with the production of proteins. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is a series of tube-like structures with folded membranes that is not covered with ribosomes and is associated with the production of lipids Golgi apparatus (Golgi bodies) The Golgi apparatus packages lipids or proteins receives from the endoplasmic reticulum delivers them throughout the cell Lysosomes Lysosomes are specialised vesicles filled with enzymes that break down and recycle old cellular structures or components. Mitochondria Mitochondria are the main site of cellular respiration within eukaryotic cells. Cell wall The cell wall is a rigid outer layer that provides structural support to the plant cell. Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis within the plant cell. Large (centre) vacuole The large vacuole stores sap and provides the plant cell with its structure.




