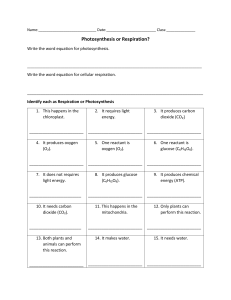
Organisms, Energy, and Matter Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. An alligator lives in a swamp with deer, birds, fish, trees, and other plants. The alligator eats a bird that eats the seeds and plants. What is the original source of the energy that the alligator gets from eating the bird? A. the flowing water in the swamp B. the energy that the bird creates C. the sunlight that the plants absorb D. the heat from the air in the swamp ____ 2. Energy is transferred between certain organisms in an ecosystem. Which of these statements explains why the sea grass is a producer? A. It uses energy from the sun to make food. B. It creates energy needed by the ecosystem. C. It is eaten by other organisms. D. It releases nutrients into the soil. ____ 3. Plant cells contain a pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll has a role in the process of photosynthesis. What does chlorophyll do? A. produces glucose from oxygen B. produces oxygen from glucose C. absorbs light energy from the sun D. absorbs glucose from the plant ____ 4. During cellular respiration, an organism’s cells break down glucose to provide energy for life activities. Which of these substances is also produced during cellular respiration? A. carbon dioxide B. fat C. oxygen D. protein ____ 5. Cellular respiration allows cells to break down glucose to release energy which is used for cell processes. Which substance do cells in the human body need to carry out cellular respiration? A. They need carbon dioxide. C. They need oxygen. B. They need chlorophyll. D. They need water. ____ 6. What are the reactants of photosynthesis? A. carbon dioxide and water B. sugar and water C. glucose and oxygen D. carbon dioxide and oxygen 7. In which part of the cell does cellular respiration take place? ____ A. cell membrane B. mitochondria C. nucleus D. ribosomes ____ 8. During cellular respiration, cells break down food to release energy. During photosynthesis, cells produce food in the form of glucose. What is one difference between these two processes? A. Cellular respiration uses oxygen and photosynthesis produces oxygen. B. Cellular respiration uses carbon dioxide and photosynthesis does not. C. Cellular respiration produces oxygen and photosynthesis does not. D. Photosynthesis produces more glucose than cellular respiration does. ____ 9. The diagram below shows part of the carbon cycle. What is happening in Step 1? A. Animals are releasing energy into the environment and storing carbon. B. Animals are decomposing and releasing carbon into the soil. C. Animals are converting carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to oxygen. D. Animals are releasing carbon dioxide through the process of cellular respiration. ____ 10. The diagram below shows part of the carbon cycle. How do decomposers fit into the cycle shown? A. They help trees capture light energy from the sun for photosynthesis. B. They are released from the factory during combustion. C. They release energy that breaks down the organic molecules that trees produce. D. They get energy and release carbon dioxide by breaking down the dead organisms. ____ 11. In the carbon cycle, how do living things store most of their energy? A. water C. organic compounds such as sugar B. light energy D. heat energy ____ 12. Select the phrase that best describes a consumer in a food chain. A. an organism that converts light energy into chemical energy B. an organism that breaks down dead plants and animals C. an organism that is at the bottom of the food chain D. an organism that gets its energy by eating plants or animals ____ 13. Green plants and algae make their own food through photosynthesis. What is photosynthesis? A. a cell process that uses energy from sunlight to convert water and oxygen into food B. a cell process that uses energy from sunlight to convert water and glucose into food C. a cell process that uses energy from sunlight to convert water and chlorophyll into food D. a cell process that uses energy from sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into food ____ 14. There is a relationship between breathing and cellular respiration. Breathing involves taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. How does the oxygen affect the process of cellular respiration? A. Oxygen and ATP combine to produce energy in the form of carbon dioxide. B. Oxygen and glucose combine to produce energy in the form of ATP molecules. C. Oxygen and hydrogen combine to produce energy in the form of ATP molecules. D. Oxygen and carbon dioxide combine to produce energy in the form of ATP molecules. ____ 15. What is the result of cellular respiration? A. Food is made and stored in cells. B. Energy is stored in the chemical bonds of food. C. Sunlight is captured and used to make food. D. ATP/energy is produced for use in cell functions. ____ 16. What is a carbon reservoir? A. a place that creates carbon. B. a place that destroys carbon. C. a place that stores carbon. ____ 17. The sun is the primary source of energy in most ecosystems. Producers use the sun’s energy to make sugar during photosynthesis. Which of the following correctly identifies the transfer of energy during photosynthesis? A. thermal energy to light energy B. thermal energy to chemical energy C. light energy to chemical energy D. chemical energy to light energy ____ 18. The products from photosynthesis provide the raw materials for cellular respiration. What products of photosynthesis are STARTING MATERIALS for cellular respiration? A. glucose and oxygen C. carbon dioxide and water B. heat and ATP D. light energy and chlorophyll ____ 19. Cellular respiration can be summarized by which equation A. C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 +6H2O + ENERGY B. 6CO2 +6H2O + SUNLIGHT = C6H12O6 + 6O2 ____ 20. Photosynthesis can be summarized by which equation? A. H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 +6H2O + ENERGY B. 6CO2 +6H2O + SUNLIGHT = C6H12O6 + 6O2 ____ 21. How does the carbon cycle follow the Law of Conservation of Matter? A. Carbon is lost in the atmosphere through the process of respiration B. Carbon is transformed and transferred however it is never created or destroyed. C. Carbon is gained through the process of decomposition. D. As carbon is cycled, it is destroyed by thermal energy. ____ 22. Which is a biotic factor in an ecosystem? A. a plant living near a stream C. the angle of the Sun B. the amount of rainfall D. the types of minerals in soil. ____ 23. Which type of reservoir stores more carbon then it releases? A. sink B. source ____ 24. Which process returns carbon compounds to the soil in the carbon cycle? A. assimilation C. fossilization B. cellular respiration D. decomposition ____ 25. Which of the Carbon Cycle takes carbon from the atmosphere? A. cellular respiration C. combustion B. photosynthesis D. humans breathing ____ 26. What does the law of conservation of energy state? A. It is important to use as little energy as possible. B. Organisms save the energy that they create. C. Organisms change energy into mass. D. Energy cannot be created or destroyed. ____ 27. Saw grass takes in light energy during photosynthesis. What happens to most of this energy? A. It is stored as chemical energy to use later for growth and development. B. It disappears as it is used up by the plant. C. It is transferred to organisms that eat the grass D. It is released through the leaves. ____ 28. A freshwater marsh is a type of ecosystem. Grasses, fish wading birds, frogs, and alligators live together in freshwater marshes. Pieces of decaying material sink to the bottom of the marsh. In which of these places can carbon be found in the marsh? A. in the atmosphere and water only B. in living things only C. in living things and decaying materials only D. in the atmosphere, water, living things, and decaying materials ____ 29. This food web shows some of the relationships found in a mangrove ecosystem. This ecosystem consists of a grove of trees with an extensive root system and the organisms that use the grove for food or shelter. Materials cycle through the ecosystem as organisms consume one another. What do the arrows in the food web represent? A. B. C. D. the relative location of organisms in the ecosystem the flow of energy from one organism in the ecosystem to another the relative sizes of organisms in the ecosystem from smallest to largest the increase in complexity of organisms from producer through consumer ____ 30. What is the difference between an abiotic and biotic factor? A. biotic is non-living; abiotic is living B. both are non-living C. biotic is living; abiotic is non-living D. both are living