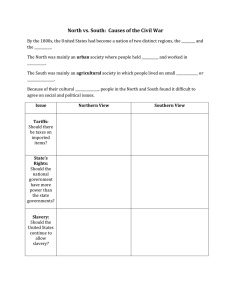
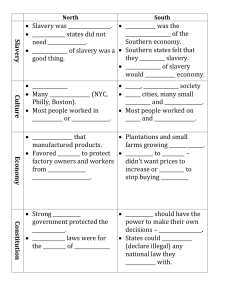
1 SUMMARY OF AMERICAN HISTORY AMERICAN HISTORY NAME INSTITUTION 2 SUMMARY OF AMERICAN HISTORY SUMMARY OF THE AMERICAN HISTORY American Yawp is a collaborative, evolving text that discourses the American history from Indigenous America, The American Revolution, The Civil war, The Reconstruction, and the Capital and Labor, among others (Ayers and Edward, 2003). this period is a settled history since there has never been any other civil war, conflict, slavery, or inequality in the recent history of the democratic United States of America. The American Civil War, which is termed as the most disastrous and bloodiest war fought on American soil, happened between the year 1861-1865 after the chaotic balloting of Abraham Lincoln. The southern states, which felt oppressed, called for secession due to, State rights, slavery, and westward expansion, which was the primary basis of the Civil War, while the northern states wanted to preserve the American Union. Military mobilization reached high levels since the war affected almost every American as it had transformed into a struggle to eliminate slavery, resulting in more than 750 000 deaths (Berry and Stephen, 2011). After 1865, slavery had been eradicated, the secession question had been solved, and America was a Union once more. Still, in many ways, some questions were unanswered, such as who will take the responsibility of rebuilding the southern states, how the Nation would become one again, and what role the African-Americans occupy in society. After the Civil war, most of the southern states lay in remnants. The infrastructure had been destroyed entirely, and according to the author, the future of the entire southern states was uncertain. The reconstruction predicament was the main question that lingered among citizens as the Radical Republicans and African Americans pressed the whole Nation to finally recognize the pronouncement of independence's assurances of equality of all individuals and have inalienable human and civil rights. The Nation commenced the reconstruction of political, 3 SUMMARY OF AMERICAN HISTORY economic, social, and racial violence to restore the American Union (Eric, 1988). The reconstruction accomplished Abraham Lincoln's dream of the re-establishment of the Union since the Civil War, and its reverberation ended forever the Legitimate slavery thought women and the African Americans continued to be second-class citizens. The economy had to be rebuilt after the Civil war, and it was achieved by both the North and South republicans including, Union soldiers, teachers, business people, farmers, and political leaders, both white and blacks, through the establishment of school systems, industries, equitable taxation and abolishment of slavery. During the reconstruction period, women wriggled to make sense of change and death. Elizabeth Cady, the leading women's rights advocate during this period, saw a chance for disenfranchised groups as she formed a Women's Loyal League in 1863, which helped abolish slavery by petitioning Parliament for a constitutional adjustment. The 13th amendment marked a triumph for the women league attesting to the value of women and the prospect for radical change. Elizabeth Cady also led women to champion for equal rights for all and advocated for women's rights. The author discusses the rise of inequality, the labor movement, the socialists, the populist movements, and the new age of labor war in the United States. Afterwards the Civil war, industries slashed workers' wages which lead to worker's strike and caused the Nation's economic decline across the country. The workers' protests led to massive destruction of poverty, especially rail property, and as the protests escalated, they almost approached a class war. The use of the military to restore peace during the protests resulted in the death of 11 individuals and wounding of several others in Baltimore, and also killing 20 more protesting in Pittsburgh. After these deaths, more chaos erupted across the country, with protesters fighting with the military while destroying property. Courts, state militia, and the police were unable to contain the 4 SUMMARY OF AMERICAN HISTORY protesters, and it forced the intervention of the federal army to calm the protests but not after more than 100 civilians had lost lives and property more than $40 destroyed in 'The Great Upheaval' (Alfred, 1990). The book American Yawp writes that the labor unrest in the United States accompanied Industrialization. The post-Civil War age saw the rise of the industrial revolution and technological inventions, which slashed production and distribution costs. Class divisions became apparent since industrial Capitalism fetched wealth and poverty since it created investors and owners and created employees. American history intersects with me as the peace and unity declared after the Civil War reigns up to the present day, and the rights of all citizens, including African-Americans and women, are upheld in the constitution. The most surprising thing about this period of American history is that it took war and blood shade on American soil for the constitution to be amended and to allow equality of all citizens under the law, abolish legal slavery under the 13th amendment, and grant blacks the right to vote under the 15th amendment. All these rights could have been guaranteed without blood shade. 5 SUMMARY OF AMERICAN HISTORY Reference Ayers, Edward L. In the Presence of Mine Enemies: War in the Heart of America, 1859– 1863. New York: Norton, 2003 Berry, Stephen, ed. Weirding the War: Stories from the Civil War’s Ragged Edges. Athens: University of Georgia Press, 2011. Eric Foner, Reconstruction: America’s Unfinished Revolution, 1863–1877 (New York: HarperCollins, 1988), xxv. [ Alfred D. Chandler Jr., Scale, and Scope: The Dynamics of Industrial Capitalism (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1990), 52.