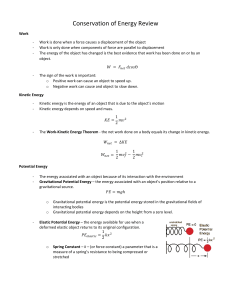
Energy, Forces, & Fields - UNIT Study Guide Name: _______________________________ Class Period: _______ DIRECTIONS: This study guide has 3 sections: 1. Energy 2. Newton’s Laws Motion 3. Contact & Non-Contact Forces Each section has a VIDEO that reviews important concepts that you should be able to model, explain and apply. Watch each video and fill out the study guide as you complete each section. PART 1: ENERGY 1. Define Kinetic & Potential Energy 2. Which is it? If the example describes Potential Energy, write a “P” next to it. If the example describes Kinetic Energy, write a “K” next to it. EXAMPLE “P” or “K” EXAMPLE A. Walking down the street D. A bowling ball rolling down an hill B. Sitting on top of a tree E. An archer with his bow & arrow drawn C. A bicyclist pedaling up a hill F. A roller coaster cart at the top of the hill “P” or “K” 3. The diagram below shows a roller coaster cart at different points along the ride. Determine which cart position matches the descriptions below. The point at which the coaster has the greatest potential energy: The point at which the coaster has the greatest kinetic energy: 4. The Law of of Conservation of Energy says that, “Energy cannot be ___________________ or _____________________ . Energy can be _____________________ from one form to another” 5. What are two factors that affect the amount of gravitational potential energy of a system? ANSWER: _______________________ & _______________________ 6. Use arrows below to indicate the relationship between mass, height, and gravitational potential energy? As Mass ____________ , Gravitational Potential Energy ______________ As Height ___________, Gravitational Potential Energy ______________ 7. What are two factors that affect the amount of kinetic energy of a system? ANSWER: _______________________ & _______________________ 8. Use arrows below to indicate the relationship between mass, height, and gravitational potential energy? As Mass ____________ , Kinetic Energy ______________ As Speed ___________, Kinetic Energy ______________ 9. You are trying to increase the Kinetic Energy of an object quickly. Based on the graph below, which variable would increase the kinetic energy faster: - Increasing the object's mass or Increasing the object's speed (velocity). Justify your answer! ANSWER to #9: 10. A student wants to know if the mass of a cart affects its speed at the bottom of a ramp. He can change the mass of the cart by adding different numbers of balls, and he can change the height of the ramp by using different numbers of blocks. Which set of tests should he compare? Explain your answer PART 2: NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION 1. Identify Newton’s Laws of Motion by definition Newton’s Laws of Motion State: Which Law is this? F = ma: The greater the force the greater the acceleration. The greater the mass, the greater the force needed to move the object. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. An object that is sitting at rest will stay at rest, and an object that is in motion will stay in motion until a force acts upon it. 2. Apply Newton’s Laws of Motion A. You were caught standing on the school bus. Your bus driver tells you to sit down because you might get hurt if they have to come to a stop quickly. Which Law of Motion explains why this is a very important safety rule? Explain your answer. B. The UofL Women’s Rowing team paddled their boat to victory against Notre Dame in a race. What Law of Motion explains how the team was able to travel across the water? Explain your answer. C. Ms. Biggs challenged Mr. Neel to a bowling ball pushing race for Field Day. Ms. Biggs brings two bowling balls for the race. The balls appeared the same, but Mr. Neel actually weighed 2 lbs. more. Which Newton’s Law of Motion explains why Ms. Biggs’ has an unfair advantage? Explain your answer. PART 3: CONTACT & NON-CONTACT FORCES 1. What is the difference between a contact force and a non-contact force? 2. The actions below are examples of different contact and non-contact forces. Identify the example as a CONTACT or NON-CONTACT force and the TYPE OF FORCE INTERACTION. EXAMPLE CONTACT OR NON-CONTACT? TYPE OF FORCE INTERACTION?