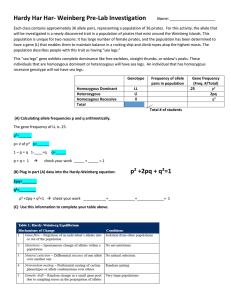
Hardy – Weinberg Equilibrium Graph Principle: If p is the frequency of A allele and q is the frequency of a allele then the expected genotype frequencies under random mating are p2 for the AA homozygotes, q2 for the aa homozygotes and 2pq for the heterozygotes. Calculation: If we take 10 random values of p, then we can calculate q from the equation p + q = 1. Now from the value of p and q we can assess p2, q2 and 2pq. We can plot a graph where the horizontal axis shows the two allele frequencies p and q and the vertical axis shows the expected genotype frequencies. p q p2 2pq q2 0 0.12 0.22 0.32 0.42 0.5 0.62 0.72 0.82 0.92 1 1 0.88 0.78 0.68 0.58 0.5 0.38 0.28 0.18 0.08 0 0 0.01 0.05 0.10 0.18 0.25 0.38 0.52 0.67 0.85 1 0 0.21 0.34 0.44 0.49 0.50 0.47 0.40 0.30 0.15 0 1 0.77 0.61 0.46 0.34 0.25 0.14 0.08 0.03 0.01 0 Table 1 Value of p, q, p2, q2 and 2pq p2 2pq q^2 1.2 Genotype Frequency 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 0.12 0.22 0.32 0.42 0.5 0.62 0.72 0.82 0.92 1 Gene frequency of A Figure 1 : Hardy-Weinberg frequencies of genotype AA, Aa and aa in relation to the frequency of the gene A (p) Interpretation: The graph shows the proportions of the three genotypes at different frequencies of the gene A; heterozygotes are most frequent when the gene frequency is 0.5. Kalpesh Jas Sem – VI B.Sc. Zoology (Honours)