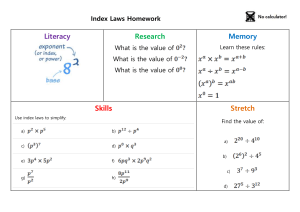
Name: ________________________________________ Block: ___________ Date: ______________________ Physics 11: Hooke’s Law Worksheet 1. (a) What is the formula relating the force of a spring and its distortion? (b) EXPLAIN WHY it is negative. 2. A force of 16 N is required to stretch a spring a distance of 40 cm from its rest position. What force (in Newtons) is required to stretch the same spring: a) twice the distance? b) three times the distance? c) one-half the distance? 3. A mass of 5.0 kg will stretch a vertical spring 3.25 cm. Draw a free body diagram (include all relevant forces and values) and calculate the spring constant. 4. A horizontal steel spring has a spring constant of 40.0 N/m. What force must be applied to the spring in order to compress it by 10.0 cm? 5. When a 14.0 kg mass hangs from a spring that has a spring constant of 550 N/m, the spring has a length of 82 cm. Determine the length of the spring before any force is applied to it. 6. Calculate the spring constant of your lab bench if it is known to bend down by 0.10 mm when a 75 kg student stands on it. 7. Spring A will stretch vertically by 20.0 cm when it has a 1.00 kg mass hanging from it. Spring B will stretch vertically by 50.0cm when it has a 1.00 kg mass hanging from it. a) Draw a free body diagram for Spring A and include all relevant forces and values. Draw a free body diagram for Spring B and include all relevant forces and values. b) Calculate the spring constant of A. c) Calculate the spring constant of B. d) Suppose that the 1.00 kg mass is hanging from the end of spring A and spring A is hanging from spring B. Assuming that the mass of the springs is negligible, calculate the total amount of stretching. e) Calculate the spring constant of the system in part (d)