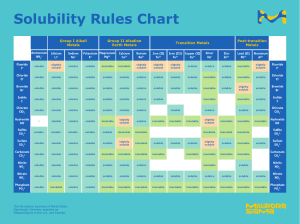
SCH3U Solutions Test Review 1. Introduction to Solutions: Vocabulary (solution, solvent, solute, solubility, miscible, immiscible, saturated, unsaturated, supersaturated etc.) Factors affecting solubility. Be able to make connections with intermolecular forces Solubility curves 2. Reactions in Solution: Qualitative Analysis (ions in solution, flame tests etc.) Reactions in solution (precipitation, gas, neutralization) how would you test for this? Predicting solubility using solubility rules (will it precipitate?) Total and net ionic equations Systematic analysis (flow charts) 3. Solution Concentration: Dilute versus concentrated Percentage concentration (v/v, w/v, m/m) ppm, ppb, ppt Molarity (mol/L) C = n/V 4. Preparing Solutions: From a pure solid (calculations and technique) By dilution C1V1 = C2V2 (calculations and technique) Lab skills (e.g. precision of different glassware i.e. graduated cylinder versus volumetric flask etc.) 5. Volumetric Stoichiometry: Determining concentration, volume, number of moles, mass of precipitate Remember: limiting reactant!! 6. Acids and Bases: Properties of acids and bases Strong versus weak; concentrated versus dilute pH calculations and indicators Titrations (calculations and technique) p. 309 #1-3, 5-9, 11-15, 17, 18 p. 358 #1-3, 9, 10 p. 403 #1, 2, 4-7, 10, 18, 19, 21 p. 408 #1, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14-18, 20-24, 28, 31-35 SCH3U Solutions Test Review 1. Introduction to Solutions: Vocabulary (solution, solvent, solute, solubility, miscible, immiscible, saturated, unsaturated, supersaturated etc.) Factors affecting solubility. Be able to make connections with intermolecular forces Solubility curves 2. Reactions in Solution: Qualitative Analysis (ions in solution, flame tests etc.) Reactions in solution (precipitation, gas, neutralization) how would you test for this? Predicting solubility using solubility rules (will it precipitate?) Total and net ionic equations Systematic analysis (flow charts) 3. Solution Concentration: Dilute versus concentrated Percentage concentration (v/v, w/v, m/m) ppm, ppb, ppt Molarity (mol/L) C = n/V 4. Preparing Solutions: From a pure solid (calculations and technique) By dilution C1V1 = C2V2 (calculations and technique) Lab skills (e.g. precision of different glassware i.e. graduated cylinder versus volumetric flask etc.) 5. Volumetric Stoichiometry: Determining concentration, volume, number of moles, mass of precipitate Remember: limiting reactant!! 6. Acids and Bases: Properties of acids and bases Strong versus weak; concentrated versus dilute pH calculations and indicators Titrations (calculations and technique) p. 309 #1-3, 5-9, 11-15, 17, 18 p. 358 #1-3, 9, 10 p. 403 #1, 2, 4-7, 10, 18, 19, 21 p. 408 #1, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14-18, 20-24, 28, 31-35