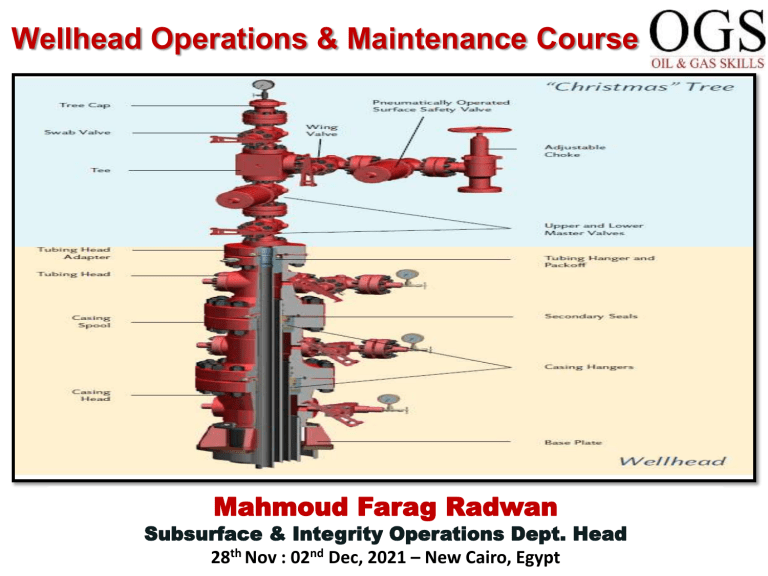
Wellhead Operations & Maintenance Course Mahmoud Farag Radwan Subsurface & Integrity Operations Dept. Head 28th Nov : 02nd Dec, 2021 – New Cairo, Egypt Presenter Name: Mahmoud Farag Radwan Short Biography Mahmoud Radwan is a Subsurface & Integrity Operations Dept. Head at AMAL Petroleum Company (AMAPETCO) with more than 13 years of experience in oil & gas industry. Mahmoud worked in Well Engineering, Intervention, Integrity & Work-over at several companies, including Badr El-Din Pet. Co. (BAPETCO), Qarun Pet. Co. (QPC) and Wadi El-Sahel Petroleum Co. (WASPETCO). Also, a freelance instructor at upstream Oil & Gas in Egypt & UAE since 2008. Mahmoud received a BSc degree in Petroleum Engineering from Al-Azhar University in 2007. Publications Evaluating Sustainable Annulus Pressure (SAP) in Sour Wells and the Possible Causes to Avoid Recurrence to the Well Integrity Annual Middle East Conference in Abu Dhabi; UAE in Apr 2015 Implementing NDT methods for maintenance and inspection to the Asset Integrity Management North Africa Conference in Cairo; Egypt in Nov 2015 Feasibility Evaluation of Using Downhole Gas-water Separation Technology in gas Reservoirs with Bottom Water; paper number: SPE-183739-MS to the 20th Middle East Oil & Gas Show and Conference in Mar 2017 http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/183739-MS Managing the Operational Challenges in Corroded Wells through Well Integrity Management System to the Improving Brownfield Performance Technical Convention, in Cairo; Egypt in Dec 2019 Safe and Economic Attractive Rigless Operations Using a Digital Slickline in Unmanned Platform with Low Structure Loads and Spacing; paper number: SPE202857-MS to the Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition & Conference (ADIPEC) in Nov 2020 http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/183739-MS Outlines Well Construction Principles Completion Components Valves Types & SOP Component Requirements Applicable to all Wellheads Components of a Wellhead & Xmas Tree Advanced wellhead Types Sweet Flowing Wells Critical Sour, Sour and Corrosive Wells Artificial Lift Wells Other Well Types How a Well is Drilled on Land Subsea Production Systems Back Pressure Valves, Testing Plugs, Bull Plugs & Fittings Introduction to API 6A (ISO 10423):Specification for Wellhead and Christmas Tree Equipment SSSV, Wellhead & Xmas Tree Integrity & Maintenance Detailed Procedures Advanced Technology (Ice Plug, Valve Drilling, Hot Tapping, UT Inspection & Seal Protection) Mahmoud Farag Radwan Casing Design : Basic Construction 1 2 3 4 5 7 9 10 11 12 6 8 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 30” conductor Conductor setting depth 20” surface casing 20” shoe Cement Formation open to C annulus 13 3/8” casing Formation open to B annulus 9 5/8” production casing Liner hanger 7” Liner TD – Total Depth Mahmoud Farag Radwan Completion Components – What’s installed 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 5/8” Production Casing 8 7 9 10 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Tubing hanger (Upper annulus barrier) SC-SSSV (Sub-surface barrier) Control line Tubing (Vertical barrier) A annulus (tubing-casing) Gas lift valves (in SPMs) Expansion joint: Tubing Seal Receptacle Anchor seal assembly Production packer Packer sealing element (Lower barrier) Tailpipe WEG 11 12 Mahmoud Farag Radwan Completion Components – Why? 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 5/8” Production Casing 8 7 9 10 11 12 Function : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Upper annulus barrier & supports tubing Protects the surface installation Hydraulically operates the SC-SSSV Conveys hydrocarbons to surface Protects production casing from attack Permit entry of lift gas annulus to tubing Accommodates expansion / contraction Ties & seals tubing string to packer Anchors tubing string to production CSG Forms lower barrier of the A annulus Allows installation of instrumentation Easy entry of production logging tools back into tailpipe Mahmoud Farag Radwan VALVES HIGH pressure (5000 psi and above) MEDIUM pressure (~1500 psi) LOW pressure (~180 psi) Flowhead Choke manifold, Sand-trap Heater & Steam-exchanger Separators Oil/Gas manifolds Pumps, Burners Tanks 1)GATE valves 2)NEEDLE valves (~sampling~) 1)BALL valves 2)PLUG valves 1)BUTTERFLY 2)GLOBE valves 1)WOM new, (McEvoy, Malbranque, Sereg old) 2)Kerotest, Autoclave 1)Mapegaz, Gachot 2)Texseal, Balon Mahmoud Farag Radwan GATE valves •Used for shut off, (on/off function) •High pressure (5, 10, 15, 20Kpsi) •ex: FH, CM, Steam-exchanger, Sandtrap •Sealing method: -metal/metal for WOM valve -grease sealing compound for McEvoy valve •Standard sizes= 3 1/16” to 4 1/16” Mahmoud Farag Radwan GATE valves GATE WOM metal/metal seal Mahmoud Farag Radwan NEEDLE valves •Used for shut off, (on/off) + Flow control (bleed off part of flow) •High pressure (5, 10, 15, 20Kpsi) •ex: instrumentation on FH, CM, Steam-exchanger, Sand-trap •Kerotest (up to 10Kpsi) •Autoclave Engineers (10, 15, 20K) •Sealing method: metal/metal Mahmoud Farag Radwan (~sizes= ¼”, ½”, ¾”) BALL / PLUG valves •Used for shut off, (on/off) •¼ turn •Medium pressure (~1500 psi) •ex: separator, burners, pumps, etc. •Sealing method: -PTFE (Teflon) seal ring or seat Standard sizes= 1” to 4” Mahmoud Farag Radwan GLOBE valves •Used for control of flow and shut off •Low pressure •Rig Water / air lines •Sealing= metal/metal •Standard sizes= 1”, 2” 3” Mahmoud Farag Radwan SAFETY GATE / BALL / PLUG valves: • must not be used for throttling (i.e.: must be fully open or fully closed) because a restricted flow through it will erode the seal or gate or seat, and the valve will not seal correctly / reliably. Mahmoud Farag Radwan SAFETY GATE valves: • it is common practice to count the number of turns taken to open / close a valve because the operator can tell if the valve has become plugged or is not seating correctly. Mahmoud Farag Radwan SAFETY GATE / GLOBE valves: • it is best to close the gate and globe valves by ¼ turn after they are fully opened and vice-versa because over tightening the valve upon closing may damage the disk and seat. Leading to seizure or leakage. Mahmoud Farag Radwan SAFETY NEEDLE valves: • when used with an instrument, the valve should only be opened enough: to permit flow and allow the instrument to register correctly. - to allow a quick closure of the valve and to isolate the dial gauge in case of a sudden increase of pressure, above the range of the gauge. One or two turns is usually sufficient. Mahmoud Farag Radwan Mahmoud Farag Radwan Mahmoud Farag Radwan Mahmoud Farag Radwan Mahmoud Farag Radwan Mahmoud Farag Radwan Mahmoud Farag Radwan Mahmoud Farag Radwan Casing Head Mahmoud Farag Radwan Casing Spool Mahmoud Farag Radwan Casing Hanger Mahmoud Farag Radwan Pack-off Flange PACK-OFF FLANGE FUNCTION • It may be used during well re-entry where anticipated pressure rise. • In temporary operations such as – Pressure testing primary seals – As a safety device when drilling out the cement that remains in the shoe joint. Tubing Head Tubing Hanger Types Mahmoud Farag Radwan Tubing Hanger Types Extended Neck Tubing Hanger Mahmoud Farag Radwan Tubing Hanger Back-Pressure Valve Mahmoud Farag Radwan Tubing Head Adapter Types Mahmoud Farag Radwan Wear Bushing Mahmoud Farag Radwan Christmas tree for a flowing well XMAS TREE XMAS TREE Surface valves manifold to control flow of well fluids & access for well intervention activities. Features: 1 LMV Manual, NOT working valve optimum conditions. 2 UMV Emergency valve (Hydraulic / Pneumatic) & cut wire. 3 FWV Permits passage of well fluids to CV. 4 CHOKE VALVE (CV) Restrict, control or regulate flow of well fluids. 5 KWV Permits entry of kill fluids into tubing or equalize. 6 SV/CV Permits entry of well interventions. Mahmoud Farag Radwan Xmas Tree Types Xmas Tree type: Solid Block (Mono Block) Xmas Tree - Contains fewer components (for high pressure wells) Composite Block Xmas Tree - Valves are located on separate block & joined by API flange. Horizontal Xmas Tree - New concept used for sub-sea completion. Mahmoud Farag Radwan Dual Solid Block Xmas Tree Mahmoud Farag Radwan CONNECTIONS Mahmoud Farag Radwan SEALS • Seal composition: –Elastomer and Graphite / Carbon Seals. –Metal Seals. • Seal types: –Primary Seals –Secondary Seals • If both are installed the wellhead can be pressure tested. Mahmoud Farag Radwan WELDED Mahmoud Farag Radwan ARTIFICIAL LIFT WELLS • Gas Lift • • ESP PCP • Plunger Lift • Sucker Rod Pump • Hydraulic Pump Special Wellhead Design The conventional wellhead should be modified to meet the artificial lift method. Each method along with the modification applied will be discussed. Mahmoud Farag Radwan BEAM PUMPING •the wellhead must be modified to seal around the reciprocating rod. •Emergency precaution in Mahmoud Farag Radwan .case of broken rod WELLHEAD EQUIPMENT • Flowing T • BOP • Stuffing Box • Lubricator Mahmoud Farag Radwan PCP LIFTING • the wellhead must be modified to seal around the rotating rod. • Emergency precaution in case of broken rod. • The rod string is supported on the wellhead Mahmoud Farag Radwan GAS LIFTING •The X-tree is used not only to control the production but also the injection of the gas Mahmoud Farag Radwan ESP LIFTING Mahmoud Farag Radwan HYDRAULIC LIFTING Mahmoud Farag Radwan PLUNGER LIFTING •the wellhead must accommodate a lubricator / “plunger catcher” installed on top of the flow cross. Mahmoud Farag Radwan INJECTION WELLHEAD –Similar in configuration to flowing wells. –The major concerns in the • wellhead are • The operation pressure. • The injected fluid Temperature (especially in STEAM INJECTION) Mahmoud Farag Radwan The injected fluid •A wise selection of the wellhead material is a must to be suitable for the injected fluid and TEMPERATURE variation. Mahmoud Farag Radwan Offshore Wellhead •Mudline Suspension •Subsea Wellhead Mahmoud Farag Radwan THE MUDLINE HANGER SYSTEM CONSISTS OF THE FOLLOWING COMPONENTS Mahmoud Farag Radwan Mahmoud Farag Radwan Mahmoud Farag Radwan A STANDARD SUBSEA WELLHEAD SYSTEM WILL TYPICALLY CONSIST OF THE FOLLOWING: • Drilling guide base. • Low-pressure housing. • High-pressure wellhead housing (typically 18¾ in.). • Casing hangers • Metal-to-metal annulus sealing assembly. • Bore protectors and wear bushings. Mahmoud Farag Radwan BIG BORE SUBSEA WELLHEAD SYSTEMS • As a result of the challenges associated with deepwater drilling. • Ocean-floor conditions in deep and ultradeep water can be extremely mushy and unconsolidated, which creates well-foundation problems that require development of new well designs to overcome the conditions. • Second, underground aquifers in deep water have been observed in far greater frequency than in shallower waters, and it quickly became clear that these zones would have to be isolated with a casing string. wellhead equipment designs would also have to change to accommodate the additional requirements. Mahmoud Farag Radwan UNITIZED WELLHEAD (COMPACT) Mahmoud Farag Radwan SH2 SPLIT SPEEDHEAD SYSTEM • No need to un-screw the BOP. • Reduces waste time in testing BOP . • Maximum pressure 15,000 psi. Pack-off Wellhead API Trim Guide Mahmoud Farag Radwan How to Order General Wellhead Equipment Data Sheet Mahmoud Farag Radwan Mahmoud Farag Radwan Leak Rate Criteria Leak rates based on API 14 B at 15 SCF / min for gas or 400 cc / min for liquid The following table shall be used to determine allowable leak rates for valve and downhole equipment leaks Test results below the rates described above are not classed as a leak so test result and should be assigned a 'Pass' Mahmoud Farag Radwan Advanced Technology (Ice Plug, Valve Drilling, Hot Tapping, UT Inspection & Seal Protection) Mahmoud Farag Radwan Thank You





