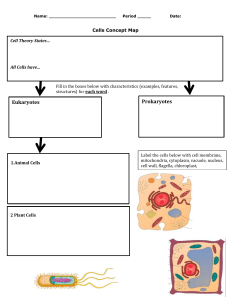
NAME:___________________YEAR AND SECTION___________________ Activity 3 1. XYLEM 2. ELALOPLASTS 3. PLANT CELL 4. MITOCHONDRIA 5. CELL 6. CHLOROPLASTS 7. RIBOSOMES 8. CHLOROPLASTS 9. ARUM 10. ARISAEMA Activity 4 Organelles CELL MEMBRANE CYTOPLASM NUCLEUS Structure nad Function The plasma membrane, or the cell membrane, provides protection for a cell. It also provides a fixed environment inside the cell, and that membrane has several different functions. One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell. Cytoplasm is the gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell. It is composed of water, salts, and various organic molecules. Some intracellular organelles, such the nucleus and mitochondria, are enclosed by membranes that separate them from the cytoplasm. The nucleolus is a region found within the cell nucleus that is concerned with producing and 1 assembling the cell's ribosomes. Following assembly, ribosomes are transported to the cell cytoplasm where they serve as the sites for protein synthesis. NUCLEOLUS NUCLEAR ENVELOPE ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM RIBOSOMES GOLGI BODY /APPARATUS LYSOSOMES MITOCHONDRIA VACOULES CELL WALL PLASTIDS is a dense, strained structure inside of the nucleus that contains ribosome. The nuclear envelope (NE) is a highly regulated membrane barrier that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells. It contains a large number of different proteins that have been implicated in chromatin organization and gene regulation a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and serves multiple functions, being important particularly in the synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of protein ribosome is a cellular particle made of RNA and protein that serves as the site for protein synthesis in the cell. is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. is a membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes. ... They break down excess or worn-out cell parts. Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles (mitochondrion, singular) that generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's biochemical reactions. A vacuole is a membrane-bound cell organelle. In animal cells, vacuoles are generally small and help sequester waste products A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane Plastids are core components of 2 CENTRAL VACOULES photosynthesis in plants and algae Chloroplasts, as well as any other pigment containing cytoplasmic organelles that enables the harvesting and conversion of light and carbon dioxide into food and energy, are plastids. The central vacuole is a large vacuole found inside of plant cells. . Activity 5 Organelles CELL MEMBRANE CYTOPLASM ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM GOLGI BODY /APPARATUS RIBOSOMES Structure and Function The plasma membrane, or the cell membrane, provides protection for a cell. It also provides a fixed environment inside the cell, and that membrane has several different functions. One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell. Cytoplasm is the gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell. It is composed of water, salts, and various organic molecules. Some intracellular organelles, such the nucleus and mitochondria, are enclosed by membranes that separate them from the cytoplasm. a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and serves multiple functions, being important particularly in the synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of protein is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. ribosome is a cellular particle made of RNA and protein that serves as the site for protein synthesis in the cell. 3 LYSOSOME PEROXISOME, MITOCHONDRIA VACOULES NUCLEUS NUCLEAR MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CHROMATIN SECRETORY VESICLE CENTRIOLES s a membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes. ... They break down excess or worn-out cell parts membrane-bound organelle occurring in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. ... Peroxisomes contain enzymes that oxidize certain molecules normally found in the cell, notably fatty acids and amino acids Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles (mitochondrion, singular) that generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's biochemical reactions. A vacuole is a membrane-bound cell organelle. In animal cells, vacuoles are generally small and help sequester waste products. In plant cells, vacuoles help maintain water balance. Sometimes a single vacuole can take up most of the interior space of the plant cell. The nucleolus is a region found within the cell nucleus that is concerned with producing and assembling the cell's ribosomes. Following assembly, ribosomes are transported to the cell cytoplasm where they serve as the sites for protein synthesis is a double membrane that encloses the cell nucleus. It serves to separate the chromosomes from the rest of the cell. The nuclear membrane includes an array of small holes or pores that permit the passage of certain materials, such as nucleic acids and proteins, between the nucleus and cytoplasm. is a dense, strained structure inside of the nucleus that contains ribosome is a substance within a chromosome consisting of DNA and protein. The secretory vesicle is a vesicle that mediates the vesicular transport of cargo e.g. hormones or neurotransmitters - from an organelle to specific sites at the cell membrane, where it docks and fuses to release its content. paired barrel-shaped organelles located in 4 CILIA FLAGELLA the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope. Centrioles play a role in organizing microtubules that serve as the cell's skeletal system. They help determine the locations of the nucleus and other organelles within the cell. Cilia are microtubule-based hair-like organelles that extend from the surface of almost all cell types of the human body. Sensory cilia act as cellular antennae to sense environmental and morphogenic cues, for example, during development. hairlike structure that acts primarily as an organelle of locomotion in the cells of many living organisms. . Flagellar motion causes water currents necessary for respiration and circulation in sponges and coelenterates. Most motile bacteria move by means of flagella. PROKARYOTICS Prokaryotics is any organism that lacks a distinct nucleus and other organelles due to the absence of internal membranes. Bacteria are among the best-known prokaryotic organisms. The from eukaryotes. lack The of internal membranes prokaryotic cell in membrane is prokaryotes made up distinguishes of them phospholipids and constitutes the cell’s primary osmotic barrier. The cytoplasm contains ribosomes, which carry out protein synthesis, and a double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) chromosome, which is usually circular. Many prokaryotes also contain additional circular DNA molecules called plasmids, with additional dispensable cell functions, such as encoding proteins to inactivate antibiotics. Some prokaryotes have flagella. Prokaryotic flagella are distinct in design and movement from the flagella found on some eukaryotes Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound structures, the most noteworthy of which is the nucleus. Prokaryotic cells tend to be small, simple cells While prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound structures, they do have distinct cellular regions. In prokaryotic cells, DNA bundles together in a region called the nucleoid. Bacteria and archaea are the two types of prokaryotes. prokaryotes do not have mitochondria. Mitochondria are only found in eukaryotic cells. This is also true of other membrane-bound structures like the nucleus and the Golgi apparatus 5 (more on these later). One theory for eukaryotic evolution hypothesizes that mitochondria were first prokaryotic cells that lived inside other cells. Over time, evolution led to these separate organisms functioning as a single organism in the form of a eukaryote. Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have a nucleus and other organelles enclosed by a plasma membrane. Organelles are internal structures responsible for a variety of functions, such as energy production and protein synthesis. Other common organelles found in many, but not all, eukaryotes include the Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts and lysosomes. Examples of eukaryotes Animals, plants, fungi, algae and protozoans are all eukaryotes. The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not. The nucleus is where eukaryotes store their genetic information. In prokaryotes, DNA is bundled together in the nucleoid region, but it is not stored within a membrane-bound nucleus. The nucleus is only one of many membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes, on the other hand, have no membrane-bound organelles. Another important difference is the DNA structure. Eukaryote DNA consists of multiple molecules of double-stranded linear DNA, while that of prokaryotes is double-stranded and circular. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes vary in several important ways - these differences include structural variation - whether a nucleus is present or absent, and whether the cell has membrane-bound organelles, and molecular variation, including whether the DNA is in a circular or linear form. Plant cells have a cell wall, but animals cells do not. ... Plant cells have chloroplasts, but animal cells do not. Chloroplasts enable plants to perform photosynthesis to make food. Plant cells usually have one or more large vacuole(s), while animal cells have smaller vacuoles, if any are present. At this point it states the diffences among the two. 6