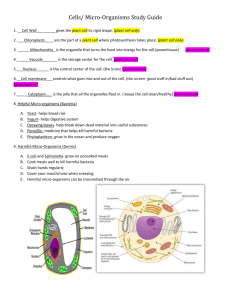
GRADE 9 BIOLOGY TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS OBJECTIVES: ü Name the transport system in animals ü List the functions of blood ü List and describe components of blood and relate their description to their individual roles ü Describe the role of blood in defending the body against diseases TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN ANIMALS q The transport system in animals is known as the circulatory system q This system is made up of: q blood vessels that take blood to and from the cells q the heart that pumps the blood FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD q Transport of: q oxygen and carbon dioxide q nutrients and products of metabolism q chemical substances such as hormones and enzymes q metabolic waste such as urea ( to be excreted) q Regulate: maintain body temperature (distribute heat) q Protect: sealing wounds, by the formation of clots q Defend: fight disease organisms COMPONENTS OF BLOOD q Blood consists of: q Plasma q Red Blood Cells q White Blood Cells q Platelets COMPONENTS OF BLOOD q Plasma q Pale, straw-colored liquid made up of q 90% water q 10% dissolved substances q Transport substances in solution to and from the body cells COMPONENTS OF BLOOD q Red Blood Cells q Flat and hollowed in the center q Do not have a nucleus q Has a lot of space for haemoglobin q Transports oxygen to body cells COMPONENTS OF BLOOD q White Blood Cells q Larger than red blood cells q Help the body fight against disease organisms q Two main types: q Lymphocytes - make antibodies and antitoxins q Phagocytes – similar to amoebae and surround and digest germs COMPONENTS OF BLOOD q Platelets q Small pieces of cells q Help the blood clot and seal up any small cuts q A scab forms and the skin repairs itself ROLE OF BLOOD IN FIGHTING DISEASES q Red Blood Cells q Haemoglobin in red cells allows blood to carry 60 times more oxygen than could be dissolved in the plasma q Iron is a part of the haemoglobin molecule q Iron deficiency results in less haemoglobin being made q This causes anaemia ROLE OF BLOOD IN FIGHTING DISEASES q Chemicals and Platelets q After getting a cut on the skin a clot is made to help stop bleeding q This clot is made from chemicals in the blood and platelets q If left uncovered a scab then forms and dries on the skin ROLE OF BLOOD IN FIGHTING DISEASES q White Blood Cells q If micro-organisms get into the blood they are attacked by the immune system q This is the system made up of the white cells in the blood White blood cell Micro-organisms (e.g. bacteria) ROLE OF BLOOD IN FIGHTING DISEASES q White Blood Cells q Lymphocytes q Have a clear cytoplasm and a large nucleus q Some bacteria produce poisonous substances called toxins q Lymphocytes produce antitoxins to neutralize these toxins preventing us from getting sick q All viruses and some bacteria have chemicals on their surfaces, called antigens q The lymphocyte produces antibodies to help the body fight off these viruses and bacteria ROLE OF BLOOD IN FIGHTING DISEASES q White Blood Cells q Phagocytes q White cells that resemble amoebae q They can surround the micro-organisms and digest them Micro-organisms (e.g. bacteria) Phagocyte