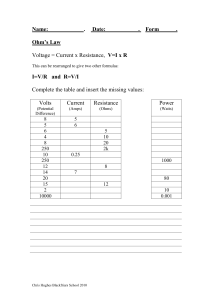
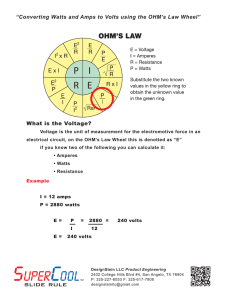
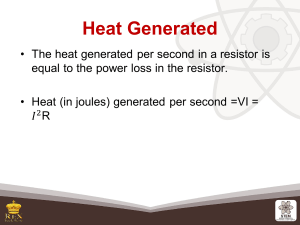
SEATWORK FOR ELECTRICAL COMPUTATIONS Submission on Tuesday April 21, 2020 Compute for electrical current (I) in amperes and electrical power (P) in watts if the following electrical values are given: Voltage (V) in volts – 230v (considering a 4% drop from 240v) Resistance (R) in ohms – 40 ohms Compute for electrical voltage (V) in volts and electrical power (P) in watts if the following electrical values are given: Current (I) in amperes – 9.58 amps Resistance (R) in ohms – 24 ohms Compute for electrical resistance (R) in ohms and electrical power (P) in watts if the following electrical values are given: Voltage (V) in volts – 230v (considering a 4% drop from 240v) Current (I) in amperes – 40 amps Compute for electrical voltage (V) in volts and electrical resistance (R) in ohms if the following electrical values are given: Power (P) in watts – 9,600 watts Current (I) in amps – 40 amps Compute for electrical voltage (V) in volts and electrical current (I) in amperes if the following electrical values are given: Power (P) in watts – 958 watts Resistance (R) in ohms – 60 ohms Compute for electrical resistance (R) in ohms and electrical current (I) in amperes if the following electrical values are given: Voltage (V) in volts – 230v (considering a 4% drop from 240v) Power (P) in watts – 1,865 watts REFER TO Lecture 6 – Principles of Electricity