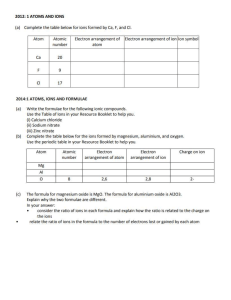
Topic 1 Planet Earth Unit 1 Introducing chemistry Unit 2 The atmosphere Unit 3 The ocean Unit 4 Rocks and minerals Key C o ncepts Planet Earth Introducing chemistry • Chemistry and our lives • Laboratory safety rules and hazard warning labels • Common apparatus in the laboratory The atmosphere • Classification of matter — element, mixture and compound • Separating oxygen and nitrogen from the air • Physical and chemical properties of a substance The ocean • Composition of sea water • Obtaining common salt from sea water • Obtaining pure water from sea water • Showing what species common salt contains • Useful materials obtained from sodium chloride • The particle theory of matter • Physical and chemical changes • • • • Rocks and minerals Metals in the Earth’s crust Extracting metals from their ores Chemical reactions of calcium carbonate Formation of chalk, limestone and marble Topic 1 Planet Earth Unit 1 Introducing chemistry 1.1 What is chemistry? 1.2 Why study chemistry? 1.3 Laboratory safety 1.4 Hazard warning labels 1.5 Common apparatus in the laboratory Unit 1 Introducing chemistry 1.1 – 1.5 Summary Hazard warning label Example(s) • Ammonium dichromate Explosive • Carbon monoxide • Hydrogen • Liquefied petroleum gas Flammable • Town gas • Ethanol • Chlorine • Carbon monoxide • Mercury Toxic • Asbestos • Suspected example: crude petroleum Carcinogenic • Concentrated nitric acid Oxidizing • Bromine • Concentrated acids • Concentrated aqueous ammonia Corrosive I • Concentrated sodium hydroxide solution • Iodine Harmful • Dilute acids J • Dilute aqueous ammonia Irritant Exam tips ♦ Oxygen supports combustion, but it is NOT flammable. ✘ ♦ Chlorine bleach is usually a 5.25% sodium hypochlorite solution. A potential hazard of mixing an acidic toilet cleanser with chlorine bleach is that a toxic gas (chlorine) is liberated. Topic 1 Planet Earth Example Explain why non-luminous flame is obtained when the air hole of a Bunsen burner is fully open. (2 marks) Answer Enough oxygen is provided when the air hole is fully open. (1) The fuel undergoes complete combustion. (1) Remarks* Remarks ➤ When using a Bunsen burner with the air hole closed, the fuel undergoes incomplete combustion. The burner gives a luminous flame. The yellow colour of the flame is due to the presence of tiny carbon particles. Unit 2 The atmosphere Unit 2 The atmosphere 2.1 The Earth 2.2 Classification of matter: pure substance and mixture 2.3 Elements and compounds 2.4 Differences between a mixture and a compound 2.5 The atmosphere 2.6 Separation of mixtures 2.7 Separating oxygen and nitrogen from the air 2.8 Physical and chemical properties 2.9 Test for oxygen Topic 1 Planet Earth 2.1 – 2.9 Summary 1 Classification of matter: matter pure substances elements (e.g. hydrogen, oxygen, iron, sulphur) can be separated by chemical methods can be separated mixtures by simple physical methods compounds (e.g. water, iron(II) sulphide) 2 A pure substance is a single substance that has nothing else mixed with it. 3 A mixture is a substance composed of two or more pure substances which have not been chemically joined together. 4 Elements are substances which cannot be broken down into anything simpler by chemical methods. 5 Compounds are substances composed of two or more elements chemically joined together. 6 The approximate percentage composition of gases in the air (in percent by volume) is as follows: Gas in air Approximate percentage (by volume) Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Other gases (including noble gases, carbon dioxide and water vapour) about 1% (noble gases — 0.9% carbon dioxide — 0.03 – 0.04% water vapour — varying amount) 7 In industry, oxygen and nitrogen in the air are separated by fractional distillation of liquid air. Unit 2 The atmosphere 8 Physical properties of a substance are properties that can be measured without changing the chemical composition of the substance. e.g. • colour • odour • taste • state • melting point • boiling point 9 Chemical properties of a substance are properties that describe its ability to form new substances. e.g. • reaction with oxygen • reaction with water • reaction with acids / alkalis 10 A simple test of oxygen is that it can relight a glowing splint. Exam tips ♦ Students should be able to tell whether a substance is a single compound. e.g. Ethanol is a single compound. Petrol is a mixture of compounds. Vinegar is a mixture of ethanoic acid and water. ♦ Students should be able to give correct wordings. e.g. Oxygen relights a glowing splint, NOT a growing splint. 4 ✘ Work in a fume cupboard, NOT a flame cupboard. 4 ✘ Example The following table gives some information of certain components in a sample of liquid air: Component Boiling point (°C) Argon –186 Nitrogen –196 Oxygen –183 10 Topic 1 Planet Earth a) Name ONE other gas found in dry air. (1 mark) b) An industrial method can be used to separate nitrogen and oxygen from the sample. i) Name the industrial method. (1 mark) ii) In what order would the components separate out when the sample undergoes the process? Explain your answer. (2 marks) Answer a) Carbon dioxide (1) b) i) Fractional distillation (1) ii) The order is: nitrogen, argon, oxygen. (1) Nitrogen has the lowest boiling point. Thus, it will be distilled off first. Oxygen has the highest boiling point. Thus, it will be distilled off last. (1) Remarks* Remarks ➤ Carbon dioxide is NOT obtained industrially from the fractional distillation of liquid air. Unit 3 The ocean Unit 3 The ocean 3.1 Sea water: a vast solution 3.2 Obtaining common salt from sea water 3.3 Obtaining pure water from sea water 3.4 Showing what species common salt contains 3.5 Test for the presence of water in a sample 3.6 Electrolysis of sea water 3.7 Uses of the products obtained by the electrolysis of sea water 3.8 The particle theory of matter 3.9 Physical and chemical changes 11 12 Topic 1 Planet Earth 3.1 – 3.9 Summary 1 Sea water contains 3.5% by mass of dissolved salts, including a) sodium chloride; b) magnesium chloride; c) sodium sulphate; and d) calcium chloride. 2 A solution forms when one substance dissolves in another. The substance that dissolves is called the solute. The substance that does the dissolving is called the solvent. solute + solvent = solution 3 A dilute solution contains a small amount of solute in a given volume of solution. A concentrated solution contains a large amount of solute in a given volume of solution. 4 A saturated solution is a solution that has dissolved the most solute it can, at a given temperature. 5 The following table summarizes some common separation methods: Separating process Method(s) of separation Example Separating a much denser insoluble solid from a liquid decantation separating coarse sand from sea water Separating an insoluble solid from a liquid filtration separating mud from muddy sea water Separating a dissolved solid (solute) from a solution evaporation or crystallization obtaining common salt from sea water Separating solvent and solute from a solution distillation obtaining pure water and salt from sea water 6 The following table lists the flame colours of some metal compounds: Compound of Flame colour Potassium lilac Sodium golden yellow Calcium brick-red Copper bluish green 7 To test for chlorides, first dissolve the sample in water, then add excess dilute nitric acid, followed by silver nitrate solution. Appearance of a white precipitate suggests that the sample is a chloride. 8 Common salt is sodium chloride. It is made up of two elements, sodium and chlorine. 9 A simple test for water is that it can turn blue cobalt(II) chloride paper pink. 10 Useful substances can be obtained from sea water by electrolysis. sea water electricity chlorine gas + hydrogen gas + sodium hydroxide solution Unit 3 The ocean 11 The particle theory of matter states that all matter is made up of very small particles. 12 a) During a physical change, no new substance is formed. b) In a chemical change, one or more new substance(s) is / are formed. 13 The following words are used to describe the changes of states of a substance. gas co n io it os p de i im bl su at melting nd en sa r e bo tio va ili n po ng ra tio n) (o on freezing solid Exam tips liquid ♦ Filtration CANNOT remove sodium chloride from sea water. ♦ To obtain salt from a salt solution, use evaporation or crystallization. To obtain both salt and water from a salt solution, use distillation. ♦ Consider a boiling tube containing hot saturated copper(II) sulphate solution. Large crystals of the salt can be obtained by placing the tube on a bench for several days. ♦ Students should be able to describe the procedure for flame test. nichrome wire concentrated hydrochloric acid (a) Dip a clean nichrome wire into concentrated hydrochloric acid Bunsen burner solid sample watch glass (b) Then dip the nichrome wire into the solid sample (c) Put the end of the wire in the Bunsen flame and observe the colour of the flame ♦ When describing a chemical test to show that water vapour is formed in a certain reaction, students may use anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride paper or anhydrous copper(II) sulphate. ♦ When describing a test for water, state the colour change of the cobalt(II) chloride paper. DO NOT just write down the colour of the paper after it meets water. ♦ H2O(l) H2O(s) is an exothermic process. 13 14 Topic 1 Planet Earth Example Classify each of the following processes as either a physical or chemical change. Explain your answer. a) Fractional distillation of petroleum (1 mark) b) Rusting of iron (1 mark) c) Formation of dry ice from carbon dioxide gas (1 mark) d) Mixing sea water with silver nitrate solution (1 mark) e) Cracking of heavy oil (1 mark) Answer a) Physical change. No new substance is formed in the process. (1) b) Chemical change. New substance (rust) is formed in the process. (1) c) Physical change. No new substance is formed in the process. (1) d) Chemical change. New substance (a white precipitate / silver chloride) is formed in the process. (1) e) Chemical change. New substances (alkenes and alkanes) are formed in the process. (1) Remarks* Remarks ➤ Electrolysis of sea water is a chemical change. Unit 4 Unit 4 Rocks and minerals 4.1 Metals in the Earth’s crust 4.2 Extracting metals from their ores 4.3 Investigating calcium carbonate 4.4 Formation of chalk, limestone and marble 4.5 Formation of limestone caves Rocks and minerals 15 16 Topic 1 Planet Earth 4.1 – 4.5 Summary 1 The individual chemical compounds that make up rocks are called minerals. Rocks from which we obtain metals are called ores. 2 Getting a metal from its ore is called extracting the metal. 3 The following table summarizes common methods for extracting metals from their ores: Extraction method Example(s) • panning for gold Physical method • extracting mercury from cinnabar Heating the ore alone • extracting silver from silver oxide Heating the ore with carbon • extracting iron from haematite Electrolysis of the molten ore • extracting aluminium from its molten ore 4 The following table summarizes the action of heat, dilute acid and water on calcium carbonate: Action of Change(s) calcium carbonate Heat CaCO3(s) heat calcium oxide + water CaO(s) + H2O(l) Dilute acid calcium hydroxide (slaked lime) Ca(OH)2(s) calcium carbonate + dilute hydrochloric acid calcium chloride + water + carbon dioxide CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) Water calcium oxide (quicklime) + carbon dioxide CaO(s) + CO2(g) CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) insoluble in water but soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid 5 Slaked lime is slightly soluble in water. The saturated solution formed is called limewater. 6 Limewater can be used to test for carbon dioxide gas. Carbon dioxide turns limewater milky due to the formation of insoluble white calcium carbonate. CO2(g) + Ca(OH)2(aq) CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) When an excess of carbon dioxide is passed into the limewater, the white precipitate disappears. This is because the precipitate dissolves to form soluble calcium hydrogencarbonate. CaCO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) Ca(HCO3)2(aq) 7 Calcium carbonate occurs naturally in three main forms — chalk, limestone and marble. 8 Solid rock can be broken down into smaller pieces and changed into other materials as a result of weathering. The wearing away of surface materials and the movement of products of weathering from where they formed to a different location is called erosion. The major causes of erosion are gravity, running water, waves, ice and wind. Unit 4 Rocks and minerals 17 ♦ Oyster shell contains mainly calcium carbonate. Exam tips ♦ Limestone can be usesd as fire-proofing additive because the decomposition of calcium carbonate is an endothermic process. ♦ Unpolluted rainwater can erode limestone because carbon dioxide in the air dissolves in unpolluted rainwater to form carbonic acid. Example An anhydrous compound X gives a brick-red flame in flame test. Upon strong heating, compound X gives off a gaseous product Y which turns blue cobalt(II) chloride paper pink and a gaseous product Z which turns limewater milky. a) i) Identify gaseous products Y and Z (2 marks) ii) Write a chemical equation for the reaction between the gaseous product Z and limewater. (1 mark) b) What can be deduced about compound X from the observation in flame test? (1 mark) c) Suggest what compound X may be. (1 mark) d) In another experiment, the gaseous product Z is passed into sodium hydroxide solution instead of limewater. Explain whether a similar observation would be made. (1 mark) Answer a) i) Y is water vapour. (1) Z is carbon dioxide. ii) Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) (1) CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) b) Compound X contains calcium. (1) (1) c) Calcium hydrogencarbonate (1) d) No. Sodium carbonate is soluble in water. (1) Remarks* Remarks ➤ The following substances can be used to distinguish between oxygen and carbon dioxide: – limewater; – burning splint; – glowing splint. Carbon dioxide would extinguish the burning splint.