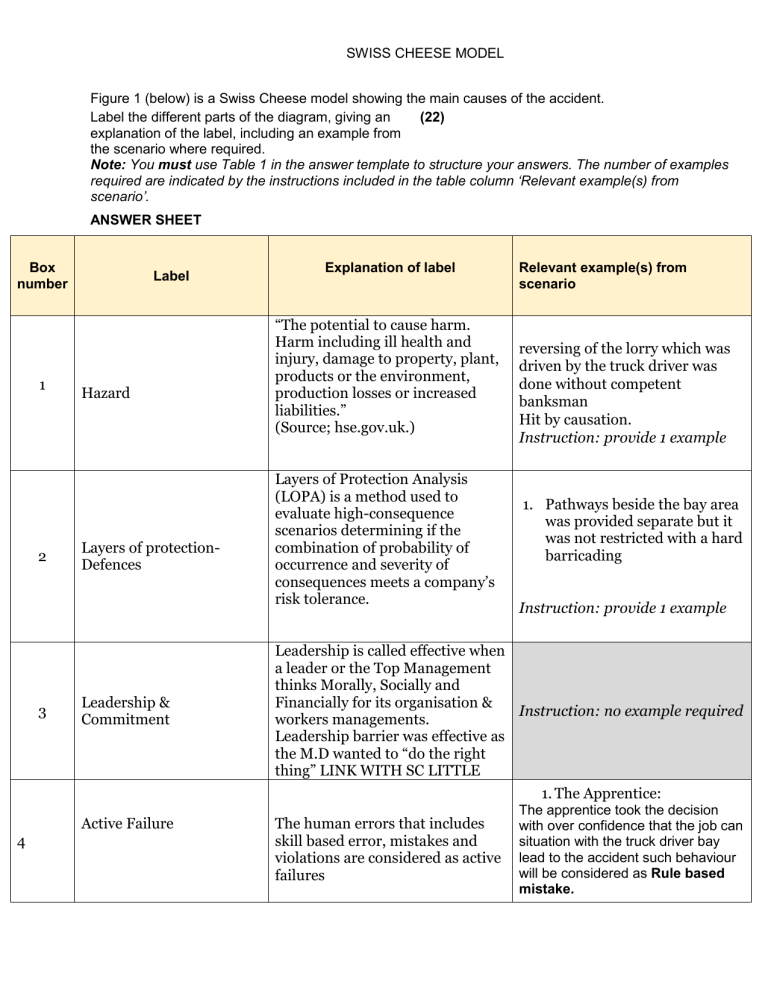
SWISS CHEESE MODEL Figure 1 (below) is a Swiss Cheese model showing the main causes of the accident. (22) Label the different parts of the diagram, giving an explanation of the label, including an example from the scenario where required. Note: You must use Table 1 in the answer template to structure your answers. The number of examples required are indicated by the instructions included in the table column ‘Relevant example(s) from scenario’. ANSWER SHEET Box number 1 2 3 4 Label Hazard Layers of protectionDefences Leadership & Commitment Active Failure Explanation of label “The potential to cause harm. Harm including ill health and injury, damage to property, plant, products or the environment, production losses or increased liabilities.” (Source; hse.gov.uk.) Layers of Protection Analysis (LOPA) is a method used to evaluate high-consequence scenarios determining if the combination of probability of occurrence and severity of consequences meets a company’s risk tolerance. Relevant example(s) from scenario reversing of the lorry which was driven by the truck driver was done without competent banksman Hit by causation. Instruction: provide 1 example 1. Pathways beside the bay area was provided separate but it was not restricted with a hard barricading Instruction: provide 1 example Leadership is called effective when a leader or the Top Management thinks Morally, Socially and Financially for its organisation & Instruction: no example required workers managements. Leadership barrier was effective as the M.D wanted to “do the right thing” LINK WITH SC LITTLE 1. The Apprentice: The human errors that includes skill based error, mistakes and violations are considered as active failures The apprentice took the decision with over confidence that the job can situation with the truck driver bay lead to the accident such behaviour will be considered as Rule based mistake. SWISS CHEESE MODEL Box number Label Explanation of label Relevant example(s) from scenario 2. The Lorries were reversing with a blind spot area, but such information from the truck driver was not identified or communicated to put a control measure of such hazard while driving. 3. reverse alarm of the lorry failed & got hit and having injuries. Instruction: provide 4 examples 1. the process of safe working it is also a latent failure factor that contributed the accident due to self-way to perform the task. 2. Closing eyes during walking on a vehicle movement zone is also an exceptional violation. Latent failures 5 Latent failures are a cause of a multiple connected conditional failures and human failures. There are multiples latent failures that are aligned together and a personal injury, property damage, environmental effects happen. 3. Lack of supervision & monitoring: The reversing was performed by the new apprentice as there were no supervisor of work for the guidance and monitoring 4. Lack of training and awareness; The new apprentice itself can be considered as a latent failure as the presence of any new untrained person at work is mobilized SWISS CHEESE MODEL Box number Label Explanation of label Relevant example(s) from scenario 5. Poor planning- competency to carry out such critical job , as there was no system of permit to work when carrying out reversing activity, it is a site management failure Instruction: provide 5 examples 6 7 8 Inadequate Site management There was no empowerment to stop policy as no intervention was done when the warehouse worker was wearing headphone for listening song, as it was prohibited to do such act. Hazard Progression Residual Risk After arranging controls measures as barriers there are still holes not mitigated or completely controls, such residual gaps are considered as residuals risks. Incident A hazard which has surpassed all the barriers with active failures and latent conditions and has caused damage to person, object or environment can be considered as incidents. Instruction: no example required Active failure - Instruction: no example required Instruction: no example required SWISS CHEESE MODEL